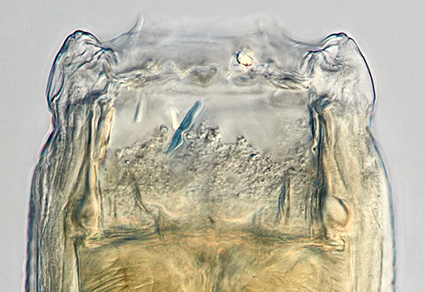
Abstract
Prof. Arthur Looss (1861–1923) was a prolific German parasitologist, who, among other things, authored descriptions of 22 new species of nematodes and 115 new species of trematodes. After his death, his collection (including type material) was split between several institutions: Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History in Washington (USA), Natural History Museum in Berlin and the Natural History Museum in Leipzig (Germany), Gothenburg Museum of Natural History and Swedish Museum of Natural History (Sweden). Here we revise all type specimens of nematodes from the A. Looss collection that are currently preserved in the Swedish Museum of Natural History (Strongylus subtilis, Sclerostomum edentatum, S. vulgare, Cyathostomum labratum, C. coronatum, C. bicoronatum, C. calicatum, C. alveatum, C. catinatum, C. nassatum, C. radiatum, C. elongatum, C. auriculatum, Triodontus minor, T. serratus, C. labiatum and Uncinaria polaris), designate and describe lectotypes wherever deemed necessary and provide catalogue access numbers to all type materials. We also revise all notes and drawings associated with new species that A. Looss described and provide previously unpublished pencilled sketches and ink print-ready drawings of some of these species (Strongylus subtilis, Cyathostomum poculatum, C. radiatum, C. elongatum, C. calicatum, C. auriculatum, Triodontus serratus, Trichostrongylus vitrinus and possibly Necator africanus).
References
Anonymous (1923) Arthur Looss, Ph.D. The British Medical Journal, 1 (3255), 884. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.1.3255.884
Baylis, H.A. (1924) Biographical notes on Bilharz, Looss and Luhe. Parasitology, 16, 332–341. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182000020205
Bredtmann, C.M., Krücken, J., Kuzmina, T., Louro, M., Madeira de Carvalho, L.M. & von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G. (2019) Nuclear and mitochondrial marker sequences reveal close relationship between Coronocyclus coronatus and a potential Cylicostephanus calicatus cryptic species complex. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 75, 103956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2019.103956
Chaves, O. (1930) Nouveau trichonema du cheval, Cylicocyclus bulbiferum n. sp. Comptes rendus des seìances de la Socieìteì de biologie, Paris, 105, 734–735.
Cram, E.B. (1924) A new Nematode, Cylindropharynx ornata from the zebra with key to related nematode parasites of the Equidae. Journal of Agricultural Research, 28, 661–672.
Creplin, F.C.H. (1845) Nachtrage zu Gurlt’s Verzeichniss der Thiere, bei welchen Entozoen gefunden worden sind. Archiv für Naturgeschichte, 11 (1), 325–330
Cummings, S.L. (1912) Review of “Anatomy and life history of Anchylostoma duodenale (Dubini) by A. Looss. Journal of the Royal Army Medical Corps, 19, 42–55.
Dubini, A. (1843) Nuovo verme intestinale umano (Anchylostoma duodenale), constitutente un sesto genere dei nematoidei proprii dell’uomo. Annali Universali di Medicina, Milano, 106, 5–13.
Ershov, V.S. (1943) Diferentsialny diagnoz nematod roda Trichonema, parazitiruischikh u loshadei [Differential diagnosis of nematodes of the genus Trichonema found in horses]. Trudy Kirovskogo Zooveterinarnogo Instituta, 5, 61–86. [in Russian]
Gibbons, L.M. & Lichtenfels, J.R. (1999) Strongylus tetracanthus Mehlis, 1831 (currently Cyathostomum tetracanthum) and C. catinatum Looss, 1900 (Nematoda): proposed conservation of usage by the designation of a neotype for C. tetracanthum. Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature, 56, 230–234. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.23083
Giles, G.M.J. (1892) On a new Sclerostoma from the large intestine of mules. A description of two new Nematode parasites found in sheep. Scientific memoirs by medical officers of the Army of India, 7, 25–30.
Hartwich, G. (1986) Zum Strongylus tetracanthus—Problem und zur Systematik der Cyathostominea (Nematoda: Strongyloidea). Mitteilungen aus dem Zoologischen Museum in Berlin, 62, 61–102. https://doi.org/10.1002/mmnz.19860620107
Hassall, A., Doss, M., Segal, D.B. & Ray, D.H. (1946) Index-Catalogue of Medical and Veterinary Zoology. Part 9. Authors: L to Lyutkevich. United States Government Printing Office, Washington. [unknown pagination]
ICZN [International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature] (1999) International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. 4th Edition. International Trust for Zoological Nomenclature, London, xxix + 306 pp.
Ihle, J.E.W. (1922) The adult strongylids (Sclerostomes) inhabiting the large intestine of the horse. Report of the Commission Appointed to Enquire into Sclerostomiasis in Holland, I (Zoological Part 1), 1–118.
Lichtenfels, J.R. (1975) Helminths of domestic equids illustrated keys to genera and species with emphasis on North American forms. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 42, 1–92.
Lichtenfels, J.R., Kharchenko, V.A. & Dvojnos, G.M. (2008) Illustrated identification keys to strongylid parasites (Strongylidae: Nematoda) of horses, zebras and asses (Equidae). Veterinary Parasitology, 156, 4–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2008.04.026
Looss, A. (1895) Strongyls subtilis n. sp., ein bisher unbekannter Parasit des Menschen in Egypten. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie und Parasitenkunde. Erste Abteilung: Medizinisch-hygienische Bakteriologie und tierische Parasitenkunde, XVIII (6), 161–169.
Looss, A. (1900a) Notizen zur Helmintologie Egyptens. III. Die Sclerostomen der Pferde und Esel in Egypten. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie, Parasitenkunde und Infektionskrankheiten, 1. Abt., Originale, XXVII (4), 50–160.
Looss, A. (1900b) Notizen zur Helmintologie Egyptens. III. Die Sclerostomen der Pferde und Esel in Egypten. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie, Parasitenkunde und Infektionskrankheiten, 1. Abt., Originale, XXVII (5), 184–192.
Looss, A. (1901) Zur Sammel- und Conservierundstechnik von Helminthen. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 24 (643), 302–304 & 24 (644), 309–318.
Looss, A. (1902) The Sclerostomidae of horses and donkeys in Egypt. Records of the Egyptian Government School of Medicine Cairo, 1902, 25–139.
Looss, A. (1904) Die Wanderung der Ancylostomum-Strongyloides-Larven von der Haut nach dem Darme. Bulletin des VI Internationalen Zoologen Kongresses zu Bern, 1904, 3.
Looss, A. (1905a) The anatomy and life history of Agchylostoma duodenale Dub. A monograph. Records of the Egyptian Government School of Medicine, 3, 1–158.
Looss, A. (1905b) Notizen zur Helmintologie Egyptens. VI. Das Genus Trichostrongylus n. g., mit zwei neuen gelegentlichen Parasiten des Menschen. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie, Parasitenkunde und Infektionskrankheiten, 1. Abt., Originale, XXXIX (4), 409–422.
Looss, A. (1911) The anatomy and life history of Agchylostoma duodenale Dub. II Development in the free state. Records of the Egyptian Government School of Medicine, 4, 167-607.
Louro, M., Kuzmina, T.A., Bredtmann, C.M., Diekmann I., Madeira de Carvalho, L.M., von Samson‑Himmelstjerna, G. & Krücken, J. (2021) Genetic variability, cryptic species and phylogenetic relationship of six cyathostomin species based on mitochondrial and nuclear sequences. Scientific Reports, 11, 8245. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-87500-8
Mehlis, E. (1831) Novae observationes de entozois. Isis, 68–99, 166–199.
Molin, R. (1861) Il Sottordine degli Acrofalli ordinato scientificamente secondo i risultamenti delle indagini anatomiche ed embriogeniche. Memorie del Reale Istituto Veneto di Scienze, Lettere ed Arti, Venezia, 9, 427–633.
Odhner, T. (1925) 6. Avdelningen för lägre evertebrater. Vetenskapsakademiens Årsbook, 1925, 201–204. https://doi.org/10.3138/chr-06-03-05
Pearson, J.C. (1964) A revision of the subfamily Haplorchinae Looss, 1899 (Trematoda: Heterophyidae). I. The Haplorchis group. Parasitology, 54, 601–676. https://doi.org/10.1017/S003118200008269X
Railliet, A. (1884) Sur une nouvelle espèce de dochmie de l’intestin du chien. Bulletin et mémoires de la Sociét Centrale de Médecine Vétérinaire, Paris, 38, 452–472.
Railliet, A. (1896) Sur les variations morphologiques des Strongyles de l’appareil digestif et un nouveau strongle de dromadaire. Comptes rendus des seìances de la Socieìteì de biologie, 10, 540–542.
Railliet, A. & Henry A. (1909) Sur la classification des Strongylidae: 1. Metastrongylinae. Comptes rendus des seìances de la Socieìteì de biologie, 66, 85–88.
Ransom, B.H. (1911) The nematodes parasitic in the alimentary tract of cattle, sheep and other ruminants. Bureau of Animal Industry Bulletin No. 127, United States Department of Agriculture, s.n., 132 pp.
Rathbun, R. (1906) Report upon the condition and progress of the U. S. National Museum during the year ending June 30, 1905. Annual Report of the Board of Regents of the Smithsonian Institution, showing the operations, expenditures, and conditions of the Institution for the year ending June 30, 1905. Report of the U. S. National Museum. Government Printing Office, Washington. [unknown pagination]
Salley, E.J., Lichtenfels, J.R. & Shaw, J.H. (1978) Index-catalogue of medical and veterinary zoology. Special publication number 4. Checklist of types in the U.S. National Parasite Collection. United States Department of Agriculture, s.n., 203 pp.
Seurat, L.G. (1917) Filaires des Reptiles et des Batraciens. Bulletin de la Sociét d’Histoire Naturelle de l’Afrique du Nord, Alger, 8, 236–242.
Stunkard, H. (1924) A new Trematode, Oculotrema hippopotami n.g., n.sp., from the eye of the hippopotamus. Parasitology, 16, 436–440. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182000020333
Yorke, W. & Macfie, J.W. (1918) Strongylidae in horses. II. Cylicostomum minutum sp. n. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology, 11, 405–409. https://doi.org/10.1080/00034983.1918.11684147