Abstract
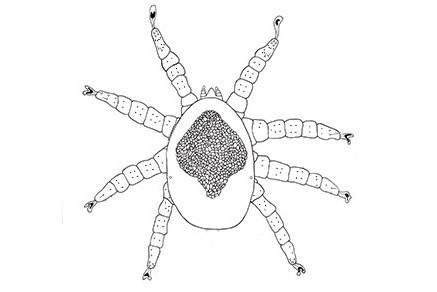
Parasitic nasal mites have been surveyed in a range of vertebrate hosts, but only two species of Rhinonyssidae have been described from procellariiform seabirds. We here describe Rhinonyssus nenecoi sp. nov., from Cape petrels, Daption capense (Procellariidae), collected in Rio Grande do Sul State, southern Brazil. The new species is morphologically most similar to R. procellaricus and R. pluvialis differing mainly by a strongly sclerotised podosomal shield with four pairs of setae, covering more than half of the idiosoma; a podosomal shield with a V-shaped posteromedial projection; an irregularly-shaped sternal shield; and a ventral opisthosoma with 3–4 pairs of setae.
References
- Beron, P. (2020) Acarorum Catalogus VI. Order Mesostigmata. Gamasina: Dermanyssoidea (Rhinonyssidae, Spinturnicidae). Pensoft & National Museum of Natural History, Sofia, 265 pp. https://doi.org/10.3897/ab.e54206
- Billerman, S.M., Keeney, B.K., Rodewald, P.G. & Schulenberg, T.S. (2022) Birds of the World. Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology, Ithaca, New York. Available from: https://birdsoftheworld.org/bow/home (accessed 29 May 2023)
- BirdLife International (2022) State of the World’s Birds 2022: Insights and Solutions for the Biodiversity Crisis. BirdLife International, Cambridge, 87 pp.
- Brünnich, M.T. (1764) Ornithologia Borealis. Typio Audreae Hartvigii Godiche, Hafniæ, 80 pp.
- Bugoni, L., Mancini, P.L., Monteiro, D.S., Nascimento, L. & Neves, T.S. (2008) Seabird bycatch in the Brazilian pelagic longline fishery and a review of capture rates in the southwestern Atlantic Ocean. Endangered Species Research, 5, 137–147. https://doi.org/10.3354/esr00115
- Bush, A., Lafferty, K., Lotz, J. & Shostak, A. (1997) Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. Journal of Parasitology, 83, 575–583. https://doi.org/10.2307/3284227
- Butenko, O.M. & Stanyukovich, M.K. (2001) New species of the rhinonyssid mites (Gamasina: Rhinonyssidae) from birds of Russia and neighbouring countries. Parazitologiia, 35, 519–530.
- Cory, A. (1881) The Eastern Menace. Kegan, Paul, Trench & Company, London, 344 pp.
- De Rojas, M.D., Doña, J. & Dimov, I. (2020) A comprehensive survey of rhinonyssid mites (Mesostigmata: Rhinonyssidae) in northwest Russia: new mite-host associations and prevalence data. Biodiversity Data Journal, 8, e49535. https://doi.org/10.3897/BDJ.8.e49535
- Dimov, I.D. (2013) A new nasal mite species of the genus Rhinonyssus (Mesostigmata: Rhinonyssidae) from Anas platyrhynchos (Anseriformes: Anatidae) in Russia. Journal of the Acarological Society of Japan, 22, 117–121. https://doi.org/10.2300/acari.22.117
- Dimov, I.D. (2020) Four new species of nasal mites Rhinonyssus (Mesostigmata, Rhinonyssidae) from Russia. Arhimed-Journal of Science and Practice, 9, 26–41.
- Dimov, I.D. & Spicer, G.S. (2013) A new species of nasal mite of the genus Rhinonyssus (Mesostigmata: Rhinonyssidae) from Leningrad Province, Russia. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 18, 291–296. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.18.3.11
- Domrow, R. (1969) The nasal mites of Queensland birds (Acari: Dermanyssidae, Ereynetidae, and Epidermoptidae). Proceedings of the Linnean Society of New South Wales, 93, 297–426.
- Evans, G.O. (1963) Observations on the chaetotaxy of the legs in the free-living Gamasina (Acari: Mesostigmata). Bulletin of the British Museum of Natural History, Zoology, 10, 277–303. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.20528
- Fain, A. (1994) Adaptation, specificity and host-parasite coevolution in mites (Acari). International Journal for Parasitology, 24, 1273–1283. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7519(94)90194-5
- Fain, A. & Johnston, D.E. (1966) Nouveaux acariens nasicoles d’oiseaux Nord-Américains (Acari: Rhinonyssidae). Bulletin de la Société Royale de Zoologie d'Anvers, 99, 375–386.
- Gastal, S.B., Mascarenhas, C.S. & Bugoni, L. (2022) Two new species of nasal mites of the genus Rhinonyssus (Acari, Mesostigmata, Rhinonyssidae) from shearwaters. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 27, 9–23. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.27.1.2
- Gretillat, S. (1961) Description de deux nouvelles espèces de Rhinonyssidae (Acarina, Mesostigmata) = Rallinyssus strandtmanni n. sp. et Larinyssus petiti n. sp. Vie et Milieu, 12, 151–160.
- Howell, S.N. & Zufelt, K. (2019) Oceanic Birds of the World: a Photo Guide. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey. 360 pp.
- Kadosaka, T., Kaneko, K. & Asanuma, K. (1987) A new species and new records of avian nasal mites (Acarina: Rhinonyssidae) from Japan. Medical Entomology and Zoology, 38, 33–43. https://doi.org/10.7601/mez.38.33
- Knee, W. (2008) Five new species of Rhinonyssidae (Mesostigmata) and one new species of Dermanyssus (Mesostigmata: Dermanyssidae) from birds of Alberta and Manitoba, Canada. Journal of Parasitology, 94, 348–374. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-1358.1
- Knee, W. & Galloway, T.D. (2016) New host and locality records for endoparasitic nasal mites (Acari: Rhinonyssidae, Turbinoptidae, and Ereynetidae) infesting birds in Manitoba, Canada. Canadian Entomologist, 149, 89–103. https://doi.org/10.4039/tce.2016.47
- Knee, W. & Proctor, H. (2006) Keys to the families and genera of blood and tissue feeding mites associated with Albertan birds. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification, 2, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.3752/cjai.2006.02
- Krantz, G.W. & Walter, D.E. (Eds.) (2009) A Manual of Acarology. 3rd Edition. Texas Tech University Press, Lubbock, Texas, viii + 807 pp.
- Linnaeus, C. (1758) Systema Naturae. Vol. 1. Laurentii Salvii, Holmiae , Stockholm, 532 pp.
- Mascarenhas, C.S., Bernardon, F.F., Gastal, S.B. & Müller, G. (2018) Checklist of the parasitic nasal mites of birds in Brazil. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 23, 1672–1692. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.23.8.15
- O'Reilly, B. (1818) Greenland, the adjacent seas, and the north-west passage to the Pacific Ocean, illustrated in a voyage to Davis's Strait, during the summer of 1817 (No. 45182). James Eastburn and Company at the Literary Rooms, Broadway, 251 pp. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.6930
- Pacheco, J.F., Silveira, L.F., Aleixo, A., Agne, C.E., Bencke, G.A., Bravo, G.A., Brito, G.R.R., Cohn-Haft, M., Maurício, G.N., Naka, L.N., Olmos, F., Posso, S.R., Lees, A.C., Figueiredo, L.F.A., Carrano, E., Guedes, R.C., Cesari, E., Franz, I., Schunck, F. & Piacentini, V.Q. (2021) Annotated checklist of the birds of Brazil by the Brazilian Ornithological Records Committee - second edition. Ornithology Research, 29, 94–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43388-021-00058-x
- Pence, D.B. (1972) The nasal mites of birds from Louisiana. I. Dermanyssids (Rhinonyssinae) from shore and marsh birds. Journal of Parasitology, 58, 153–168. https://doi.org/10.2307/3278266
- Pence, D.B. (1973) The nasal mites of birds from Louisiana. IX. Synopsis. Journal of Parasitology, 59, 881–892. https://doi.org/10.2307/3278429
- Pence, D.B. (1975) Keys, species and host list, and bibliography for nasal mites of North American birds (Acarina: Rhinonyssinae, Turbinoptinae, Speleognathinae, and Cytiditidae). Special Publication, Museum of Texas Tech University, 8, 1–148. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.156478
- Schreiber, E.A. & Burger, J. (Eds.) (2001) Biology of Marine Birds. CRC Press, New York, New York, 722 pp. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420036305
- Spicer, G.S. (1987) Prevalence and host-parasite list of some nasal mites from birds (Acarina: Rhinonyssidae, Speleognathidae). Journal of Parasitology, 73, 259–264.
- https://doi.org/10.2307/3282076
- Statius Müller, P.L. (1776) Des Ritters Carl von Linné Königlich Schwedischen Leibarztes &c. &c. vollständigen Natursystems Supplements- und Register-Band über alle sechs Theile oder Classen des Thierreichs. Mit einer ausführlichen Erklärung. Nebst drey Kupfertafeln. bey Gabriel Nicolaus Raspe, Nürnberg, 536 pp.
- Strandtmann, R.W. (1948) The mesostigmatic nasal mites of birds. I. Two new genera from shore and marsh birds. Journal of Parasitology, 34, 505–514. https://doi.org/10.2307/3273318
- Trouessart, E. (1894) Première note sur les Acariens des fosses nasales des Oiseaux. Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires de la Société de Biologie, Series 10, 1 (29), 723–724.
- Trouessart, E. (1895) Note sur un acarien parasite des fosses nasales de l’Oie domestique. Revue des Sciences Naturelles apliquées, Buttetin de la Société Nationale dÁcclimation, 42, 392–394.
- Vanstreels, R.E.T., Proctor, H., Snyman, A., Hurtado, R., Ludynia, K., Parsons, N.J. & Pistorius, P.A. (2018) Nasal mites (Mesostigmata: Rhinonyssidae) in African penguins (Spheniscus demersus). Parasitology, 146, 121–127. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182018000999