Abstract
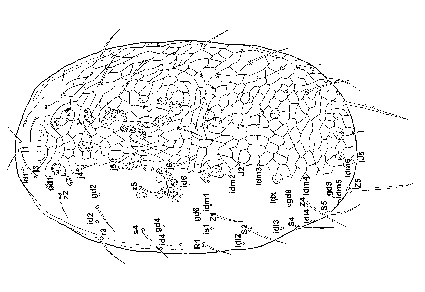
This paper reports the results of our studies of the morphological ontogeny of Neoseiulus cucumeris (Oudemans) based primarily on specimens reared in a laboratory at Manaaki Whenua – Landcare Research, Auckland, New Zealand. We describe all postembryonic stages and illustrate them in detail: the larva, protonymph, deutonymph (male and female), and adult female and male.
References
- Athias-Henriot, C. (1971) Nouvelles notes sur les Amblyseiini (Gamasides podospermiques, Phytoseiidae) 1. La dépilation des génuaux et tibias des pattes. Acarologia, 13 (1), 4–15.
- Beard, J.J. (1999) Taxonomy and biological control: Neoseiulus cucumeris (Acarina: Phytoseiidae), a case study. Australian Journal of Entomology, 38 (2), 51–59. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-6055.1999.00096.x
- Beard, J.J. (2001) A review of Australian Neoseiulus Hughes and Typhlodromips De Leon (Acari: Phytoseiidae: Amblyseiinae). Invertebrate Taxonomy, 15 (1), 73–158. https://doi.org/10.1071/IT99017
- Brodeur, J., Bouchard, A. & Turcotte, G. (1997) Potential of four species of predatory mites as biological control agents of the tomato russet mite, Aculops lycopersici (Massee) (Eriophyidae). Canadian Entomologist, 129 (1), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.4039/Ent1291-1
- Brødsgaard, H.F. & Hansen, L.S. (1992) Effect of Amblyseius cucumeris and Amblyseius barkeri as biological control agents of Thrips tabaci on glasshouse cucumbers. Biocontrol Science and Technology, 2 (3), 215–223. https://doi.org/10.1080/09583159209355235
- Chant, D.A. (1958) Immature and adult stages of some British Phytoseiidae Berl., 1916 (Acarina). Journal of the Linnean Society of London, Zoology, 43, 599–643. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1958.tb01581.x
- Chant, D.A. & McMurtry, J.A. (2007) Illustrated Keys and Diagnoses for the Genera and Subgenera of the Phytoseiidae of the World (Acari: Mesostigmata). Indira Publishing House, West Bloomfield, Michigan, 219 pp.
- Collyer, E. (1957) Two new species of the genus Typhlodromus Scheuten, 1857 (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Annual Magazine of Natural History, 12, 199–203. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222935708655947
- Demite, P.R., Moraes, G.J. de, McMurtry, J.A., Denmark, H.A. & Castilho, R.C. (2023) Phytoseiidae Database. Available from: www.lea.esalq.usp.br/phytoseiidae (accessed 06 March 2023)
- Easterbrook, M.A., Fitzgerald, J.D. & Solomon, M.G. (2001) Biological control of strawberry tarsonemid mite Phytonemus pallidus and two-spotted spider mite Tetranychus urticae on strawberry in the UK using species of Neoseiulus (Amblyseius) (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Experimental and Applied Acarology, 25 (1), 25–36. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010685903130
- Evans, G.O. & Till, W.M. (1979) Mesostigmatic mites of Britain and Ireland (Chelicerata: Acari‐Parasitiformes): An introduction to their external morphology and classification. The Transactions of the Zoological Society of London, 35 (2), 139–262. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1979.tb00059.x
- Fang, X.D., Lu, H.L., Ouyang, G.C., Xia, Y.L., Guo, M.F. & Wu, W.N. (2013) Effectiveness of two predatory mite species (Acari: Phytoseiidae) in controlling Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae). Florida Entomologist, 96 (4), 1325–1333. https://doi.org/10.1653/024.096.0411
- Fouly, A.H. & El-Laithy, A.Y.M. (1992) Immature stages and life history of the predatory mite species Amblyseius barkeri (Hughes, 1948) (Acarina, Gamasida, Phytoseiidae). Deutsche Entomologische Zeitschrift, 39 (4–5), 427–435. https://doi.org/10.1002/mmnd.4800390419
- Gerson, U., Smiley, R. & Ochoa, R. (2003) Mites (Acari) for Pest Control. Wiley-Blackwell, Hoboken, New Jersey, 560 pp. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470750995
- Hao, H., Li, P., Xu, T., Wu, Q., Zhang, F. & Peng, Z. (2021) Preliminary evaluation of the control effect of two predatory mite species on Eotetranychus sexmaculatus in rubber trees in Hainan Province, China. Systematic & Applied Acarology, 26 (12), 2287–2296. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.26.12.7
- Kakkar, G., Kumar, V., Seal, D.R., Liburd, O.S. & Stansly, P.A. (2016) Predation by Neoseiulus cucumeris and Amblyseius swirskii on Thrips palmi and Frankliniella schultzei on cucumber. Biological Control, 92 (1), 85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2015.10.004
- Karg, W. (1971) Acari (Acarina), Milben, Unterordnung Anactinochaeta (Parasitiformes): Die freilebenden Gamasina (Gamasides), Raubmilben. VEB Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena, Germany, 475 pp. [in German]
- Khaustov, V.A., Doker, I., Joharchi, O. & Khaustov, A.A. (2022a) Morphological ontogeny and complementary description of Neoseiulus subsolidus (Beglyarov) (Acari: Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae). Zootaxa, 5187 (1), 249–269. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5187.1.14
- Khaustov, V.A., Doker, I., Joharchi, O., Kazakov, D.V., Khaustov, A.A., Moradi, M., Fang, X.D. & Klimov, P. (2022b) A new, broadly distributed species of predacious mites, Neoseiulus neoagrestis sp. nov., (Acari: Phytoseiidae) discovered through GenBank data mining and extensive morphological analyses. Systematic & Applied Acarology, 27 (10), 2038–2061. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.27.10.14
- Klerk, M.L. de & Ramakers, P.M.J. (1986) Monitoring population densities of the phytoseiid predator Amblyseius cucumeris and its prey after large scale introductions to control Thrips tabaci on sweet pepper. Faculteit Landbouwwetenschappen Rijksuniversiteit Gent, 51 (3a), 1045–1048.
- Knapp, M., van Houten, Y., van Baal, E. & Groot, T. (2018) Use of predatory mites in commercial biocontrol: current status and future prospects. Acarologia, 58(Suppl), 72–82. https://doi.org/10.24349/acarologia/20184275
- Li, D.-D., Yi, T.-C. & Jin, D.-C. (2020) Morphological changes in Neoseiulus californicus (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Zootaxa, 4857 (1), 71–96. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4857.1.5
- Li, G.Y. & Zhang, Z.-Q. (2016) Some factors affecting the development, survival and prey consumption of Neoseiulus cucumeris (Acari: Phytoseiidae) feeding on Tetranychus urticae eggs (Acari: Tetranychidae). Systematic and Applied Acarology, 21 (5), 555–566. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.21.5.1
- Lv, J.L., Wang, E.D. & Xu, X.N. (2017) Industrialization of natural enemies is a whole chain of system engineering, Plant Protection, 43 (3), 1–7.
- Ma, M., Fan, Q.-H. & Zhang, Z.-Q. (2018a) Morphological ontogeny of Amblydromalus limonicus (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Systematic and Applied Acarology, 23 (9), 1741–1765. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.23.9.3
- Ma, M., Fan, Q.-H. & Zhang, Z.-Q. (2018b) Ontogenetic changes in the morphology of Eharius chergui (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Zootaxa, 4540 (1), 23–39. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4540.1.5
- Ma, M., Fan, Q.-H. & Zhang, Z.-Q. (2019) Ontogenetic changes in the morphology of Phytoseius leaki Schicha, 1977 (Acari: Phytoseiidae). International Journal of Acarology, 45 (1–2), 56–68. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647954.2018.1544664
- Ma, M., Fan, Q.-H. & Zhang, Z.-Q. (2020a) Neoseiulus kikuyu sp. nov. (Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae): descriptions of all life stages from New Zealand. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 25 (11), 2098–2114. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.25.11.13
- Ma, M., Fan, Q.-H. & Zhang, Z.-Q. (2020b) Ontogenetic changes in the morphology of Neoseiulus barkeri (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Zootaxa, 4900 (1), 5–19. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4900.1.4
- MacGill, E. (1939) A gamasid mite (Typhlodromus thripsi n. sp.), a predator of Thrips tabaci Lind. Annals of Applied Biology, 26 (2), 309–317.
- McMurtry, J.A. & Croft, B.A. (1997) Life-styles of phytoseiid mites and their roles in biological control. Annual Review of Entomology, 42, 291–321. http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ento.42.1.291
- McMurtry, J.A., Moraes, G.J. de & Sourassou, N.F. (2013) Revision of the lifestyles of phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and implications for biological control strategies. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 18 (4), 297–320. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.18.4.1
- Metwally, A. & Sanad, A.S. (2005) Description of the immature and adult stages of Neoseiulus arundonaxi n. sp. (Acari: Phytoseiidae) from Egypt. Bulletin of the Entomological Society of Egypt, 82, 63–70.
- Moraes, G.J. de, McMurtry, J.A., Denmark, H.A. & Campos, C.B. (2004) A revised catalog of the mite family Phytoseiidae. Zootaxa, 434, 1–494. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.434.1.1
- Negm, M.W., Matsuda, T., Kayukawa, T., Ho, C.-C., Hsu, Y.-T., Kongchuensin, M., Konvipasruang, P. & Gotoh, T. (2021) Morphological ontogeny and molecular analyses of geographic strains of two closely related Neoseiulus species (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Acarologia, 61 (2), 432–452. https://doi.org/10.24349/acarologia/20214440
- Oudemans, A.C. (1930) Acarologische Aanteekeningen. CII. Entomologische Berichten, 8, 69–74. [in German]
- Patel, K. & Zhang, Z.-Q. (2017) Prey preference and reproduction of predatory mites, Amblybromalus [sic.] limonicus and Neoseiulus cucumeris, on eggs and 1st instar nymphs of the tomato/potato psyllid. International Journal of Acarology, 43 (6), 468–474. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647954.2017.1349177
- Rowell, H.J. & Chant, D.A. (1979) Observations on the ontogeny of setae in the family Phytoseiidae (Acarina: Gamasina). Canadian Journal of Zoology, 57 (3), 670–682. https://doi.org/10.1139/z79-080
- Sarwar, M., Wu, K. & Xu, X. (2009) Evaluation of biological aspects of the predacious mite, Neoseiulus cucumeris (Oudemans) (Acari: Phytoseiidae) due to prey changes using selected arthropods. International Journal of Acarology, 35 (6), 503–509. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647950903468240
- Shipp, J.L. & Whitfield, G.H. (1991) Functional response of the predatory mite, Amblyseius cucumeris (Acari: Phytoseiidae), on western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Environmental Entomology, 20 (2), 694–699. https://doi.org/10.1093/ee/20.2.694
- Swirski, E., Ragusa, S., van Emden, H. & Wysoki, M. (1973) Description of immature stages of three predaceous mites belonging to the genus Amblyseius Berlese (Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae). Israel Journal of Entomology, 7, 69–87.
- van Houten, Y.M., van Stratum, P., Bruin, J. & Veerman, A. (1995) Selection for non‐diapause in Amblyseius cucumeris and Amblyseius barkeri and exploration of the effectiveness of selected strains for thrips control. Entomologia Experimentalis & Applicata, 77 (3), 289–295. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1570-7458.1995.tb02326.x
- Weintraub, P.G., Kleitman, S., Mori, R., Shapira, N. & Palevsky, E. (2003) Control of broad mites (Polyphagotarsonemus latus (Banks)) on organic greenhouse sweet peppers (Capsicum annuum L.) with the predatory mite, Neoseiulus cucumeris (Oudemans). Biological Control, 26, 300–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1049-9644(03)00069-0
- Wu, W.N. & Fang, X.D. (2021) Phytoseiidae Systematics and Management of Pests. Guangdong Science and Technology Press, Guangzhou, 428 pp. [in Chinese]
- Xin, J.-L., Liang, L.-R. & Ke, L.-S. (1981) A new species of the genus Amblyseius from China (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). International Journal of Acarology, 7, 75–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647958108683247
- Xu, X.N., Lv, J.L. & Wang, E.D. (2015) Predatory mite research in mass rearing and field applications, Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 31 (5), 647–656.
- Yari, S., Hajiqanbar, H., Farazmand, A., Rashed, A. & Fathipour, Y. (2023) Efficacy assessment of Neoseiulus cucumeris at different release rates in control of Frankliniella occidentalis on rose plants under laboratory and microcosm conditions. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 28 (3), 607–618. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.28.3.14
- Zhang, Z. (2003) Mites of Greenhouses: Identification, Biology and Control. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, 240 pp. https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851995908.0000
- Zhang, Y.-X., Lin, J.-Z., Zhang, G.-Q., Chen, X., Ji, J. & Tang, Q. (2011) Research and application of Neoseiulus cucumeris (Oudemans) for control of Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) on sweet pepper in plastic greenhouse. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 26 (1), 91–97.
- Zhang, B., Ma, M. & Fan, Q.-H. (2021) Morphological ontogeny of Neoseiulus zwoelferi (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Zootaxa, 5086 (1), 7–28. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5086.1.4