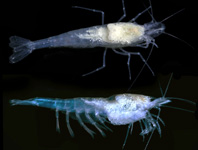
Abstract
A new species of stygobiotic atyid shrimp genus Troglocaris (Xiphocaridinella) Dormitzer, 1853 from underground stream and lakes of Kumistavi (Prometheus) Cave, Tskaltubo, Imereti region, Western Georgia is described based on morphology and DNA analysis. Troglocaris (Xiphocaridinella) kumistavi sp. nov. clearly differs from all Caucasian congeners by (1) long slender dorsally and ventrally armed rostrum with sting-like tip turned upward, (2) very slender fingers of pereiopod II both in males and females and (3) distally expanded telson with 5–7 pairs of distal spines. These features are rather unique within the known Caucasian Troglocaris (Xiphocaridinella) and show some morphological similarities with Dinaric species of the genus. Neotype of Troglocaris (Xiphocaridinella) kutaissiana (Sadowsky, 1930) is also designated based on the material from Tskaltsitela Cave, Kutaisi, Georgia.
References
Avise, J.C. (2000) Phylogeography: the history and formation of species. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA, 447 pp.
Birštein, Ya. A. (1939) O peshernysh krevetkah Abhazii [About cave shrimps of Abkhazia]. Zoologichesky Zhurnal, XVIII, 960–974. [in Russian]
Christodoulou, M., Anastasiadou, Ch., Jugovic, J. & Tzomos, T. (2016) Freshwater Shrimps (Atyidae, Palaemonidae, Typhlocarididae) in the Broader Mediterranean Region: Distribution, Life Strategies, Threats, Conservation Challenges and Taxonomic Issues. In: Kawai, T. & Cumberlidge, N. (Eds.), A Global Overview of the Conservation of Freshwater Decapod Crustaceans. Springer International Publishing AG, Basel, pp. 199–236.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-42527-6_7Hebert, P.D.N., Cywinska, A., Ball, S.L. & De Waard, J.R. (2003) Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B, 270, 313–322.
https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2002.2218Juzbaš’jan, S.M. (1940) On a cave shrimp from Shakuran. Trudy biologiceskoj stancii Narkomprosa Gruzinskoj SSR, 1, 73–86. [in Russian]
Jugovic, J., Jalžić, B., Prevorčnik, S. & Sket, B. (2012) Cave shrimps Troglocaris s. str. (Dormitzer, 1853), taxonomic revision and description of new taxa after phylogenetic and morphometric studies. Zootaxa, 3421, 1–31.
Jugovic, J., Prevorčnik, S., Blejec, A. & Sket, B. (2011) Morphological differentiation in the cave shrimps Troglocaris (Crustacea: Decapoda: Atyidae) of the Dinaric karst—a consequence of geographical isolation or adaptation? Journal of Zoological Systematic and Evolutionary Researches, 49 (3), 185–195.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0469.2010.00611.xJugovic, J., Prevorčnik, S., Aljančič, G. & Sket, B. (2010) The atyid shrimp (Crustacea: Decapoda: Atyidae) rostrum: phylogeny versus adaptation, taxonomy versus trophic ecology. Journal of Natural History, 44, 41–42, 2509–2533.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2010.502258Knowlton, N. & Weigt, L.A. (1998) New dates and new rates for divergence across the Isthmus of Panama. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B, 265, 2257–2263.
https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.1998.0568Knowlton, N., Weight, L.A., Solorzano, L.A., Mills, D.K. & Bermingham, E. (1993) Divergence in proteins, mitochondrial DNA and reproductive compatibility across the Isthmus of Panama. Science, 260, 1629–1632.
https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8503007Lefébure, T., Douady, C.J., Gouy, M. & Gibert, J. (2006) Relationships between morphological taxonomy and molecular divergence within Crustacea: proposal of a molecular threshold to help species delimitation. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 40 (2), 435–447.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2006.03.014Lushai, G., Smith, D.A.S., Goulson, D., Allen, J.A. & Maclean, N. (2003) Mitochondrial DNA clocks and the phylogeny of Danaus butterflies. Insect Science and Its Application, 2, 309–315.
https://doi.org/10.1017/s1742758400012376Marin, I.N. (2015) Atlas of Decapod Crustaceans of Russia. KMK Scientific Press, Moscow, 145 pp.
Marin, I. & Sokolova, A. (2014) Redescription of the stygobiotic shrimp Troglocaris (Xiphocaridinella) jusbaschjani Birštein, 1948 (Decapoda: Caridea: Atyidae) from Agura River, Sochi, Russia, with remarks on other representatives of the genus from Caucasus. Zootaxa, 3754 (3), 277–298.
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3754.3.3Sadowsky, A.A. (1930) Xiphocaridinella kutaissiana nov. gen. et sp. (fam. Atyidae) iz podzemnoi peshchery pod Kutaisom [Xiphocaridinella kutaissiana nov. gen. et sp. (fam. Atyidae) from subterranean cave near Kutaisi]. Zakavkazskij kraevedstenny sbornik naučnoissledovatel’nogo kraevedstvenogo kabineta Universiteta Tiflis, 1, 93–104. [in Russian]
Sites, J.W. & Marshall, J.C. (2004) Operational criteria for delimiting species. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 35, 199–227.
https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.35.112202.130128Sket, B. & Zakšek, V. (2009) European cave shrimp species (Decapoda: Caridea: Atyidae), redefined after a phylogenetic study; redefinition of some taxa, a new genus and four new Troglocaris species. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 155, 786–818.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.2008.00473.xZakšek, V., Sket, B. & Trontelj, P. (2007) Phylogeny of the cave shrimp Troglocaris: evidence of a young connection between Balkans and Caucasus. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 42, 223–235.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2006.07.009