Abstract
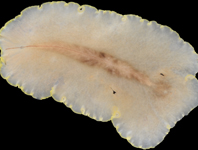
We describe a new species of polyclad flatworm, Pericelis flavomarginata sp. nov., from the intertidal and subtidal zones along localities on the Pacific coast of Japan. Pericelis flavomarginata sp. nov. is characterized by i) the dorsal surface of the body fringed by a lemon-yellow line except for the tip of tentacles, with a narrow brown midline running from the anterior edge of the body to the posterior end of the pharynx, ii) the pair of marginal tentacles with the tips extending and tapering, and iii) the presence of a common gonopore. Our molecular phylogenetic analysis revealed that selected Pericelis species were divided into two clades, each of which may be agreed with a characteristic dorsal color pattern. Additionally, we report an observation on the feeding behavior of P. flavomarginata sp. nov. on the polychaete Iphione muricata (Savigny in Lamarck, 1818).
References
Akaike, H. (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 19, 716–723.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TAC.1974.1100705
Boom, R., Sol, C.J.A., Salimans, M.M.M., Jansen, C.L., Wertheim-van Dillen, P.M.E., & Van der Noordaa, J. (1990) Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 28, 495–503.
https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.28.3.495-503.1990
Castresana, J. (2002) Gblocks. Version 0.91b. Online version. Available from: http://molevol.cmima.csic.es/castresana/ Gblocks_server.html (accessed 31 January 2020)
Collingwood, C. (1876) On thirty-one species of marine planarians, collected partly by the late Dr. Kelaart, FLS, at Trincomalee, and partly by Dr. Collingwood, FLS, in the Eastern Seas. Transactions of the Linnean Society of London, Series 2, Zoology, 1 (3), 83–98.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1876.tb00435.x
Curini-Galletti, M., Campus, P. & Delogu, V. (2008) Theama mediterranea sp. nov. (Platyhelminthes, Polycladida), the first interstitial polyclad from the Mediterranean. Italian Journal of Zoology, 75 (1), 77–83.
https://doi.org/10.1080/11250000701690525
Darriba, D., Taboada, G.L., Doallo, R. & Posada, D. (2012) jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Natural Methods, 9, 772–772.
https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2109
Dittmann, I.L., Dibiasi, W., Noreña, C. & Egger, B. (2019) Description of the snail-eating flatworm in marine aquaria, Pericelis tectivorum sp. nov. (Polycladida, Platyhelminthes). Zootaxa, 4565 (3), 383–397.
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4565.3.5
Du Bois-Reymond Marcus, E. & Marcus, E. (1968) Polycladida from Curaçao and faunistically related regions. Studies on the Fauna of Curaçao and other Caribbean Islands, 101, 1–133.
Edgecombe, G.D. & Giribet, G. (2006) A century later—a total evidence re-evaluation of the phylogeny of scutigeromorph centipedes (Myriapoda: Chilopoda). Invertebrate Systematics, 20, 503–525.
https://doi.org/10.1071/IS05044
Faubel, A. (1984) The Polycladida, Turbellaria. Proposal and establishment of a new system. Part II. The Cotylea. Mitteilungen aus dem Hamburgischen Zoologischen Museum und Institut, 80, 189–259.
Felsenstein, J. (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution, 39, 783–791.
https://doi.org/10.2307/2408678
Gmelin, J.F. (1791) Vermes. In: Gmelin, J.F. (Ed.), Caroli a Linnaei Systema Naturae per Regna Tria Naturae. Tom. 1 (6). 13th Edition. G.E. Beer, Leipzig, pp. 3021–3910.
https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.36932
Grube, A.E. (1840) Actinien, Echinodermen und Würmer des adriatischen und Mittelmeers, nach eigenen Sammlungen be-schrieben. Verlag von J.H. Bon, Königsberg, 92 pp.
https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.23025
Hyman, L.H. (1955) A further study of the polyclad flatworms of the West Indian region. Bulletin of Marine Science, 5 (4), 259–268.
Hyman, L.H. (1959) A further study of Micronesian polyclad flatworms of the West Indian region. Bulletin of Marine Science of the Gulf and Caribbean, 5, 258–268.
Iwase, F., Uchida, H., Nomura, K., Fukuda, T. & Misaki, H. (1990) Okinawa Kaichu Seibutsu Zukan [Illustrated Guide to Marine Life in Okinawa]. Shinsei Zukan Series. Vol. 11. Sazan Press, Okinawa, 258 pp. [in Japanese]
Jie, W.B., Kuo, S.C., Wu, S.C. & Lee, K.S. (2013) Unreported predatory behavior on crustaceans by Ilyella gigas (Schmarda, 1859) (Polycladida: Ilyplanidae), a newly-recorded flatworm from Taiwan. Platax, 10, 57–71.
Katoh, K., Rozewicki, J. & Yamada, K.D. (2017) MAFFT online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 20, 1160–1166.
https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbx108
Kumar, S., Stecher, G. & Tamura, K. (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33, 1870–1874.
https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Laidlaw, F.F. (1902) The marine Turbellaria, with an account of the anatomy of some of the species. The Fauna and Geography of the Maldive and Laccadive Archipelagoes, 1, 282–312.
Littlewood, D.T.J. (1994) Molecular phylogenetics of cupped oysters based on partial 28S rRNA gene sequences. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 3, 221–229.
https://doi.org/10.1006/mpev.1994.1024
Marshall, O.J. (2004) PerlPrimer: cross-platform, graphical design for standard, bisulphite and real-time PCR. Bioinformatics, 20 (15), 2471–2472.
https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bth254
Meixner, A. (1907) Polycladen von der Somaliküste, nebst einer Revision der Stylochinen. Zeitschrift für wissenschaftliche Zoologie, 88, 368–498.
Newman, L.J. & Cannon, L.R.G. (2003) Marine Flatworms: The World of Polyclads. CSIRO Publishing, Collingwood, 97 pp.
https://doi.org/10.1071/9780643101197
Okada, Y., Uchida, S. & Uchida, T. (1965) New Illustrated Encyclopedia of the Fauna of Japan. Vol.1. Hokuryu-kan Publishing, Tokyo, 679 pp. [in Japanese]
Ono, A. (2015) Flatworms Illustrated. Seibundoshinkosha, Tokyo, 223 pp. [in Japanese]
Ooishi, S. (1970) Marine invertebrate fauna of the Ogasawara and Volcano Islands collected by S. Ooishi, Y. Tomida, K. Izawa and S. Manabe. In: Toba Aquarium and Asahi Shinbun Publishing Company (Ed.), Report on the Marine Biological Expedition to the Ogasawara (Bonin) Islands, 1968. Asahi Shinbun Publishing Company, Tokyo, pp. 75–95. [in Japanese]
Oya, Y. & Kajihara, H. (2017) Description of a new Notocomplana species (Platyhelminthes: Acotylea), new combination and new records of Polycladida from the northeastern Sea of Japan, with a comparison of two different barcoding markers. Zootaxa, 4282 (3), 526–542.
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4282.3.6
Poulter, J.L. (1974) A new species of the genus Pericelis, a polyclad flatworm from Hawaii. In: Riser, N.W. & Morse, M.P. (Eds.), Biology of the Turbellaria. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp. 93–107.
Prudhoe, S. (1985) A Monograph on Polyclad Turbellaria. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 259 pp.
Ramos-Sánchez, M., Bahia, J. & Bastida-Zavala, J.R. (2020) Five new species of cotylean flatworms (Platyhelminthes: Polycladida: Cotylea) from Oaxaca, southern Mexican Pacific. Zootaxa, 4849 (1), 49–83.
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4819.1.3
Ronquist, F. & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics, 19, 1572–1574.
Savigny, J.C. (1818) Les Annelides. In: Lamarck, J.B.D. (Ed.), Histoire naturelle des animaux sans vertèbres. Dèterville and Verdière, Paris, pp. 302–374.
Schmarda, L.K. (1859) Neue wirbellose Thiere beobachtet und gesammelt auf einer Reise um die Erde 1853 bis 1857. Vol. 1. Bd. I. Turbellarien, Rotatorien und Anneliden. Wilhelm Engelmann, Leipzig, 66 pp.
https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.14426
Schwendinger, P.J. & Giribet, G. (2005) The systematics of the south-east Asian genus Fangensis Rambla (Opiliones: Cyphophthalmi: Stylocellidae). Invertebrate Systematics, 19 (4), 297–323.
https://doi.org/10.1071/IS05023
Sonnenberg, R., Nolte, A.W. & Tautz, D. (2007) An evaluation of LSU rDNA D1–D2 sequences for their use in species identification. Frontiers in Zoology, 4, 1–12.
https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-9994-4-6
Stamatakis, A. (2014) RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics, 30, 1312–1313.
https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033
Whiting, M.F. (2002) Mecoptera is paraphyletic: multiple genes and phylogeny of Mecoptera and Siphonaptera. Zoologica Scripta, 31 (1), 93–104.
https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0300-3256.2001.00095.x
Woodworth, W.M. (1898) Some planarians from the Great Barrier Reef of Australia. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology of Harvard College, 32 (4), 61–67.