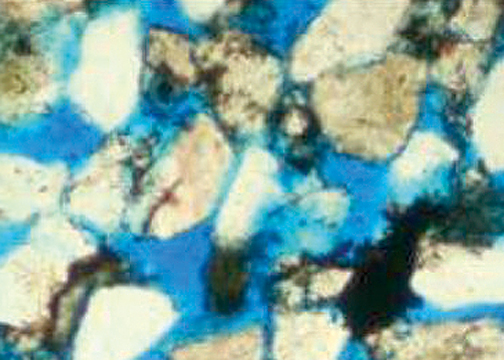
Abstract
The Mesozoic–Cenozoic clastic rocks in the Tabei Uplift form one of the most hydrocarbon-rich zones in the Tarim Basin of China. Understanding how diagenesis has affected the petrophysical properties of the sandstone is crucial for developing regional exploration strategies. Although most studies have investigated the physical conditions during sedimentation and chemical processes during diagenesis, the hydrochemical environment during sedimentation and subsequent diagenesis has received little attention. This study employed petrographic observations, paleo-geothermal reconstructions, and paleoenvironmental analysis to constrain the regional climatic conditions, hydrochemical environment of deposition, and diagenetic features of clastic rocks in the Tabei Uplift. The sandstone at depths of 3500–6000 m is located mainly in the A phase of the middle diagenetic stage, and exhibits three types of diagenesis. Triassic–Jurassic sandstones are dominated by silica, kaolinite, and chlorite cements, Cretaceous sandstones by mainly carbonate cements, and Paleogene sandstones by carbonate and evaporite cements. These diagenetic stages correspond to paleoclimatic changes during the earliest Late Jurassic and the maximum marine transgressions of the Proto-Tethys during the Paleogene, thereby highlighting the influence of climatic change and transgressions on the water conditions during deposition and the type of diagenesis.
References
- Ajdukiewicz, J. M. & Lander, R. H. (2010) Sandstone reservoir quality prediction: The state of the art. AAPG bulletin, 94 (8), 1083–1091. https://doi.org/10.1306/intro060110
- Bjørlykke, K. (1983) Diagenetic Reactions in Sandstones. Sediment Diagenesis, 115, 169–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-7259-9_3
- Bjørlykke, K. (2014) Relationships between depositional environments, burial history and rock properties. Some principal aspects of diagenetic process in sedimentary basins. Sedimentary Geology, 301, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2013.12.002
- Chen, L., Lin, C., Li, H. & Xiang, S. (2017) Sedimentary characteristies of the lower sandstone part of Kumugeliemu group in the western Tabei uplift. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 41 (5), 23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2013.12.002
- Compiling Group for Xinjiang Regional Stratigraphic Chart (1981) Regional stratigraphic chart of northwestern China, branch of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, 496 pp. [In Chinese]
- Fuchtbauer, H. (1983) Facies controls on sandstone diagenesis. Sendiment diagenesis, 115, 269–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-7259-9_5
- Garzanti, E. (2019) Petrographic classification of sand and sandstone. Earth Science Reviews, 192, 545–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.12.014
- Gu, J.Y., Jia, J.H. & Fang H. (2002) Reservoir characteristics and factors of high porosity and permeability in the Tarim Basin. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47, 9–15. [In Chinese] https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02902813
- Han, D.L, Li, Z, Han, Y.X., Liu, J.Q, Li, W.F. & Li, S.L. (2009) Sealing feature of burial diagenesis environment and its controls on differentiation of cementation in Cretaceous sandstone reservoir in Kelasu structure zone, Kuqa depression. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25 (1), 2351–2362. [In Chinese]
- Hendrix, M.S., Graham, S.A., Carroll, A.R., Sobel, E.R., McKnight, C.L., Schulein, B.J. & Wang, Z. (1992) Sedimentary record and climatic implications of recurrent deformation in the Tian Shan: Evidence from Mesozoic strata of the north Tarim, south Junggar, and Turpan basins, northwest China. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 104 (1), 53–79. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1992)104<0053:SRACIO>2.3.CO;2
- Huang, S.J., Huang, K.K., Feng, W.L., Tong, H.P., Liu, L.H. & Zhang, X.H. (2009) Mass exchanges among feldspar, kaolinite and illite and their influences on secondary porosity formation in clastic diagenesis—a case study on the Upper Paleozoic, Ordos Basin and Xujiahe Formation, Western Sichuan Depression. Geochimica, 38 (5), 498–506. [In Chinese]
- Jia, C.Z. & Pang, X.Q. (2015) Research processes and main development directions of deep hydrocarbon geological theories. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 36 (12), 1457–1469. [In Chinese]
- Jin, X.H., Yan, X.B., Li, T.J. & Zou, Y.R. (2008) A discussion on gas and oil exploration activities and discovery patterns in the Tarim Basin. Oli & Gas Geology, 4 (1), 45–52. [In Chinese]
- Li, W.G., Zhang, X.P. & Zhong, Y.M. (2005) Formation mechanism of secondary dissolved pores in arcose. Oli & Gas Geology, 26 (2), 220–223. [In Chinese]
- Li, Z., Song, W., Peng, S., Wang, D. & Zhang, Z. (2004) Mesozoic–Cenozoic tectonic relationships between the Kuqa subbasin and Tian Shan, northwest China: constraints from depositional records. Sedimentary Geology, 172 (3-4), 223–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2004.09.002
- Li, Z., Chen, J.S. & Guan, P. (2006) Scientific problems and frontiers of sedimentary diagenesis research in oil-gas-bearing basins. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22 (8), 2113–2122. [In Chinese]
- Liu, J.D., Qi, L.X., Tian, J.C., Li, Z.J. & Zhang, X.B. (2014) Tectonic evolution and sedimentary framework of the Tarim Basin. Chinese Science Publishing House, Beijing, 346 pp. [In Chinese]
- Luo, J.L., Li, C., Lei, C., Cao, J.J. & Song K.P. (2020) Discussion on research advances and hot issues in diagenesis of clastic-rock reservoirs. Journal of Paleogeography, 22 (6), 1021–1040. [In Chinese]
- McLennan, S. M. (2001) Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2 (4). https://doi.org/10.1029/2000GC000109
- Morad, S., Al-Ramadan, K., Ketzer, J.M. & De Ros, L.F. (2010) The impact of diagenesis on the heterogeneity of sandstone reservoirs: A review of the role of depositional facies and sequence stratigraphy. AAPG bulletin, 94 (8), 1267–1309. https://doi.org/10.1306/04211009178
- Muhs, D.R., Bettis, E.A., Been, J. & McGeehin, J.P. (2001) Impact of climate and parent material on chemical weathering in loess‐derived soils of the Mississippi River valley. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65 (6), 1761–1777. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2001.1761
- Qi, L.X., Li, Z.J. & Lv, H.T. (2020) Atlas of tectonic-sedimentary evolution and hydrocarbon exploration in the Tarim Superimposed Basin. Chinese Science Publishing House, Beijing, 224 pp. [In Chinese]
- Qiu, L.W., Jiang, Z.X., Cao, Y.C., Qiu, R.H. & Chen, W.X. (2001) Alkaline diagenesis and its influence on a reservoir in the Biyang Depression. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 31 (9), 752–759. [In Chinese] https://doi.org/10.1360/02yd9065
- Singer, A. (1984) The paleoclimatic interpretation of clay minerals in sediments—a review. Earth-Science Reviews, 21 (4), 251–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-8252(84)90055-2
- Sun, D.Q., Li, W.H., Lu, S.F., Liu, X.P, He, T.H., Zhu, P.F., Wang, X.Z, Ying, J.F. & Wang, J.M. (2020) Reservoir characteristics and controlling faceors of Shushanhe Formation on Yingmaili Area of Tabei Uplift. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 44 (6), 82–93. [In Chinese]
- Tang, T.F., Xue, Y.S. & Yu, C.L. (1992) Marine Sedimentary Characteristics and Environments from Late Cretaceous to Early Tertiary in the West Part of Tarim Basin of Xinjiang. Chinese Science Publishing House, Beijing, 175 pp. [In Chinese with English abstract]
- Tian, J.F., Chen, Z.L., Fan, Y.F., Li, P.P. & Song, L.J. (2008) The occurrence, growth mechanism and distribution of authigenic chlorite in sandstone. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 27 (2), 200–206. [In Chinese]
- Tribovillard, N., Algeo, T.J., Lyons, T. & Riboulleau, A. (2006) Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: an update. Chemical geology, 232 (1-2), 12–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.02.012
- Wu, G.K., Lin, C.S., Liu, Y.F., Liu, J.Y., Yang, X.Z. & Li, H. (2019) Characteristics of major unconformities and paleo-geomorphology during the Mesozoic key transformation stages in Kuqa-Tabei area. Oil & Gas Geology, 40 (4), 763–777. [In Chinese]
- Xia, Y.T., Wang, R., Yang, H.C., Shi, W.Z., Bahetiyaer, A., Tan, S., Zhang, X. & Xu, Z. (2024) Characteristics and main controlling factors of the tight sandstone reservoirs around the paleo-uplift in the southern Tianshan area, Tarim Basin. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 43 (2), 16–27. [In Chinese]
- Xie, X.N., Cheng, J.M. & Meng, YL. (2009) Basin fluid flow and associated diagenetic processes. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 27 (5), 863–871. [In Chinese with English abstract]
- Xu, X.H., Zhou, Q.F. & Zhang, L. (2004) Oil and gas reserves and their distribution in Tarim basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 25 (3), 300–313. [In Chinese]
- Xu, Y., Cao, Y., Liu, C., Zhang, H. & Nie, X. (2020) The history of transgressions during the Late Paleocene-Early Eocene in the Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin: constraints from COS-Sr isotopic geochemistry. Minerals, 10 (9), 834 pp. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10090834
- Yang, H.J., Liu, Y.F., Su, Z. & Han, J.F. (2020) The main controlling factors for the formation of high quality clastic reservoirs in deeply buried strata of Tabei Uplift. Geological Review, 66 (1), 169–179. [In Chinese with English abstract]
- Yang, Y.T., Guo, Z.X. & Luo, Y.J. (2017) Middle-Late Jurassic tectonostratigraphic evolution of Central Asia, implications for the collision of the Karakoram-Lhasa Block with Asia. Earth-Science Reviews, 166, 83–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.01.005
- Yi, Z.Y., Liu, Y.Q. & Meert, J.G. (2019) A true polar wander trigger for the Great Jurassic East Asian Aridification. Geology, 31 (2), 1112–1116. https://doi.org/10.1130/G46641.1
- Ying, F.X., He, D.B., Long, Y.M. & Lin, X.S. (2003) Division of clastic diagenetic stage (SY/T 5477-2003). State economic and trade commission. [In Chinese]
- Yu, B.S. & Lai, X.Y. (2006) Carbonic acid system of groundwater and the solubility of calcite during diagenesis. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 24 (5), 627–635. [In Chinese]
- Zhang, R.H., Zeng, Q.L., Li, J., She, M. & Yu, C.F. (2019) Physical Simulation of Multi⁃Period Dissolution in Cretaceous Reservoirs of Kelasu Tectonic Belt, Kuqa Depression. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 40 (1), 34–40. [In Chinese with English abstract]
- Zhang, R.H., Zou, W.H., Chen, G, Zhao, J.L., Zhang, H.L., Wu, J. & Li, X.J. (2018a) Characteristics and hydrocarbon exploration significance of the huge Lower Cretaceous lacustrine sand bar in the northern Tarim Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 39 (8), 845–857. [In Chinese]
- Zhang, S.J., Hu, X.M., Han, Z., Li, J. & Garzanti, E. (2018b) Climatic and tectonic controls on Cretaceous-Palaeogene sea-level changes recorded in the Tarim epicontinental sea. Palaeogeograpy, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 501, 92–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.04.008
- Zheng, J.M. & Ying, F.X. (1997) Reservoir characteristics and diagenetic model of sandstone intercalated in coal-bearing strata (acid water medium). Acta Petrolei Sinica, 18 (4), 19–24. [In Chinese]
- Zhu, R.K., Guo, H.L., Gao, Z.Y., Han, D., Zhang, L.J., Sun, Y.S. & Cheng, M. (2007) Probe into influence factors to the physical properties of the Cretaceous and Eocene reservoir in northern Tarim Basin. Geological Review, 53 (5), 624–630. [In Chinese]
- Zhou, Z. (2001) Stratigraphy of the Tarim Basin. Chinese Science Publishing House, Beijing, 359 pp. [In Chinese]