Abstract
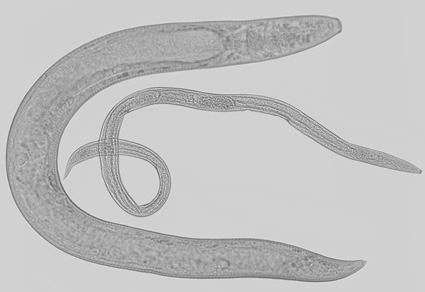
Haliplectus shahinae n. sp. and H. sandspitensis n. sp. two free-living marine nematodes of the family Haliplectidae Chitwood, 1951 collected from mangrove areas of Sandspit backwater, Karachi, Pakistan, are being described and illustrated. Both new species belong to a group of species characterized by the presence of a bipartite basal esophageal bulb with striated or unstriated valve plates. H. shahinae n. sp. is characterized by its comparatively shorter body length (0.4–0.44 mm); annulated cuticle; amphidial fovea at 6–9 µm from the anterior end; bipartite basal bulb with unstriated valve plates; reproductive system mono-prodelphic with reflexed ovary, presence of post uterine sac and vulva at 52–57% of body length and tail short conoid, straight, 1.5–1.8 times anal body width long. H. sandspitensis n. sp. is characterized by more than 1 mm body length (1.0–1.2 mm); annulated cuticle; amphidial fovea at 8–12 µm from the anterior end; bipartite basal bulb with striated valve plates; didelphic reproductive system, with the vulva at 40–47% of body length and tail elongated, conoid, 1.4–2.2 times anal body width long. A dichotomous identification key is provided for the valid species of Haliplectus Cobb, 1913.
References
- Andrássy, I. (1973) Nematoden aus strand-und hohlenbiotopen von Kuba. Acta Zoologica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae, 19 (3‒4), 233‒270.
- Blome, D. (1982) Systematik der Nematoda eines Sandstrandes der Nordseeinsel Sylt. Mikrofauna des Meeresbodens, 86, 1‒194.
- Chitwood, B.G. (1951) North American marine nematodes. The Texas Journal of Science, 3, 617‒672.
- Chitwood, B.G. (1956) A revision of the genus Haliplectus Cobb, 1913. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 23 (1), 78‒87.
- Cobb, N.A. (1913) New Nematode genera found inhabiting fresh water and non-brackish soils. Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences, 3 (16), 432‒444. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.20323
- Cobb, N.A. (1918) Estimating the nema population of soil. United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Technical Circular, 1, 1‒47.
- Coles, J.W. (1965) Two new species of marine nematodes from the British coast. The Annals and Magazine of Natural History, Series 13, 8 (86), 65‒70. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222936508651540
- De Coninck, L.A.P. (1943) Sur quelques espèces nouvelles de nématodes libres des eaux et des terres saumâtres de l’Islande. Biologisch Jaarboek, 10, 193‒220.
- Gadea, E. (1973) Sobre la filogenia interna de los Nematodos. Publicación del Instituto de Biologiá Aplicada, 54, 87‒92.
- Gerlach, S.A. (1950) Über einige Nematoden aus der Familie der Desmodoriden. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 145, 178‒198.
- Gerlach, S.A. (1957) Marine Nematoden aus dem Mangrove-Gebiet von Cananéia (Brasilianische Meeres-Nematoden III). Abhandlungen der Mathemathik-naturwissenschaftlichen Klasse, Akademie der Wissenschaften und Literatur, Mainz, 5, 129‒176.
- Gerlach, S.A. (1963) Die Gattung Haliplectus (Chromadorida, Leptolaimidae), zugleich ein Beitrag zur Morphologie und Phylogenie der Nematoden. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 171, 96‒113.
- Gerlach, S.A. (1967) Freilebende Meeres-Nematoden von den Sarso-Inseln (Rotes Meer): 3. Beitrag der Arbeitsgruppe Litoralforschung. Meteor Forschungsergebnisse, Reihe D, Biologie, 2, 19‒43.
- Gharahkhani, A., Pourjam, E., Leduc, D. & Pedram, M. (2022) The nematode genus Haliplectus Cobb, 1913 (Chromadorea: Haliplectidae): phylogenetic relationships, description of a new species from the Persian Gulf, southern Iran, and a tabular key to valid species. Nematology, 24 (6), 639–655. https://doi.org/10.1163/15685411-bja10153
- Heyns, J. & Swart, A. (1993) Studies on Haliplectus Cobb, 1913. New and known species from Seychelles (Nematoda: Haliplectidae). Fundamental and applied Nematology, 16 (3), 199‒209.
- Holovachov, O. (2014) Order Plectida Gadea, 1973. In: Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. (Ed.), Handbook of zoology. Gastrotricha, Cycloneuralia, and Gnathifera. Vol. 2. Nematoda. De Gruyter, Berlin, pp. 487‒535. https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110274257.487
- Hope, W.D. (1971) The current status of the systematics of marine nematodes. In: Hulings, N.C. (Ed), Proceedings of the first International Conference on Meiofauna. Smithsonian Contribution to Zoology, No. 76, pp. 33‒36.
- Hopper, B.E. (1969) Marine nematodes of Canada. II. Marine nematodes from the Minas Basin—Scots Bay area of the Bay of Fundy, Nova Scotia. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 47 (4), 671‒690. https://doi.org/10.1139/z69-114
- Nasira, K. & Shahina, F. (2007) Free-living marine nematodes from Arabian Sea: a review. Pakistan Journal of Nematology, 25 (2), 223‒280.
- Nasira, K. & Shahina, F. (2012) Marine nematode fauna from mangrove areas of Pakistan. International Journal of Phycology and Phycochemistry, 8 (2), 213‒218.
- Nasira, K. & Turpeenniemi, T.A. (2004) Haliplectus dorsalis Cobb in Chitwood, 1956 and Spilophorella candida Gerlach, 1951 (Nematoda: Chromadorida) from Arabian sea of Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Nematology, 22 (1), 17‒23.
- Nasira, K., Shahina, F., Kamran, M. & Ali, R. (2010) Free-living marine nematodes of sandspit backwater mangrove area, Karachi. Pakistan Journal of Nematology, 28 (1), 149‒151.
- Nemys eds. (2024) Nemys: World database of nematodes. Haliplectus Cobb, 1913. Available from: https://nemys.ugent.be/aphia.php?p=txdetails&id=2391 (accessed 23 February 2024)
- Pastor de Ward, C.T. (1984) Nematodes marinos de la Ria Deseado (Leptolaimina Leptolaimidae, Haliplectidae) Santa Cruz, Argentina. Physis A, 42 (103), 87‒92.
- Platt, H.M. & Warwick, R.M. (1980) Significance of free-living nematodes to the littoral ecosystem. In: Price, J.H., Irvine, D.E.G. & Farnham, W.F. (Eds.), The shore environment, Vol. 2. Ecosystem. Academic Press, London, pp. 729‒759.
- Saifullah, S.M. (2005) Utilization of mangrove resources in Pakistan. In: Rabbani, M.M., Tabrez, A.R. & Khan, T.M.A. (eds), Utilization of marine resources. Islamic Education, Scientific and Cultural Organization and (Morocco) N.I.O., City Press, Karachi, pp. 147‒157.
- Schulz, E. (1934–1935) Die Tierwelt des Küestengrundwassers bei Schilksee (Keiler Bucht), IV: Nematoden aus dem Küstengrundwasser. Schriften des Naturwissenschaftlichen Vereins für Schleswig-Holstein, 20 (2), 435‒467.
- Schuurmans Stekhoven, J.H. Jr. (1943) Freilebende marine Nematoden des Mittelmeeres. IV. Freilebende marine Nematoden der Fischereigründe bei Alexandrien. Zoologische Jahrbücher Jena, Systematik, 76 (4), 323‒378.
- Seinhorst, J.W. (1959) A rapid method for the transfer of nematodes from fixative to anhydrous glycerin. Nematologica, 4 (1), 67‒69. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529259X00381
- Shahina, F., Siddiqi, M.R. & Nasira, K. (2014) Six new species of Haliplectus Cobb, 1913 (Nematoda: Haliplectidae) from mangroves of Karachi, Pakistan. International Journal of Nematology, 24 (1), 68‒80.
- Shekhawat, M.S. & Dixit, A.K. (2005) Mangroves can save us from Tsunami. Agrobios Newsletter, 4, 57‒59.
- Siddiqi, M.R. (2012) Descriptions of Geohaliplectus andrassyi gen. n., sp. n., Haliplectus bruneiensis sp. n. (Nematoda: Haliplectidae). International Journal of Nematology, 22 (1 & 2), 41‒46.
- Swart, A., Heyns, J. & Furstenberg, J.P. (1992) Studies on Haliplectus Cobb, 1913. Description of Haliplectus algoensis n. sp. (Nematoda: Haliplectidae, Suborder Leptolaimina). South African Journal of Zoology, 27 (2), 41‒44. https://doi.org/10.1080/02541858.1992.11448260
- Vinciguerra, M.T. & Zullini, A. (1980) New or rare species of nematodes from Italian sand dunes. Animalia, 7 (1/3), 29‒44.
- Warwick, R.M., Platt, H.M. & Somerfield, P.J. (1998) Free living marine nematodes. Part III, Monohysterids. In: Barnes, R.S.K. & Crothers, J.H. (Eds.), Synopses of the British Fauna. New Series. No. 53. Field Studies Council, Shrewsbury, pp. 296.
- Yeates, G.W. (1967) Studies on nematodes from dune sands. 2. Araeolaimida. New Zealand Journal of Science, 10 (1), 287‒298.
- Zhou, R., Chen, Y., Shih, Y. & Guo, Y. (2022) Two new free-living marine nematode species of the genus Haliplectus Cobb, 1913 (Haliplectidae) from mangroves of Shenzhen, Guangdong province, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10 (11), 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111694