Abstract
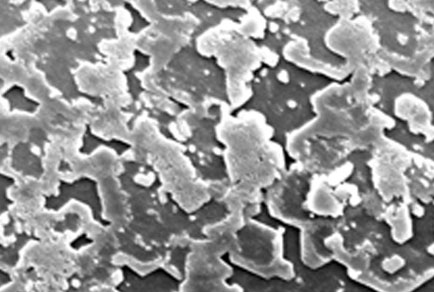
Atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations have greatly increased since the beginning of the industrial age. This has led to a decline in global ocean pH by 0.1 units, and continued decline of 0.3–0.5 units is predicted by the end of 2100. Acidification of the ocean has led to decreased calcification rates and dissolution of calcareous structures in a range of marine species. Shells of the pearl oyster Pinctada fucata exposed to acidified seawater (pH 7.8 and pH 7.6) for 28 days were 25.9% and 26.8% weaker than controls (pH 8.1–8.2), respectively, but there was no reduction in the organic content of shells exposed to acidified condi-tions. Scanning electron microscopy analysis of the growing edge of nacre lining the shells of P. fucata showed that shells exposed to acidified conditions (pH 7.6) showed signs of malformation and/or dissolution, when compared to controls. The reduction in shell strength and the possible nacre malformation could have broad impacts on the ecology of pearl oysters and consequences for the cultured pearl industry that relies on them.