Abstract
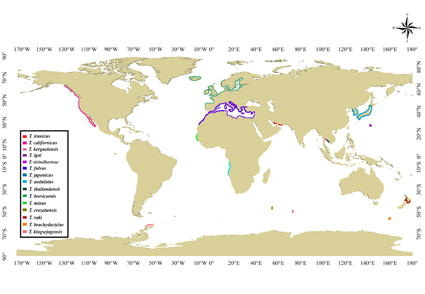
Here we present some hypothetical phylogenetic relationships and the evolutionary history of the harpacticoid copepod genus Tigriopus Norman, 1869 using morphological data. Cladistic analyses were performed with 21 morphological characters, including 15 ingroup and eight outgroup species. Inferred topology from Bayesian inference supported the monophyletic status of the genus, and revealed two main evolutionary lineages. One of these lineages (the brachydactylus-iagi lineage) comprises species from the Indo-Pacific, the northern Pacific, the southern Pacific, and the southern Atlantic; it is supported by the tetrasetose female P5 endopod. The fulvus-angulatus lineage is composed of three clusters with species from the north Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea (the fulvus-brevicornis clade), the northwestern Pacific and the Indo-Pacific (the japonicus-sirindhoranae clade), and from the southern Pacific, the Indian Ocean, and the Southern Ocean (the crozettensis-angulatus clade). The groundpattern of the mandibular basis of the fulvus-angulatus lineage seems to include a bisetose mandibular basis, and, the presence of three setae on this segment in the japonicus-sirindhoranae clade is interpreted here as a character reversal. Biogeographic analyses suggest that the tropical Indo-Pacific region is the most probable ancestral area of the genus that diversified through vicariance events.
References
Anton R.F., Schrödl M. (2013) The gastropod-crustacean connection: towards the phylogeny and evolution of the parasitic copepod family Splanchnotrophidae. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 167, 501–530. https://doi.org/10.1111/zoj.12338
Baker, C.F. (1912) Notes on the Crustacea of Laguna Beach. First Annual Report of the Laguna Marine Laboratory 1, 100–117.
Barreto, F.S., Schoville S.D., Burton R.S. (2015) Reverse genetics in the tide pool: knock-down of target gene expression via RNA interference in the copepod Tigriopus californicus. Molecular Ecology, 15, 868–879. https://doi.org/ 10.1111/1755-0998.12359
Barreto, F.S., Watson, E.T., Lima, T.G., Willett, C.S., Edmands, S., Li, W., Burton, R.S. (2018) Genomic signature of mitonuclear coevolution across populations of Tigriopus californicus. Evolutionary Ecology, 2, 1250–1257. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-018-0588-1
Bozi, C.B. (1960) Le genre Tigriopus Norman (Copépodes Harpacticoïdes) et ses formes européennes; recherches morphologiques et expérimentales. Archives de zoologie expérimentale et Générale, 98 (3), 167–269.
Bradford, J. (1967) The genus Tigriopus Norman (Copepoda, Harpacticoida) in New Zealand with a description of a new species. Transaction Royal Society of New Zealand. Zoology, 10 (6), 51–59.
Burton, R.S., Metz, E.C., Flowers, J.M., Willett, C.S. (2005) Unusual structure of ribosomal DNA in the copepod Tigriopus californicus: intergenic spacer sequences lack internal sub repeats. Gene, 344, 105–113. https:/doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2004.09.001
Candeias, A. (1959) Contribution to the knowledge of the harpacticoids (Crustacea Copepoda) from the littoral of Angola. Publicações culturais da Companhia de Diamantes de Angola, 45, 77–104.
Chullasorn, S., Dahms, H.D., and Klangsin, P. (2013) A new species of Tigriopus (Copepoda: Harpacticoida: Harpacticidae) from Thailand with a key to the species of the genus. Journal of Natural History, 47, 427–447. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2012.757660
Chullasorn, S., Ivanenko, V.N., Dahms, H.U., Kangtia, P., Yang, W.X. (2012) A new species of Tigriopus (Copepoda, Harpacticoida, Harpacticidae) from Thailand with the description of its naupliar development. Helgoland Marine Research, 66 (2), 139–151.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10152-011-0254-3
Dahms, H.U., Chullasorn, S., Kangtia, P., Ferrari, F.D., Hwang, J.S. (2007) Naupliar development of Tigriopus japonicus Mori, 1932 (Copepoda: Harpacticidae). Journal of zoology studies, 46 (6), 746–759.
Dana, J.D. (1846) Notice of some genera of Cyclopacea. The Am. J. of Sci. Arts, 2nd Series. 1(2), 225–230 [1 March1846] [subsequently published in The Annals and Magazine of Natural History 18 (118), 181–185; 1 Sept 1846] https://doi.org/10.1080/037454809494408
Dybdahl, M.F. (1994) Extinction, recolonization and the genetic structure of the tidepool copepod population. Evolutionary Ecology, 8, 113–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01238245
Edamands, S. (1999) Heterosis and outbreeding depression in interpopulation crosses spanning a wide range of divergence. Evolution, 53, 1757–1768. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1999.tb04560.x
Edmands, S. (2001) Phylogeography of the intertidal copepod Tigriopus californicus reveals substantially reduced population differentiation at northern latitudes. Molecular Ecology, 10, 1743–1750. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0962-1083.2001.01306.x
Fischer, S. (1860) Beiträge zur Kenntniss der Entomostraceen. Abhandlungen der Bayerischen Akademie der Wissenschaften. 8, 1–645.
Foley, B.R., Rose, C.G., Eundle, D.E., Leong, W., Moy, G.W., Burton. R.S., Edmands, S. (2011) A gene-based SNP resource and linkage map for the copepod Tigriopus californicus. BMC Genomics, 12, 568–575. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-568
Handschumacher, L., Steinarsdóttir, M.B., Edmands, S., Ingólfsson, A. (2010) Phylogeography of the rock-pool copepod Tigriopus brevicornis (Harpacticoida) in the northern North Atlantic, and its relationship to other species of the genus. Marine Biology, 157, 1357–1366.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-010-1415-7
Hou, Z., Li, S. (2017) Tethyan changes shaped aquatic diversification. Aquatic diversification in the Tethyan region, Biological reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 93 (2), 874–896. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12376
Huelsenbeck, J.P., Ronquist, F. (2001) MrBayes: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinform. 17, 754–755. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/17.8.754
Itô, T. (1979) Descriptions and records of marine Harpacticoid Copepods from Hokkaido, VII. Journal of the Faculty of Science, Hokkaido University. Series 6, Zoology, 22 (21), 42–68
Itô, T. (1980) Three species of the genus Zaus (Copepoda, Harpacticoida) from Kodiak Island, Alaska. Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory, 25 (1–4), 51–77. https://doi.org/10.5134/175993
Kangtia, P., Dahms, H.U., Song, S.J., Myoung, J.G., Park, J. & Khim, J.S. (2014) On the occurrence of a ne species of benthis copepod, Zaus wonchelleei (Harpacticoida, Harpacticidae), in a macroalgal habitat from Tongyong, Korea. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington, 127 (4), 585–602.
https://doi.org/10.2988/0006-324x-127.4.585
Karanovic, T., Kim, K. (2014) Suitability of cuticular pores and sensilla for harpacticoid copepod species delineation and phylogenetic reconstruction. Arthropod Structure & Development, 43, 615–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asd.2014.09.003
Kelly, L.S., Snell, T.W. (1998) Role of surface glycoproteins in mate guarding of the marine harpacticoid Tigriopus japonicus. Marine Biology, 130, 605–612. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050282
Ki, J.S., Lee, K.W., Park, H.G., Chullasorn, S., Dahms, H.U., Lee. J.S. (2009) Phylogeography of the copepod Tigriopus japonicus along Northwest Pacific rim. Journal of Plankton Research, 1 (2), 209–221. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbn100
Kim, I.C., Kim, Y.J., Lee, Y.M., Kim, B.G., Park, T.J., Kim, H.S., Jung, M.M., Williams, T.D., Lee, W., Lee, J.S. (2004) cDNA cloning of translationally controlled tumor protein/histamine releasing factor (TCTP/HRF) from the intertidal harpacticoid copepod Tigriopus japonicus. DNA sequencing, 15, 159–163. https://doi.org/10.1080/1042517042000199960
Kim, I.C., Kim, Y.J., Song, S.J., Lee, J.S., Lee, W. (2003) The intertidal harpacticoid copepod Tigriopus japonicus (Crustacea: Copepoda) β-actin gene: cloning, sequence and intraspecies variation. DNA sequencing, 14, 279–284.
https://doi.org/10.1080/1085566031000141135
Koga, F. (1970) On the life history of Tigriopus japonicus Mori (Copepoda). Journal of Oceanography, 26, 11–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02764551
Kwok, K.W.H., Leung, K.M.Y. (2005) Toxicity of antifouling biocides to the intertidal harpacticoid copepod Tigriopus japonicus (Crustacea, Copepoda): effects of temperature and salinity. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 51, 830–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.02.036
Lee, K.W., Hwang, D.S., Rhee, J.S., Ki, J.S., Park, H.G., Ryu, J.C., Raisuddin, S., Lee, J.S. (2008) Molecular cloning phylogenetic analysis and developmental expression of a vitellogenin (Vg) gene from the internal copepod Tigriopus japonicus. Comparative Biochemistry & Physiology B, 150, 395–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2008.04.009
Lee, Y.M., Kim, I.C., Jung, S.O., Lee, J.S. (2005) Analysis of 686 expressed sequence tags (ESTs) from the intertidal harpacticoid copepod Tigriopus japonicus (Crustacea, Copepoda). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 51, 757–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.02.014
Lee, S., Kim, K., Le,e W. (2014) A new species of Harpacticella Sars, 1908 (Copepoda, Harpacticoida), from a tidal pool on Jeju Island, Korea. Zookeys, 445, 13–30. https://doi.org/ 10.3897/zookeys.445.7831
Marcial, H.S., Hagiwara, A., Snell, T.W. (2003) Estrogenic compounds affect development of harpacticoid copepod Tigriopus japonicus. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 22, 3025–3030. https://doi.org/10.1897/02-622.
McAllen, R., Taylor, A.C., Davenport, J. (1999) The effect of temperature and oxygen partial pressure on the rate of oxygen consumption of the high-shore rock pool copepod Tigriopus brevicornis. Comparative Biochemistry & Physiology B. 123, 195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1095-6433(99)00050-1
Müller, O.F. (1776) Zoologiae Danicae Prodromus, seu Animalium Daniae et Norvegiae indigenarum characteres, nomina et synonyma imprimis popularium. M. Hallager, Havniae (The Hague), 1–274. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.13268
Nazari, F., Mirshamsi, O., Martínez, Arbizu, P. (2021) Tigriopus iranicus sp. nov., a new species of Harpacticidae (Copepoda, Crustacea) from Iran, with a redescription of T. raki Bradford, 1967. Zookeys, 1035, 115–144. https//doi. Org/10.3897/zookeys.1035.61584
Norman, A.M. (1869) Shetland Final Dredging Report. Part II. On the Crustacea, Tunicata, Polyzoa, Echinodermata, Actinozoa, Hydrozoa, and Porifera. British Association for the Advancement of Science, 38, 247–336.
Park, E.O., Lee, S., Cho Mijin, Yoon, S.H., Lee, Y., Lee, W. (2014). A new species of the genus Tigriopus (Copepoda: Harpacticoida: Harpacticidae) from Antarctica. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington, 127 (1), 138–154. https://doi.org/10.2988/0006-324X-127.1.138
Poppe, S.A. (1884) Ueber die von den Herren Dr. Arthur und Aurel Krause im nördlichen Stillen Ocean und Behringsmeer gesammelten freilebenden Copepoden. Archiv für Naturgeschichte, 50 (1), 281–304, pls. 20–24.
Raisuddin, S., Kwok, K.W.H., Leung, K.M.Y., Schlenk, D., Lee, J.S. (2007) The copepod Tigriopus: A promising marine model organism for ecotoxicology and environmental genomics. Aquatic Toxicology, 83, 161–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.04.005
Rambaut, A. (2018) FigTree v 1.4.4.: Tree figure drawing tool. Available from: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (Accessed 19 Sept. 2022)
Rambaut, A., Drummond, A.J., Xie, D., Baele, G., Suchard, M.A. (2018) Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Systematic Biology. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syy032
Seo, J.S., Lee, Y.M., Park, H.G., Lee, J.S. (2006) The intertidal copepod Tigriopus japonicus small heat shock protein 20 gene (Hsp 20) enhance thermotolerance of transformed Escherichia coli. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 340, 901–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.12.086
Soyer, J., Thiriot-Quiévreux, C., Colomines, J.C. (1987) Description de deux espèces jumelles du groupe Tigriopus angulatus (Copepoda, Harpacticoida) dans les archipels Crozet et Kerguelen (Terres Australes et Antarctiques Françaises). Zoologica Scripta, 16 (2), 143–154. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-6409.1987.tb00061.x
Swofford, D. (2002) Paup. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (and other methods). Version 4.0b10. Sunderland, MA (USA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.
Vecchioni, U., Marrone, F., Rodilla, M., Belda, E.J., Arculeo, M. (2019) An account on the taxonomy and molecular diversity of a marine rock-pool dweller, Tigriopus fulvus (Copepoda, Harpacticoida). Ciencias marinas, 45 (2), 59–75. https://doi.org/10.7773/cm.v45i2.2946
Veevers, J.J., McElhinny, M.W. (1976) The separation of Australia from other continents. Earth-Science Reviews, 12, 139–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-8252(76)90003-9
Vervoort, W. (1964) Free-living Copepoda from Ifaluka Atoll in the Caroline Islands with notes on related species. Smithsonian Institution Washington, D. C. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.03629236.236.1
Watkins, R.L. (1987) Description of new species of Bradyellopsis and Perissocope (Copepoda: Harpacticoida) from the California coast with revised keys to the genera. Journal of Crustacean Biology, 7 (2), 380–395. https://doi.org/10.2307/1548617
Wells, J.B.J. (1968) New and rare Copepoda Harpacticoida from the Isles of Scilly. Journal of Natural History, 2, 398–424. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222936800770391
Yu, Y., Harris, A.J., Xingjin, H. (2011) RASP (Reconstruct Ancestral State in Phylogenies) 1.1. Available from: http://mnh.scu.edu.cn/soft.blog. RASP.
Yu, Y., Harris, A.J., Xingjin, H. (2010) S-DIVA (Statisrical Dispersal-Vicariance Analysis): a tool for inferring biogeographic histories. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 56, 848–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2010.04.011