Abstract
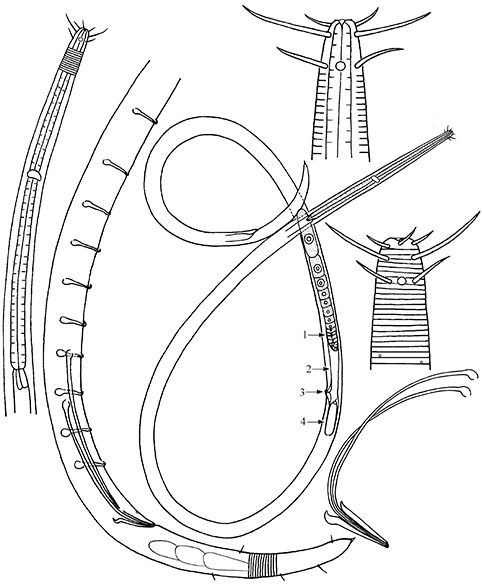
A new species of Setostephanolaimus Tchesunov, 1994, S. longiseta sp. nov. was discovered in an intertidal sand beach along the Rizhao coast of the Yellow Sea. It is characterized by its long and slender body, long cephalic setae (longer than 20 µm and 16 µm in males and females, respectively) and subcephalic setae, long spicules (longer than 90 µm), gubernaculum with dorsal hooked apophyses, along with presence of 10–12 tubular precloacal supplements in males. Updated dichotomous key for species of the genus Setostephanolaimus is also given.
References
Bezerra, T.N., Decraemer, W., Eisendle-Flöckner, U., Hodda, M., Holovachov, O., Leduc, D., Miljutin, D., Mokievsky, V., Peña Santiago, R., Sharma, J., Smol, N., Tchesunov, A., Venekey, V., Zhao, Z. & Vanreusel, A. (2021) Nemys: World Database of Nematodes. Available from: http://nemys.ugent.be (accessed 9 January 2021) https://doi.org/10.14284/366
Boucher, G. & Helléouët, M.N. (1977) Nématodes des sables fins infralittoraux de la Pierre Noire (Manche occidentale). III. Araeolaimida et Monhysterida. Bulletin du Museum nationale d’histoiro naturelle, Paris, 427, 85–122.
Ditlevsen, H. (1918) Marine freeliving nematodes from Danish waters. Videnskabelige Meddelelser fra Naturhistorisk Forening, 70 (7), 147–214.
Fadeeva, N.P. & Mordukhovich, V.V. (2007) New and known Leptolaimidae (Nematoda, Chromadoria) species in the Sea of Okhotsk and the Sea of Japan. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 86, 3–15.
Gadea, E. (1973) Sobre la filogenia interna de los Nematodos. Instituto de Biologia Aplicada, 54, 87–92.
Gerlach, S. A. (1953) Die Nematodenbesiedlung des Sandstrandes und des Küstengrundwassers an der italienischen Küste I. Systematischer Teil. Archivio Zoologico Italiano, 37, 517–640.
Holovachov, O. (2014) Swedish Plectida (Nematoda). Part 7. Setostephanolaimus tchesunovi sp. n. from the west coast of Sweden. Zootaxa, 3847 (4), 576–582. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3847.4.7
Huang, Y. & Sun, J. (2019) Paramonohystera weihaiensis sp. nov. (Xyalidae, Nematoda) from the intertidal beach of the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 37 (4), 1403–1408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-8225-7
Jensen, P. (1976) Free-living marine nematodes from a sublittoral station in the North Sea off the Belgian Coast. Biologisch Jaarboek Dodonaea, 44, 231–255.
Jonge, V.N. & Bouwman, L.A. (1977) A simple density separation technique for quantitative isolation of meiobenthos using the colloidal silica Ludox-TM. Marine Biology, 42, 143–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391564
Lorenzen, S. (1969) Freilebende Meeresnematoden aus dem Schlickwatt und den Salzwiesen der Nordseeküste. Veroeffentlichungen des Instituts fuer Meeresforschung in Bremerhhaven, XI, 195–238.
McIntyre, A.D. & Warwick, R.M. (1984) Meiofauna techniques. In: Holme, N.A. & McIntyre, A.D. (Eds.), Methods for the study of marine benthos. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp. 217–244.
Micoletzky, H. (1924) s.n. Weitere Beiträge zur Kenntnis freilebender Nematoden aus Suez, (I), 132, 225–262.
Schuurmans Stekhoven, J.H. Jr. (1935) Nematoda: Systematischer Teil, Nematoda errantia. Grimpe, G. and E. Wagler, Die Tierwelt der Nord- und Ostsee (Leipzig 1935), 173 pp.
Tchesunov, A.V. (1994) Description of a marine free-living nematode Stephanolaimus graciosus sp. n. and erection of Setostephanolaimus gen. n. (Chromadoria: Leptolaimidae). Russian Journal of Nematology, 2, 79–82.
Vadhyar, K.J. (1981) A new and two known species belonging to subfamily Leptolaiminae (Leptolaimidae, Nematoda), from polluted intertidal sand in Scotland. Cahiers de Biologie Marine, 22 (3), 313–321.
Zhai, H.X., Wang, C.M. & Huang, Y. (2020) Two new species of Antomicron Cobb, 1920 (Nematoda: Leptolaimidae) from Jiaozhou Bay, China. Journal of Natural History, 54, 1199–1212. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2020.1781948