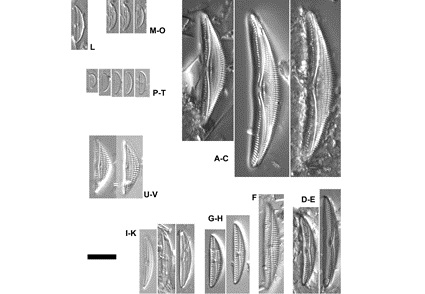
Abstract
During a survey of benthic diatoms from the Bulgarian Black Sea coast near the historic town of Sozopol, we found a high diversity of Amphora sensu lato taxa at a single site and on a single type of artificial substratum. A total of 40 taxa from the current genera Amphora, Halamphora, Seminavis and Tetramphora were recognized during light microscopy (LM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observations. We were able to identify with a high degree of certainty only 6 taxa based on the literature, whereas for 19 taxa (or almost 50% of all taxa) we could not find even sufficiently similar species, and they remained unidentified to species level. Many of the species had small valve dimensions. The paper presents all taxa with short morphometric data and microphotographs under LM and SEM, where possible. All taxa are discussed and compared with similar known taxa. The illustrative materials in earlier works from the Black Sea and species descriptions, where such were available, were also consulted. Diversity of Amphora sensu lato in the Black Sea coastal waters seems to be underestimated, whereas some of the past records are uncertain. A discussion on the current state of knowledge of Amphora sensu lato species from the Black Sea is given.
References
<p>Álvarez-Blanco, I. & Blanco, S. (2014) Benthic diatoms from Mediterranean coasts. <em>Bibliotheca Diatomologica</em> 60: 1–409.</p>
<p>Archibald, R.E.M. & Schoeman, F.R. (1984) <em>Amphora coffeaeformis</em> (Agardh) Kützing: a revision of the species under light and electron microscopy. <em>Journal of South African Botany</em> 3: 83–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-4618(16)30061-4</p>
<p>Balycheva, D.S. & Ryabushko, L.I. (2017) Benthos microalgae of the Lebyazhy’i ostrova Reserve in the Black Sea. <em>Nature Conservation Research</em> 2 (Suppl. 2): 9–18. [in Russian] https://doi.org/10.24189/ncr.2017.027</p>
<p>Bodeanu, N. (1976) Nouveaux diatomees benthiques du secteur Roumain de la mer Noire. <em>Roumain Cercetari Marine</em> 9: 59–70.</p>
<p>Borysova, O., Kondakov, A., Palcari, S., Rautalahti-Miettinen, E., Stolberg, F. & Daler, D. (2005) <em>Eutrophication in the Black Sea region; impact assessment and causal chain analysis.</em> University of Kalmar, Kalmar, Sweden, 60 pp. [ISBN 9189584503]</p>
<p>Clavero, E., Grimalt, J.O. & Hernández-Mariné, M. (2000) The fine structure of two small <em>Amphora</em> species. <em>A. tenerrima</em> Aleem and Hustedt and <em>A. tenuissima</em> Hustedt. <em>Diatom Research</em> 15: 195–208. https://doi.org/10.1080/0269249X.2000.9705495</p>
<p>Danielidis, D.B. & Mann, D.G. (2002) The systematics of <em>Seminavis</em> (Bacillariophyta): the lost identities of <em>Amphora angusta, A. ventricosa</em> and <em>A. macilenta. European Journal of Phycology</em> 37: 429–448. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0967026202003724</p>
<p>Desianti, N., Potapova, M. & Beals, J. (2015) Examination of the type materials of diatoms described by Hohn and Hellerman from the Atlantic Coast of the USA. <em>Diatom Research</em> 30: 93–116. https://doi.org/10.1080/0269249X.2014.1000020</p>
<p>Edler, L. (Ed.) (1979) Recommendations on methods for marine biological studies in the Baltic Sea. Phytoplankton and chlorophyll. <em>Baltic Marine Biologists Publication</em> 5: 1–38.</p>
<p>Edlund, M.B., Shinneman, A.L.C. & Levkov, Z. (2009) Diatom biodiversity in Mongolia: A new amphoroid diatom from saline lakes in western Mongolia, <em>Amphora soninkhishigae</em> sp. nov. <em>Acta Botanica Croatica </em>68: 251–262. https://hrcak.srce.hr/41428</p>
<p>Garcia, M. (2007) <em>Seminavis atlantica</em> Garcia, a new psammic diatom (Bacillariophyceae) from southern Brazilian sandy beaches. <em>Brazilian Journal of Biology </em>67: 765–769. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-69842007000400026</p>
<p>Giffen, M. (1971) Marine litoral diatoms from the Gordon’s Bay, Region of False Bay Cape Province, South Africa. <em>Botanica Marina</em> 14: 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1515/botm.1971.14.s1.1</p>
<p>Giffen, M. (1973) Diatoms from marine litoral of Steenberg’s Cove in St. Helena Bay, Cape Province, South Africa. <em>Botanica Marina</em> 16: 32–48. https://doi.org/10.1515/botm.1973.16.1.32</p>
<p>Grasshoff, K., Kremling, K. & Ehrhardt, M. (Eds.) (1999) <em>Methods of seawater analysis</em>. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, Weinheim, 634 pp. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527613984</p>
<p>Gregory, W. (1857) On new forms of marine Diatomaceae found in the Firth of Clyde and in Loch Fyne, illustrated by numerous figures drawn by K.K. Greville, LL. D., F. R. S. E. <em>Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh</em> 21: 473–542. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0080456800032269</p>
<p>Guslyakov, N.E. (1987) New species of the genus <em>Amphora (Bacillariophyta) </em>from the Black Sea. <em>Botanical Journal (Botanicheskii Zhurnal) </em>72: 1391–1395.+2 Pl. [in Russian]</p>
<p>Guslyakov, N.E., Zakordonetz, O.A. & Gerasimyuk, V.P. (1992) <em>Atlas of benthic diatoms from the northwestern part of the Black Sea and adjacent reservoirs</em>. Naukova Dumka, Kiev, 112 pp.+140 pl. [in Russian]</p>
<p>Hasle, G.R. & Fryxell, G.A. (1970) Diatoms: cleaning and mounting for light and electron microscopy. <em>Transactions of the American Microscopical Society</em> 89: 469–474. https://doi.org/10.2307/3224555</p>
<p>Hendey, N.I. (1973) Some benthic diatoms from the coast of Cornwall in the neighbourhood of Porthleven. <em>In</em>: Simonsen, R. (Ed.) <em>Proceedings of the Second Symposium on Recent and Fossil Marine Diatoms</em>, <em>London, 4–9 September 1972</em>. <em>Beihefte zur Nova Hedwigia</em> 45: 291–332.</p>
<p>Juhlin-Dannfelt, H. (1882) On the diatoms of the Baltic Sea. <em>Bihang till Kongliga Svenska Vetenskaps-Akademiens Handlingar</em> 6: 1–52.</p>
<p>Kaleli, M.A., Kulikovskiy, M.S. & Solak, C.N. (2017) Some new records for marine diatom flora of Turkey from Akliman, Sinop (Black Sea). <em>Turkish Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences</em> 17: 1387–1395. https://doi.org/10.4194/1303-2712-v17_6_32</p>
<p>Kociolek, J.P., Blanco, S., Coste, M., Ector, L., Liu, Y., Karthick, B., Kulikovskiy, M., Lundholm, N., Ludwig, T., Potapova, M., Rimet, F., Sabbe, K., Sala, S., Sar, E., Taylor, J.,Van de Vijver, B., Wetzel, C.E., Williams, D.M., Witkowski, A. & Witkowski, J. (2021)<em> DiatomBase</em>. Available from: http://www.diatombase.org (accessed 6 October 2021).</p>
<p>Levkov, Z. (2009) <em>Amphora </em>sensu lato. <em>Diatoms of Europe </em>5: 1–916.</p>
<p>Lokhova, D.S. (2012) Species composition, ecological and phytogeographical characteristics of glass plates periphyton diatoms at different terms of their exposure (Karantinnaya Bay, The Black Sea). <em>Optimization and Protection of Ecosystems (Ekosistemii, ih optimizacia i ohrana)</em> 7: 33–38. [in Russian]</p>
<p>López-Fuerte, F.O., Sala, S.E., Lora-Vilchis, M.C. & Murugan, G. (2020) <em>Halamphora siqueirosii</em> (Bacillariophyta), a new diatom species isolated from a hypersaline evaporation pond in Baja California Peninsula, Mexico. <em>Phytotaxa</em> 451: 132–144. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.451.2.3</p>
<p>Mann, D.G. (1994) The systematic of amphoroid diatoms: the life history of <em>A. arcus. Nova Hedwigia</em> 58: 335–352.</p>
<p>Milchakova, N.A., Nevrova, E.L. & Evstigneeva, I.K. (2002) Phytoperiphyton on concrete substrate in the Black Sea (Ukraine). <em>Algologia </em>12: 96–110. [in Russian]</p>
<p>Murray, J.W., Stewart, K., Kassakian, S., Krynytzky, M. & DiJulio, D. (2007) Oxic, suboxic, and anoxic conditions in the Black Sea. <em>In</em>: Yanko-Hombach, V., Gilbert, A.S., Panin, N. & Dolukhanov, P.M. (Eds.) <em>The Black Sea Flood Question: Changes in Coastline, Climate, and Human Settlement.</em> Springer, Dordrecht, pp. 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-5302-3_1</p>
<p>Nevrova, E.L. (2013а) Taxonomic diversity and structure of benthic diatom taxocene (Bacillariophyta) at Sevastopol Bay (the Black Sea). <em>Marine Ecological Journal (Morskiy Ekologichniy Journal)</em> 3: 55–67. [in Russian]</p>
<p>Nevrova, E.L. (2013b) Structure and taxonomical diversity of benthic diatom at estuarines of rivers Belbek and Chernaya (South-West Crimea, Ukraine). <em>Algologia</em> 23: 471–492. [in Russian] https://doi.org/10.15407/alg23.04.471</p>
<p>Nevrova, E. (2014a) Benthic diatoms (Bacillariophyta) at Zernov’s Phyllophora Field (Northern-Western part of the Black Sea): taxonomic diversity and structure of taxocene. <em>Marine Ecological Journal (Morskiy Ekologichniy Journal)</em> 3: 47–58. [in Russian]</p>
<p>Nevrova, E.L. (2014b) Taxonomic diversity and environmental assessment of benthic diatoms at Balaklava Bay (south-western Crimea, The Black Sea, Ukraine). <em>Algologia</em> 24: 47–66.+2 Pl. [in Russian] https://doi.org/10.15407/alg24.01.047</p>
<p>Nevrova, E.L. (2015a) Evaluation of benthic diatoms diversity (Bacillariophyta) near Karadag shore. <em>In</em>: Gayevskaya, A.V. & Morozova, A.L. (Eds.) <em>100 years of the T.I. Vyazemsky’s Karadag Scientific Station: issue of scientific papers. </em>N.Orianda, Simferopol, pp. 462–492.</p>
<p>Nevrova, E.L. (2015b) <em>Benthic diatoms (Bacillariophyta) of the Black Sea: diversity and structure of the taxocenes from various biotopes</em>. Author’s Dissertation Summary. Maks Press, Moscow, 47 pp.</p>
<p>Nevrova, E.L. (2016) The composition and structure of the benthic diatom taxocene (Bacillariophyta) near Cape Fiolent (the Crimea, the Black Sea). <em>Russian Journal of Marine Biology</em> 42: 392–401. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063074016050072</p>
<p>Nevrova, E. & Petrov, A. (2019a) Benthic diatoms species richness at Dvuyakornaya Bay and other coastal sites of Crimea (the Black Sea) under various environments. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science</em> 0: 506–520. https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.20319</p>
<p>Nevrova, E.L. & Petrov, A.N. (2019b) Assessment of benthic diatoms taxonomic diversity at coastal biotopes with different anthropogenic impact (Crimea, the Black Sea). <em>Turkish Journal of Botany</em> 43: 608–618. https://doi.org/10.3906/bot-1903-43</p>
<p>Nevrova, E., Witkowski, A., Kulikovskiy, M., Lange-Bertalot, H. & Kociolek, J.P. (2013) A revision of the diatom genus <em>Lyrella</em> Karayeva (Bacillariophyta: Lyrellaceae) from the Black Sea, with descriptions of five new species. <em>Phytotaxa</em> 83: 1–38. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.83.1.1</p>
<p>Ognjanova-Rumenova, N. (1995) Diatoms as indicators of palaeoenvironmental change occurred during the Holocene in the Bay of Sozopol (Bulgarian Black Sea coast). <em>Phytologia Balcanica</em> 2: 27–39.</p>
<p>Ognjanova-Rumenova, N. & Zaprjanova, D. (1998) Siliceous microfossil stratigraphy of sediment profile ‘F’ connected with archaeological excavations in coastal wetlands in the Bay of Sozopol (Bulgarian Black Sea coast). Part 1: Taxonomical documentation, diatom biostratigraphy and ecological analysis of the diatom flora. <em>Phytologia Balcanica</em> 4: 65–80.</p>
<p>Ognjanova-Rumenova, N., Zaprjanova, D. & Popova, E. (1998) Siliceous microfossil stratigraphy of sediment profile ‘F’ connected with archaeological excavations in coastal wetlands in the Bay of Sozopol (Bulgarian Black Sea coast). Part 2: Palaeoenvironmental interpretations. <em>Phytologia Balcanica</em> 4: 39–50.</p>
<p>Ognjanova-Rumenova, N., Filipova-Marinova, M. & Popova, E. (1999) Analysis of vegetation-environment relationships in the Bay of Sozopol, Bulgarian Black Sea coast by the CCA method. <em>Acta Paleobotanica</em> (Suppl. 2): 589–593.</p>
<p>Park, J. & Koh, C.-H. (2012) Taxonomic studies on Korean marine benthic diatoms – LM and SEM observations on the diatom genus <em>Amphora </em>(Bacillariophyceae) from Korean tidal flats with the first recordings of <em>A. arenicola, A. beaufortiana </em>and <em>A. maletractata </em>var. <em>constricta. Ocean Science Journal </em>47: 101–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-012-0011-9</p>
<p>Petrov, A. & Nevrova, E. (2007) Database on Black Sea benthic diatoms (Bacillariophyta): its use for a comparative study of diversity pecularities under technogenic pollution impacts. <em>In</em>: Berghe, E.W., Appeltans, W., Costello, M.J. & Pissierssens, P. (Eds.) <em>Proceedings of Ocean Biodiversity Informatics: an international conference on marine biodiversity data management, Hamburg, 29 November–1 December 2004. </em>VLIZ Special Publication. Vlaams Instituut voor de Zee (VLIZ), Oostende, pp. 153–165.</p>
<p>Petrov, A.N. & Nevrova, E.L. (2013) Extrapolative estimation of benthic diatoms (Bacillariophyta) species diversity in different marine habitats of the Crimea (Black Sea). <em>International Journal of Biodiversity</em>: Article ID 975459, 12 pp. + Suppl. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/975459</p>
<p>Petrova, V., Temniskova, D., Valeva, M. & Passy, S. (1991) Taxonomic analysis and phytocoenologic characteristics of benthic diatom flora from the Bulgarian Black Sea shelf. <em>In</em>: <em>Proceedings of the Black Sea Symposium, Ecological problems and economical prospects, Istanbul, 16–18 September 1991</em>. The Black Sea Foundation for Education, Culture and Protection of Nature, Istanbul, pp. 267–270.</p>
<p>Potapova, M., Veselá, J., Smith, C., Minerovic, A. & Aycock, L. (Eds.) (2021) <em>Diatom New Taxon File at the Academy of Natural Sciences (DNTF-ANS), Philadelphia</em>. Available from: http://dh.ansp.org/dntf (accessed 13 October 2021).</p>
<p>Proshkina-Lavrenko, A.I. (1963) <em>Diatoms from the Black Sea benthos</em>. Akademii Nauk USSR, Moscow-Leningrad, 243 pp. [in Russian]</p>
<p>Regulation No. H-4 of 14.09.2012 on characterization of surface water. <em>Official Gazette of the Republic of Bulgaria 22/2013 and 79/2014</em>. Available from: http://www.fao.org/faolex/results/details/en/c/LEX-FAOC174346 (accessed 21 November 2021) [in Bulgarian]</p>
<p>Round, F.E., Crawford, R.M. & Mann, D.G. (1990) <em>The Diatoms. Biology and morphology of the genera</em>. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 747 pp.</p>
<p>Ryabushko, L.I. (2020) Microphytobenthos of Zernov’s Phyllophora Field (the Black Sea). <em>Ekosystems (Ekosistemii)</em> 23: 16–31. [in Russian]</p>
<p>Ryabushko, L.I., Balycheva, D.S. & Ryabushko, V.I. (2017) Microphytobenthos Diatoms of the Black Sea: Biodiversity and Ecology. <em>Ecologica Montenegrina </em>14: 48–59. https://doi.org/10.37828/em.2017.14.6</p>
<p>Ryabushko, L.I., Lishaev, D.N. & Kovrigina, P. (2019) Species diversity of epilithon diatoms and the quality of the waters of the Donuzlav Gulf ecosystem (Crimea, the Black Sea). <em>Diversity</em> 11: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11070114</p>
<p>Ryabushko, L.I., Firsov, U.K., Torskaya, A.V. & Toichkin, A.M. (2005) Methodical aspects of investigation of microepiphytes of <em>Cystoseira barbata</em> (Stackhouse) C. Ag. depending on its age for bionindication of the Black Sea coastal ecosystems state. <em>Ecological safety of coastal and shelf zones and integrated use of shelf resources (Ekologichna bezpeka priberezhnoí i shelfovoí zoni i kompleksnoto izpolzvane na resursite shel’fu) </em>12: 540–553. [in Russian]</p>
<p>Sala, S.E., Sar, E.A., Hinz, F. & Sunesen, I. (2006) Studies on <em>Amphora</em> subgenus <em>Halamphora </em>(Bacillariophyta): the revision of some species described by Hustedt using type material. <em>European Journal of Phycology</em> 41: 155–167. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670260600556609</p>
<p>Sar, E.A., Sala, S.E., Hinz, F. & Sunesen, I. (2004) An emended description of <em>Amphora</em> <em>tumida</em> Hustedt (Bacillariophyceae). <em>Diatom Research</em> 19: 71–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/0269249X.2004.9705608</p>
<p>Schoeman, F.R. & Archibald, R.E.M. (1986) Observations on <em>Amphora</em> species (Bacillariophyceae) in the British Museum (Natural History). V. Some species from the subgenus <em>Amphora</em>. <em>Journal of South African Botany</em> 52: 425–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-6299(16)31507-1</p>
<p>Simonsen, R. (1992) The diatom types of Heinrich Heiden in Heiden & Kolbe 1928. <em>Bibliotheca Diatomologica</em> 24: 1–100. + 86 pl.</p>
<p>Stepanek, J.G. & Kociolek, J.P. (2013) Several new species of <em>Amphora</em> and <em>Halamphora</em> from the western USA. <em>Diatom Research</em> 28: 61–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/0269249X.2012.735205</p>
<p>Stepanek, J.G. & Kociolek, J.P. (2016) Re-examination of Mereschkowsky’s genus <em>Tetramphora</em> (Bacillariophyta) and its separation from <em>Amphora</em>. <em>Diatom Research</em> 31: 123–148. https://doi.org/10.1080/0269249X.2016.1183344</p>
<p>Stepanek, J.G. & Kociolek, J.P. (2018) <em>Amphora</em> and <em>Halamphora</em> from coastal and inland waters in the United States and Japan. <em>Bibliotheca Diatomologica</em> 66: 1–260.</p>
<p>Temniskova-Topalova, D., Petrova-Karadzhova, V. & Valeva, M.T. (1994) Taxonomic composition of benthic algae (<em>Bacillariophyta</em>) of the Bulgarian Black Sea shelf . <em>Algologia </em>4: 39–47. [in Russian]</p>
<p>Van de Vijver, B., Kopalová, K., Zidarova, R. & Levkov, Z. (2014) Revision of the genus <em>Halamphora </em>(Bacillariophyta) in the Antarctic Region. <em>Plant Ecology and Evolution</em>147: 374–391. https://doi.org/10.5091/plecevo.2014.979</p>
<p>Wachnicka, A.H. & Gaiser, E.E. (2007) Characterization of <em>Amphora</em> and <em>Seminavis</em> from South Florida, U.S.A. <em>Diatom Research</em> 22: 387–455. https://doi.org/10.1080/0269249X.2007.9705722</p>
<p>Witkowski, A., Lange-Bertalot, H. & Metzeltin, D. (2000) Diatom flora of marine coasts I. <em>Iconographia Diatomologica </em>7: 1–925.</p>
<p>Witkowski, A., Kulikovskiy, M., Nevrova, E., Lange-Bertalot, H. & Gogorev, R. (2010) The genus <em>Navicula</em> in ancient basins. I. Two novelties from the Black Sea. <em>Plant Ecology and Evolution</em> 143: 307–317. https://doi.org/10.5091/plecevo.2010.421</p>