Abstract
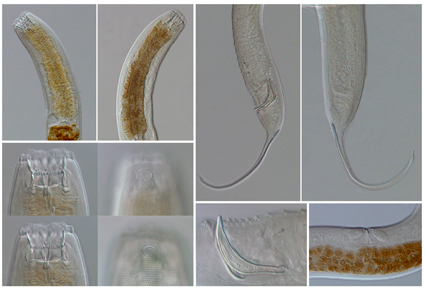
Three new species of free-living marine nematodes belonging to the genera Subsphaerolaimus, Halichoanolaimus and Belbolla are described from the mangrove wetlands of western Taiwan Island. Subsphaerolaimus danshuiensis sp. nov. is characterized by a body length of 1345–1693 µm, subcephalic setae 22.5–65.0 µm long, cervical setae 16.5–33.0 µm long, an “L”-shaped spicule 66.9–76.4 μm long, and a gubernaculum with a caudally-dorsally directed apophysis 16.4–23.0 µm long. Halichoanolaimus sicaoensis sp. nov. is characterized by an amphidial fovea with 3.5–3.75 turns, a conico-cylindrical tail with the cylindrical portion approximately 3/4 of the total tail length, and 13–14 not equidistant papillose precloacal supplements. Belbolla forkyspicula sp. nov. is characterized by seven oesophageal bulbs, a short tail, a spicule with a proximal fork, and two winged supplements. Differentiating characteristics of the genera Subsphaerolaimus, Halichoanolaimus and Belbolla are provided. Types are deposited in the College of Fisheries, Jimei University.
References
- Allgén, C.A. (1933) Freilebende Nematoden aus dem Trondhjemsfjord. Capita Zoologica, 4 (2), 56–57.
- Allgén, C.A. (1940) Über einige norwegische marine. Tiefen-Nematoden. Folia Zoologica et Hydrobiologica, 10 (1), 268–269.
- Allgén, C.A. (1951) Pacific freeliving marine nematodes. (Papers from Dr. Th. Mortensen's pacific expedition 1914-16 (Papers from Dr. Th. Mortensen’s Pacific Expedition 1914–16. LXXVI). Videnskabelige Meddelelser Fra Dansk Naturhistorisk Forening Kebenhavn, 113, 263–411.
- Andrássy, I. (1973) Über vier homonyme Nematodengattungen. Nematologica, 19 (3), 403–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-5687(73)90044-3
- Bastian, H.C. (1865) Monograph of the Anguillulidae, or Free Nematoids, Marine, Land, and Freshwater; with Descriptions of 100 New Species. The Transactions of the Linnean Society of London, 25 (2), 73–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1865.tb00179.x
- Belogurov, O.I. & Belogurova, L.S. (1980) Morphology of Belbolla intarma sp. n., Diagnosis and a Table for the Determination of the Species of the Genus Belbolla (Morfologiia Belbolla intarma dlia Opredeleniia Vidov Roda Belbolla). Biologiya Morya, 4, 74–77.
- Belogurov, O.I. & Fadeeva, N.P. (1980) Notes on the genus Halichoanolaimus (Nematoda, Choanolaimidae) with the description of two new species. Zoologicheski Zhurnal, 59 (5), 656–665.
- Chitwood, B.G. (1933) A revised classification of the Nematoda. The Journal of Parasitology, Papers in Helminthology, Ninth Annual Meeting, 20 (2), 115–148.
- Chitwood, B.G. (1951) North American marine nematodes. The Texas Journal of Science, 4, 638–639.
- Cobb, N.A. (1915) Nematodes and their relationships. United States Department of Agriculture—Agriculture Research, 457–490.
- Cobb, N.A. (1920) One hundred new nemas (type species of 100 new genera). Contributions to a Science of Nematology, 9, 217–343.
- Daschenko, O.I. & Belogurov, O.I. (1991) The morphology of free-living marine nematode Halichoanolaimus bispirae sp. n. (Nematoda, Chromadorida, Choniolaimidae) from polychaetes colony. In: Fadeev, V.I., Zvyagintsev, A.Yu., Kubanin, A.A. & Bagaveeva, E.V. (Eds.), Biological studies of benthos and fouling in the Sea of Japan. DVO AN USSR, Vladivostok, pp. 98–104.
- De Coninck, L.A. & Schuurmans Stekhoven, J.H. (1933) The freeliving marine nemas of the Belgian Coast. II With general remarks on the structure and the system of nemas. Mémoires Du Musee Royal Histoire Naturelle de Belgique, 58, 3–163.
- De Ley, P. & Blaxter, M.L. (2002) Systematic Position and Phylogeny. In: Lee, D.L. (Ed.), The Biology of Nematodes. Taylor & Francis, London and New York, pp. 1–30. https://doi.org/10.1201/b12614-2
- de Man, J.G. (1888) Sur quelques nématodes libres de la mer du Nord, nouveaux ou peu connus. Mémoires de la Société Zoologique de France, 1, 36–39.
- de Man, J.G. (1922) Neue freilebende Nematoden aus der Zuidersee. Tijdschrift der Nederlandsche Dierkundige Vereeniging, 2 (18), 124–134.
- Ditlevsen, H. (1919) Marine freeliving nematodes from Danish waters. Videnskabelige Meddelelser fra Dansk naturhistorisk Forening i Kjøbenhavn, 70 (7), 174–177.
- Ditlevsen, H. (1921) Papers from Dr. Th. Mortensens Pacific Expedition 1914–16. III Marine free-living Nematodes from the Auckland and Campbell Islands. Videnskabelige Meddelelser fra Dansk naturhistorisk Forening i Kjøbenhavn, 73, 1–39.
- Filipjev, I.N. (1916) Free living nematodes in the collection of the Zoological Museum of the Imperial Academy of Sciences in Petrograd. Annales du Museu Zoologique de Academie des Sciences Petrograd, 21, 59–116.
- Filipjev, I.N. (1917) Un Nématode libre nouveau de la mer Caspienne, Chromadorissa gen. nov. Chromadoridae, Chromadorini) (in Russian French Res). Russk Zoologichesky Zhurnal, 2, 24–30.
- Filipjev, I.N. (1918) Free-living marine nematodes of the Sevastopol area. Transactions of the Zoological Laboratory and the Sevastopol Biological Station of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Series II, No 4, 1–577.
- Filipjev, I.N. (1929) Classification of freeliving Nematoda and relations to parasitic forms. Journal of Parasitology, 15, 281–282.
- Gagarin, V.G. & Long, P.K. (2017) Description of two new species of free-living nematodes: Halochoanlaimus stagnalis sp. nov. and Actionema dolichurum sp. nov. from Artificial Reservoirs in Vietnam. Amurian zoological journal, 9 (3), 131–142. https://doi.org/10.33910/1999-4079-2017-9-3-131-142
- Gagarin, V.G. & Nguyen, V.T. (2015) Subsphaerolaimus minor sp n. and Micromicron cephalatum Cobb, 1920 (Nematoda) from the Yen River Estuary of Vietnam. Zootaxa, 3 (3994), 396–410. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3994.3.4
- Gagarin, V.G. & Nguyen, V.T. (2016) Two new nematode species (Nematoda) from the mangroves of the Yen River Delta, Vietnam. Inland Water Biology, 9 (1), 39–47. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082916010065
- Gagarin, V.G. & Nguyen, D.T. (2016) Adoncholaimus minor sp. n. and Belbolla vietnamica sp. n. (Nematoda, Enoplida) from mangrove the Yen River Estuary in Vietnam. International Journal of Nematology, 26 (1a2), 1–8.
- Gerlach, S.A. (1955) Zur Kenntnis der freilebenden marinen Nematoden von San Salvador. Zeitschrift für wissenschaftliche Zoologie, 158 (2–4), 269–271.
- Gerlach, S.A. (1956) Brasilianische Meeres-Nematoden I. Boletim do Instituto Oceanográfico, São Paulo Tomo, 5 (1–2), 3–69.
- Gerlach, S.A. (1964) Revision der Choniolaiminae und Selachinematinae (freilebende Meerses-Nematoden). Mitteilungen aus dem Hamburischen zoologischen Museum und Institut, 61, 23–49.
- Gourbault, N. & Boucher, G. (1981) Nématodes abyssaux (Campange Walda du N/O "Jean Charcot") III. Une sous-famille et six espèces nouvelles de Sphaerolaimidae. Bulletin of the Natural History Museum Zoology, 1 (4), 1035–1052. https://doi.org/10.5962/p.304621
- Gourbault, N. & Vincx, M. (1985) Nématodes abyssaux (Campagne Walda du N/O "Jean Charcot"). V. Espèces nouvelles de Selachinematidae, dépourvues d'anus. Cahiers de Biologie Marine, 26 (1), 87–97.
- Guo, Y.Q. & Warwick, R.M. (2001) Three new species of free-living nematodes from the Bohai Sea, China. Journal of Natural History, 35, 1575–1586. https://doi.org/10.1080/002229301317092333
- Hasbrouck, E.R. (1966) Halichoanolaimus raritanensis n. sp. (Chromadoroidea: Cyatholaimidae) from New Jersey. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 33 (1), 23–25.
- Hopper, B.E. (1961) Marine nematodes from the coast line of the Gulf of Mexico. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 39, 183–199. https://doi.org/10.1139/z61-023
- Huang, Y., Guo, Y.Q. & Zhai, H.X. (2022) Free-living Marine Nematodes from the East China Sea. Science Press, Beijing, 358 pp. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-3836-7
- Huang, Y. & Zhang, Z.N. (2005) Three new species of the genus Belbolla (Nematoda: Enoplida: Enchelidiidae) from the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of Natural History, 39 (20), 1689–1703. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222930400023750
- Inglis, W.G. (1961) Two new species of free-living marine nematodes from the west coast of Scotland. Hydrobiologia, 18 (4), 284–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00046473
- Inglis, W.G. (1968) Interstitial nematodes from St. Vincent's Bay, New-Caledonia. Expedition Francaise sur les Recifs Coralliens de la Nouvelle-Caledonie, Paris. Editions de la Fondation Singer-Polignac, 2, 29–74.
- Jensen, P. (1992) Predatory nematodes from the deep-sea: description of species from the Norwegian Sea, diversity of feeding types and geographical distribution. Cahiers De Biologie Marine, 33 (1), 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02458624
- Juario, J.V. (1974) Neue freilebende Nematoden aus dem Sublitoral der Deutschen Bucht. Veröffentlichungen des Instituts fürMeeresforschung in Bremerhaven, 14, 275–303.
- Leduc, D. (2020) New and known Halichoanolaimus de Man, 1886 species (Nematoda: Selachinematidae) from New Zealand’s continental margin. European Journal of Taxonomy, 726, 59–82. https://doi.org/10.5852/ejt.2020.726.1175
- Leduc, D. & Zhao, Z.Q. (2016) Molecular characterisation of five nematode species (Chromadorida, Selachinematidae) from shelf and upper slope sediments off New Zealand, with description of three new species. Zootaxa, 4132 (1), 59–76. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4132.1.5
- Lorenzen, S. (1966) Diagnosen einiger freilebender Nematoden von der schleswig-holsteinischen Westküste. Veröffentlichungen des Instituts fürMeeresforschung in Bremerhaven, 10, 31–48.
- Lorenzen, S. (1978) Postembryonalentwicklung von Steineria- und Sphaerolaimide narten (Nematoden) und ihre Konsequenzen für die Systematik. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 200 (1/2), 53–78.
- Luc, M. & De Coninck, L. (1959) Contribution a l'etude des Dipteres du littoral marin de la region de Roscoff. Archives de Zoologie Experimentale et Generale, 98, 103–165.
- McIntyre, A.D. & Warwick, R.M. (1984) Meiofauna techniques. In: Holme, N.A. & McIntyre, A.D. (Eds.), Methods for the study of marine benthos. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp. 217–244.
- Micoletzky, H. (1921) Die freilebenden Erd-Nematoden mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der Steiermark und der Bukowina, zugleich mit einer Revision sämtlicher nicht mariner, freilebender Nematoden in Form von Genus-Beschreibungen und Bestimmungsschlüsseln. Archiv für Naturgeschichte Berlin, 87, 1–650.
- Micoletzky, H. (1930) LIII. Freilebende marine Nematoden vond den Sunda-Inseln: I. Enoplidae. In: Kreis, H.A. (Ed.), Papers from Dr. Th. Mortensen's Pacific Expedition 1914-16 LIII). Videnskabelige Meddelelser fra Dansk naturhistorisk Forening i Kjøbenhavn, 87, 232–339.
- Nasira, K., Shahina, F. & Shamim, S. (2014) Descriptions of Bathyeurystomina minima sp. n. and Belbolla longispiculata sp. n. with observations on Pareurystomina vaughtae and Eurystomina indica (Enoplida: Enchelidiidae) from Pakistan. International Journal of Nematology, 24 (1), 87–96.
- Nemys (Eds.) (2023) Nemys: World Database of Nematodes. Available from: https://nemys.ugent.be (accessed 4 October 2023) https://doi.org/10.14284/366
- Nguyen, V.T. & Gagarin, V.G. (2009) Three species of monhysterids (Nematoda, Monhysterida) from mangrove forest of the Me Kong river estuary, Vietnam. Vietnam Journal of Biology, 31 (2), 8–15. https://doi.org/10.15625/0866-7160/v31n2.808
- Okhlopkov, J.R. (2002) Free-living nematodes of the families Selachinematidae and Richtersiidae in the White Sea (Nematoda, Chromadoria) Zoosystematica Rossica, 11 (1), 41–55. https://doi.org/10.31610/zsr/2002.11.1.41
- Rho, H.S., Lee, H., Lee, H.J. & Min, W. (2020) A new free-living marine nematode species of the genus Belbolla (Enoplida, Enchelidiidae) from a subtidal zone of the East Sea, Korea, with some ecological and biogeographical information. Korean Journal of Environmental Biology, 38 (4), 578–585. https://doi.org/10.11626/KJEB.2020.38.4.578
- Schuurmans Stekhoven, J.H. (1950) Free-living marine nemas of the Mediterranean. I. The Bay of Villefranche. Mémoires de l'Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de Belgique, deuxième Série = Verhandelingen van het Koninklijk Belgisch Instituut voor Natuurwetenschappen. 2 (37). Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de Belgique, Bruxelles, 220 pp.
- Sergeeva, N.G. (1973) New Species of Free Living Nematodes from the Order Chromadorida in the Black Sea (Novye Vidy Svobodnozhivushchikh Nematod Chernogo Moria iz otriada Chromadorida). Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 52 (8), 1238–1241.
- Ssaweljev, S. (1912) Zur Kenntnis der freilebenden Nematoden des Kolafjords und des Relictensee Mogilnoje. Travaux de la Société (Impériales) des Naturalistes de Saint-Petersbourg, 42 (2–3), 108–126.
- Tchesunov, A.V. (2014) Order Desmodorida De Coninck, 1965. In: Shmidt-Rhaesa, A. (Ed.), Handbook of Zoology Gastrotricha, Cyclioneura and Gnathifera. Vol. 2. Nematoda. De Gruyter, Hamburg, pp. 373–398.
- Timm, R.W. (1954) A survey of the marine nematodes of Chesapeake Bay, Maryland. The Catholic University of America Press, Washington, D.C., 70 pp.
- Timm, R.W. (1961) The marine nematodes of the Bay of Bengal. Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences, 1 (1), 1–88.
- Turpeenniemi, T.A., Nasira, K. & Maqbool, M.A. (2001) A New Genus, Five New and Five Known Species of Free-Living Marine Nematodes (Nematoda: Monhysterida, Chromadorida) from Arabian Sea of Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Nematology, 19 (1 & 2), 1–31.
- Vitiello, P. (1970) Nématodes libres marins des vases profondes du Golfe du Lion. II. Chromadorida. Téthys, 2 (2), 449–500.
- Wang, M.N., Guo, W. & Wang, C.M. (2022) Two new species, Parabathylaimus gracilis sp. nov. and Belbolla sinica sp. nov. (Nematoda: Enoplida), from Yangma Island of the Yellow Sea, China. Zootaxa, 5200 (4), 344–354. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5200.4.3
- Warwick, R., Platt, H.M. & Somerfield, P. (1998) Free-living marine nematodes: Part III. Monhysterids. Synopses of the British Fauna No. 53. Field Studies Council, 1998, 14–22.
- Wieser, W. (1959) Free-living nematodes and other small invertebrates of Puget Sound beaches. University of Washington Publications in Biology, 19, 1–179.
- Zograf, J., Trebukhova, Y. & Pavlyuk, O. (2015) New deep-sea free-living marine nematodes from the Sea of Japan: the genera Siphonolaimus and Halichoanolaimus (Nematode: Chromadorea) with keys to species identifications. Zootaxa, 3911 (1), 63–80. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3911.1.3