Abstract
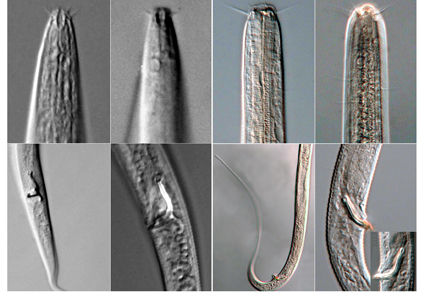
Two new species of free-living marine nematodes belonging to the family Xyalidae are described from the Yellow Sea, China. Amphimonhystrella sinica sp. nov. is characterized by rhomboid-shaped buccal cavity, circular amphidial fovea relatively far from anterior end of body, slender L-shaped spicules with cephalated proximal end and hooked distal end, tubular gubernaculum with ventrally curved apophyses, slender tail conico-cylindrical with half cylindrical distal part. Cobbia zhangi sp. nov. is characterized by having three similar equal-sized teeth, anterior sensilla arrangement 6+10, slightly curved spicules cephalated proximally and tapered distally, gubernaculum rod-like without apophysis, tail with posterior three fourths filiform part. Updated dichotomous keys to species of Amphimonhystrella and Cobbia are given. Considering the descriptions in the present work, the two genera contain now 9 and 12 valid species, respectively; this study complemented the species diversity of nematodes in Chinese sea area.
References
- Chitwood, B.G. (1951) North American marine nematodes. Texas Journal of Science, 3, 627–672.
- Chu, M.D., Hao, Y.D. & Huang, M. (2023) Two new species of Chromadorida (Nematoda) from the intertidal zone of the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of Natural History, 57 (25–28), 1387–139. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2023.2241187
- Clark, K.R. & Warwick, R.M. (2001). A further biodiversity index applicable to species list: variation in taxonomic distinctness. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 216, 265–278. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps216265
- Datta, T.K., Bhowmik, M. & Choudhury, A. (2018) Cobbia bengalensis sp. nov. (Xyalidae: Monhysterida) from an eroding island of Sundarban, India. Zootaxa, 4444 (2), 179–188. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4444.2.6
- de Jonge, V.N. & Bouwman, L.A. (1977) A simple density separation technique for quantitative isolation of meiobenthos using the colloidal silica Ludox-TM. Marine Biology, 42, 143–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391564
- de Man, J.G. (1907) Sur quelques espèces nouvelles ou peu connues de nématodes libres vivant sur les côtes de la Zélande. Tijdschrift Der Nederlandsche Dierkundige Vereeniging, 10, 227–244.
- Fadeeva, N.P. & Malysheva, M V. (1991) Xyalidae nematodes from the Kraternaya Bight. In: Zhirmunsky, A.V. & Tarasov, V.G. (Eds.), Shallow-water Vents and Ecosystem of the Kraternaya Bight (Ushishir Volcano, Kuriles). Vol 2. Biota DVO RAN Press, Vladivostok, pp. 154–162.
- Filipjev, I.N. (1918) Free-living marine nematodes of the Sevastopol area. Transactions of the Zoological Laboratory and the Sevastopol Biological Station of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Series 2, 4. [translated from Russian]
- Filipjev, I.N. (1929) Classification of freeliving Nematoda and relations to parasitic forms. Journal of Parasitology Urbana, 15, 281–282.
- Fonseca, G. & Bezerra T.N. (2014) Order Monhysterida Filipjev, 1929. In: Schmidt-Rhaesa A. (Ed.), Handbook of Zoology. Gastrotricha, Cycloneuralia and Gnatifera. Vol. 2. Nematoda. de Gruyter, Berlin, pp. 435–465. https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110274257.435
- Gagarin, V.G. & Thanh, N.V. (2009) Three new species of Monhysterids (Nematoda, Monhysterida) from a mangrove forest in the Mekong River Delta, Vietnam. Zoologičeskij žurnal, 88 (10), 1170–1178.
- Gagarin, V.G. & Tú', N.D. (2021) Two New Species of the Order Monhysterida Filipjev, 1929 (Nematoda) from the Van Uc River Mouth in Vietnam. Inland Water Biology, 14 (5), 517–527. [https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1134/S1995082921050059] https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082921050059
- Gagarin, V.G. & Gusakov, V.A. (2023). Amphimonhystrella tropica sp. n. and Oncholaimus mekongis sp. n. (Nematoda) from the Mekong River, Vietnam. Inland Water Biology. 16, 2, 174–184. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082923020050
- Gerlach, S.A. (1953) Die Nematodenbesiedlung des Sandstrandes und des Küstengrundwassers an der italienischen Küste I. Systematischer Teil. Archo Zoologico Italiano, 37, 517–640.
- Hao, Y.D., Chu, M.D. & Huang, Y. (2022) Trefusia brevicauda sp. nov. and Conilia parasinensis sp. nov. (Nematoda, Enoplida) from the Yellow Sea, China. Cahiers de Biologie Marine, 63 (3), 257–267. https://doi.org/10.21411/CBM.A.1F973A65
- Higgins, R.P. & Thiel, H. (1988) Introduction to the Study of Meiofauna. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, D.C., 488 pp.
- Hodda, M. (2022) Phylum Nematoda: feeding habits for all valid genera using a new, universal scheme encompassing the entire phylum, with descriptions of morphological characteristics of the stoma, a key, and discussion of the evidence for trophic relationships. Zootaxa, 5114 (1), 318–451. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5114.1.3
- Huang, Y. & Guo, Y.Q. (2022) Free-living marine nematodes from the East China Sea. Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd., Singapore, 409 pp. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-3836-7
- Huang, Y. & Zhang, Z. (2010) Two new species of Xyalidae (Nematoda) from the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 90 (2), 391–397. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0025315409000794
- Inglis, W.G. (1983) An outline classifi cation of the phylum Nematoda. Australian Journal of Zoology, 31, 243–255. https://doi.org/10.1071/ZO9830243
- Lambshead, P.J.D. (2004) Marine nematode biodiversity. In: Chen, Z.X., Chen, S.Y. & Dickson, D.W. (Eds.), Nematology: Advances and Perspectives. Vol 1. Nematode Morphology, Physiology and Ecology. CABI, Wallingford, pp. 438–468. https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851996455.0438
- Lo Russo, V. & Pastor de Ward, C.T. (2012) Neochromadora alejandroi sp. n. (Chromadorida: Chromadoridae) and Cobbia macrodentata sp. n. (Monhysterida: Xyalidae), two new species of free-living marine nematodes from the Patagonian coast. Nematology, 14 (7), 805–815. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854112x627327
- Long, F.K., Tu, N.D. & Gagarin, V.G. (2020) Daptonema paramonovi sp. n (Nematoda, Monhysterida) from a mangrove habitat in Vietnam. Zoological Journal Russian Academy of Sciences, 99 (6), 616–621. https://doi.org/10.31857/S0044513420060100
- Lorenzen, S. (1977) Revision der Xyalidae (freilebende Nematoden) auf der Grundlage einer kritischen Analyse von 56 Arten aus Nord- und Ostsee. Veroff. Inst. Meeresforsch. Bremerh, 16, 197–261.
- McIntyre, A.D. & Warwick, R.M. (1984) Meiofauna techniques. In: Holme, N.A. & McIntyre, A.D. (Eds.), Methods for the study of marine benthos. Blackwell Scientific Publications. Blackwell Publishing, Ltd., Oxford, pp. 217–244.
- Nemys eds. (2024) Nemys: World Database of Nematodes. Available from: https://nemys.ugent.be (accessed 1 March 2024)
- Schratzberger, M., Gee, J.M., Rees, H.L., Boyd, S.E. & Wall, C.M. (2000) The structure and taxonomic composition of sublittoral meiofauna assemblages as an indicator of the status of marine environments. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 80 (6), 969–980. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315400003039
- Tchesunov, A.V. & Miljutina, M.A. (2005) Three new minute nematode species of the superfamily Monhysteroidea from Arctic Abyss. Zootaxa, 1051 (1), 19–32. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.1051.1.2
- Timm, R.W. (1961) The marine nematodes of the Bay of Bengal. Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy Science, 1 (1), 25–88.
- Sun, J., Huang, M. & Huang, Y. (2021) Four new species of free-living marine nematode from the sea areas of China. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 39 (4), 1547–1558. [https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00343-020-0195-2] https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-020-0195-2
- Wang, C., An, L. & Huang, Y. (2018) Two new species of Xyalidae (Monhysterida, Nematoda) from the East China Sea. Zootaxa, 4514 (4), 583–592. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4514.4.11
- Warwick, R.M. & Platt, H.M. (1973) New and little known marine nematodes from a Scottish sandy beach. Cahiers de Biologie Marine, 14, 135–158.
- Wieser, W. (1959) Free-living nematodes and other small invertebrates of Puget Sound beaches. University of Washington Publications in Biology 19. University of Washington Press, Seattle, Washington, 179 pp., 109 figs., 96 pls.
- Zhai, H.X., Wang, C.M. & Huang, Y. (2020) Sabatieria sinica sp. nov. (Comesomatidae, Nematoda) from Jiaozhou Bay, China. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 38 (2), 539–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-9030-z
- Zhai, H.X., Geng, C.X. & Sun, J. (2022) Two new species of Xyalidae (Nematoda: Monhysterida) from intertidal zone of the Bohai Sea, China. Zootaxa, 5222 (2), 133–144. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5222.2.2