Abstract
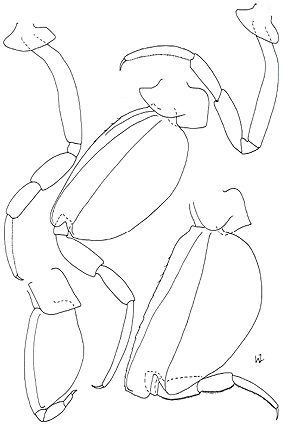
This is the first comprehensive taxonomic review of the family Brachyscelidae. The family is currently mono-generic following the review of Zeidler (2016). There are 17 nominal species referable to the genus Brachyscelus in the literature including two old references to species that most likely represent species of Brachyscelus. However, most are regarded junior synonyms of the two better known species B. crusculum Spence Bate, 1861 and B. globiceps (Claus, 1879). The taxonomic status of all nominal species was re-determined by the examination of extant type material or from the original literature reference if type material could not be found. In conclusion, five species of Brachyscelus are recognized as valid. Brachyscelus crusculum is the most common and widespread species and is most often recorded in the literature, but it is likely that some of these literature records are erroneous because other species have been confused with it in the past. The other species recognized are B. globiceps, B. macrocephalus Stephensen, 1925, B. rapacoides Stephensen, 1925 and B. rapax (Claus, 1871). Brachyscelus globiceps and B. macrocephalus are well established species and the validity of B. rapacoides was recently confirmed by Zeidler et al. (2018) but the validity of B. rapax is difficult to determine because type material could not be found and the original description by Claus (1871) and later figure (Claus 1887) are very inadequate. However, the species is tentatively recognized here based on several specimens which are most likely this species as according to Claus (1871, 1887). Brachyscelus is widely distributed in tropical and warm-temperate regions of the world’s oceans including the Mediterranean Sea. Species are preferentially associated with medusae and to a lesser extent with salps.
References
Barkhatov, V.A. & Vinogradov, M.E. (1988) Hyperiid amphipods of the subantarctic and adjacent areas in the central part of the Pacific Ocean. In: Vinogradov, M.E. & Flint, M.V. (Eds.), Ekosistemy subantarkticheskoi zony Tikhogo okeana. Nauka, Moscow, pp. 228–245. [In Russian; English translation: Subantarctic zone ecosystems in the Pacific, pp. 166–177]
Barkhatov, V.A., Vinogradov, M.E. & Vinogradov. G.M. (1999) Boundaries of the areals of hyperiid amphipods in the epipelagic part of the Southern Subtropical Frontal Zone of the Pacific Ocean. Oceanology, 39 (6), 806–812. [In Russian; English translation: Okeanologiya, 39 (6), 1999, pp. 887-894]
Barnard, K.H. (1930) Crustacea. Part X1: Amphipoda. British Antarctic (Terra Nova) Expedition 1910, Zoology, 8 (4), 307–454.
Barnard, K.H. (1931) Amphipoda. Great Barrier Reef Expedition 1928–29, Scientific Reports, 4 (4), 111–135.
Barnard, K.H. (1932) Amphipoda. Discovery Reports, 5, 1–326. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.27664
Barnard, K.H. (1937) Amphipoda. John Murray Expedition 1933–34, Scientific Reports, 4 (6), 131–201.
Barnard, K.H. (1940) Contributions to the crustacean fauna of South Africa. XII. Further additions to the Tanaidacea, Isopoda, and Amphipoda, together with keys for the identification of the hitherto recorded marine and fresh-water species. Annals of the South African Museum, 32 (5), 381–543.
Blainville, H.M.D. de (1821) Hyale, Hyalaea (Malacoz.). In: Cuvier, F. (Ed.), Dictionnaire des Sciences Naturelles, Volume 22. Levrault, Strasbourg & Le Normant, Paris, pp. 65–83.
Boone, L. (1935) Scientific results of the World Cruise of the yacht “Alva”, 1931, William K. Vanderbilt, Commanding. Crustacea: Anomura, Macrura, Euphausiacea, Isopoda, Amphipoda and Echinodermata: Asteroidea and Echinoidea. Bulletin of the Vanderbilt Marine Museum, 6, 1–264, plates 1–96.
Bosc, L.A.G. (1802) Histoire naturelle des Crustacés, contenant leur Description et leurs Moeurs, Vol. 1, 148–152. [Paris, in two volumes]
Bovallius, C. (1887a) Systematical list of the Amphipoda Hyperiidea. Bihang till Kungliga Vetenskaps-Akademiens Handlingar, 11 (16), 1–50. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.5127
Bovallius, C. (1887b) Arctic and Antarctic hyperids. Ur “Vega”-expeditionens Vetenskapliga iakttagelser, 4, 543–582, plates 40–47.
Bovallius, C. (1890) The Oxycephalids. Nova Acta Regiae Societatis Scientiarum Upsaliensis, series iii, 14, 1–141, plates 1–7.
Bowman, T.E. & Gruner, H.-E. (1973) The families and genera of Hyperiidea (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology, No. 146, 1–64. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.00810282.146
Brandt, J.F. (1834–1835) Prodromus descriptionis animalium ab H. Mertensio in orbis terrarum circumnavigatione observatorum. Fasciculus 1. Polypos, Acalephas, Discophoras et Siphonophoras, nec non Echinodermata continens/auctore, Johanne Friderico Brandt. Recueil Actes des séances publiques de l’Acadadémie impériale des Science de St. Petersbourg, 1834, 201–275.
Browne, W.E., Haddock, S.H.D. & Martindale, M.Q. (2007) Phylogenetic analysis of lineage relationships among hyperiid amphipods as revealed by examination of the mitochondrial gene, cytochrome oxidase 1 (CO1). Integrative and Comparative Biology, 47 (6), 815–830. https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/icm093
Brusca, G.J. (1973) Pelagic Amphipoda from the waters near Oahu, Hawaii, excluding the family Scinidae. Pacific Science, 27 (1), 8–27.
Brusca, G.J. (1981) Annotated keys to the Hyperiidea (Crustacea: Amphipoda) of North American coastal waters. Technical Reports of the Allan Hancock Foundation, 5, 1–76.
Brusca, R.C. & Hendrickx, M.E. (2005) Crustacea 4. Peracarida: Lophogastrida, Mysida, Amphipoda, Tanaidacea & Cumacea. In: Hendrickx, M.E., Brusca, R.C. & Findley, L.T. (Eds.), Listado y Distribución de la Macrofauna del Golfo de California, México. Parte 1. Invertebrados. A Distributional Checklist of the Macrofauna of the Gulf of California, Mexico. Part 1. Invertebrates. Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum, Tucson, Arizona, pp. 139–154.
Bucklin, A., Ortman, B.D., Jennings, R.M., Nigro, L.M., Sweetman, C.J., Coply, N.J., Sutton, T. & Wiebe, P.H. (2010) A “Rosetta Stone” for metazoan zooplankton: DNA barcode analysis of species diversity of the Sargasso Sea (Northwest Atlantic Ocean). Deep-Sea Research II, 57, 2234–2247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2010.09.025
Bulycheva, A.I. (1955) Hyperiids (Amphipoda: Hyperiidea) of the north-west Pacific Ocean. Akademiya Nauk SSSR, Doklady, 102 (5), 1047–1050. [In Russian]
Burridge, A.K., Tump, M., Vonk, R., Goetze, E. & Peijnenburg, K.T.C.A. (2016) Diversity and distribution of hyperiid amphipods along a latitudinal transect in the Atlantic Ocean. Progress in Oceanography, 12 pp. [Available on line 8 September 2016.] https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2016.08.003
Carus, J.V. (1885) Prodromus Faunae Mediterraneae sive Descriptio Animalium Maris Mediterranei incolarum quam comparata silva rerum quatenus innotuit adjectis locis et nominibus vulgaribus eorumque auctoribus in commodum Zoologorum congessit Julius Victor Carus. Vol. I. Pars II. Arthropoda. [Stuttgart, 1885]
Chamisso, A. (1819) De animalibus quibusdam e classe Vermium Linnaeana, in Circumnavigatione terrae auspicante Comte N. Romanzoff, duce Ottone de Kotzbae, annis 1815–1818 peracta, Berolini, Dummlerum.
Chevreux, E. (1893) Quatrième campagne de l’Hirondelle, 1888. Sur les Crustacés Amphipodes recueillis dans l’estomac des Germons. Bulletin de la Société Zoologique de France, 18, 70–74., figs. 1–9.
Chevreux, E. (1900) Amphipodes provenant des campagnes de I’Hirondelle (1885–1888). Résultats des Campagnes scientifiques accomplies sur son Yacht, par Albert 1er, Prince Souverain de Monaco, 16 (i–iv), 1–195, plates 1–18.
Chevreux, E. (1935) Amphipodes provenant des campagnes du Prince Albert 1er, de Monaco. In: Résultats des Campagnes scientifiques accomplies sur son Yacht, par Albert 1er, Prince Souverain de Monaco, 90, 1–214, plates 1–16.
Chevreux, E. & Fage, L. (1925) Amphipodes. Faune de France, 9, 488 pp., 438 figs.
Claus, C. (1871) Untersuchungen über den Bau und der Verwandtschaft der Hyperiden. Nachrichten von der Königliche Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften und der Georg-Augustus-Universität zu Göttingen, Yahre 1871, 149–157.
Claus, C. (1873) Grundzüge der Zoologie. Zum Gebrauche an Universitäten und Höheren Lehranstalten sowie zum Selbststudium. Second Edition. Marburg & Leipzig, (Marburg Akademische Buchdruckerei, 1873), v–xii + 1171 pp.
Claus, C. (1876) Grundzüge der Zoologie. Zum Gebrauche an Universitäten und Höheren Lehranstalten sowie zum Selbststudium. Third Edition. Marburg & Leipzig, 1875, v–xii + 740 pp.
Claus, C. (1879) Die Gattungen und Arten der Platysceliden in Systematischer Übersicht. Arbeiten aus dem Zoologischen Institut der Universität zu Wien und der Zoologischen Station Triest, 2, 1–52. [147–198]
Claus, C. (1880) Grundzüge der Zoologie. Zum wissenschaftlichen Gebrauche. Fourth Edition. Marburg, 1880, v–vii + 822 pp.
Claus, C. (1887) Die Platysceliden. Alfred Hölder, Vienna, 77 pp., plates 1–25.
Cocco, A. (1832) Su di alcuni nuovi Crustacei dé mari di Messina Lettera del dott. Anastasio Cocco al celebre dott. William Elford Leach uno dé conservatori del Museo britannico in Londra. Effemeridi scientifiche e letterarie per la Sicilia, 2 (6), 202–209. Giugno, 1832.
Cocco, A. (1833) Descrizione di alcuni Crustacei di Messina per Anastasio Cocco. Giornale di Scienze Lettre e Arti per la Siclia, 44 (11). Palermo, 1833.
Coleman, C.O. (1994) Comparative anatomy of the alimentary canal of hyperiid amphipods. Journal of Crustacean Biology, 14 (2), 346–370. https://doi.org/10.2307/1548914
Copilaş-Ciocianu, D., Borko, Š. & Fišer, C. (2020) The late blooming amphipods: Global change promoted post-Jurassic ecological radiation despite Palaeozoic origin. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 143 (2020) 106664, 12 pp. [online 26 Oct. 2019] https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2019.106664
Costa, A. (1867) Saggio della collezione de’ Crostacei del Mediterraneo Del Museo Zoologico della Università di Napoli spedito alla Esposizione di Parigi del 1867. Annurio del Museo Zoologico della R. Universtà di Napoli. Anno iv, 1864, pp. 38–46, plate iii. Napoli, 1867.
Costa, F., Krapp, T. & Ruffo, S. (2009) Atlante degli Anfipodi Mediterranei. Guida illustrata a colori. – Atlas of Mediterranean amphipods. Guide with colour illustrations. Ugo Mursia Editore, Milano, 210 pp.
Costa, O.G. & Costa A. (1840) Catalogo de’ Crostacei del Regno Napoli, pp. 1–7.
Cuvier, G. (1804) Mémoire sur les Thalides (Thalia Browne) et sur les Biphores (Salpa Forskål). Annales du Muséum Nationale d’Historie Naturelle Paris, 4, 360–382.
Dakin, W.J. & Colefax, A.N. (1940) The plankton of the Australian coastal waters off New South Wales, Part 1. University of Sydney, Department of Zoology, Monograph, No. 1, 1–215.
Dana, J.D. (1853) Crustacea, Part II. United States Exploring Expedition, 14, 689–1618. [Plates 1–96 published in 1855]
De Broyer, C. & Jażdżewski, K. (1993) Contribution to the marine inventory. A checklist of the Amphipoda (Crustacea) of the Southern Ocean. Documents de travail de l’Institut royal des Sciences naturelles de Belgique, 73, 1–154.
Della Chiaje, S. (1823–1831) Memorie sulla storia e notomia degli Animali senza Vertebre del Regno di Napoli, vols i–iv, Atlas. Napoli 1823–1831.
Dick, R.I. (1970) Hyperiidea (Crustacea: Amphipoda) Keys to South African genera and species, and a distribution list. Annals of the South African Museum, 57 (3), 25–86.
Eschscholtz, F. (1829) System der Acalephen. Eine ausfűhrliche Beschreibung aller Medusenartigen Strahltiere. Ferdinand Dűmmler, Berlin, 190 pp.
Escobar-Briones, E., Winfield, I., Ortiz, M., Gasca, R. & Suárez, E. (2002) Chapter 17. Amphipoda.. In: Llorente-Bousquets, J. & Morrone, J.J. (Eds.), Biodiversidad, taxonomía y biogeografía de artrópodos de México: Hacia una síntesis de su conocimiento. Volumen III. Comisión Nacional para el conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad/Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. Bayer, Mexico, pp. 341–371.
Espinosa-Leal, L., Escribano, R., Riquelme-Bugueño, R. & Corredor-Acosta, A. (2021a) Distribution and biodiversity patterns of hyperiid amphipods across the coastal-offshore gradient of the sub-tropical Southeastern Pacific. Marine Biodiversity, 51, 13, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-020-01152-x
Espinosa-Leal, L., Medellin-Mora, J., Corredor-Acosta, A. & Escribano, R. (2021b) The community structure of hyperiid amphipods associated with two seamount regions in the South-east Pacific. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0025315420001344
Evans, A.C. (1967) Syntypes of Decapoda described by William Stimpson and James Dana in the collections of the British Museum (Natural History). Journal of Natural History, 1, 399–411.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00222936700770391
Evans, F. (1961) The planktonic Crustacea of the Petula transatlantic expedition. Proceedings of the Linnaean Society of London, 172 (2), 189–207. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.1961.tb00887.x
Fabricius, J.C. (1775) Systema Entomologiae, sistens Insectorum Classes, Ordines, Genera, Species, adjectis synonymis, locis, descriptionibus, observationibus. Flensbergi et Lipziae, 832 pp.
Forsskål, P. (1775) Descriptiones Animalium, Avium, Amphibiorum, Piscium, Insectorum, Vermium; quae in Itinere Orientali Observavit Petrus Forskål. Prof. Haun. Post Mortem Auctoris Ed. Carsten Neibuhr. Adjuncta est Materia Medica Kahirina atque Tabula Maris Rubri Geographica. Hauniae, 1–9 + i–xxxiv + 1–164, 1 map.
Fowler, G.H., (1904) Biscayan Plankton: Appendix on the distribution of the Amphipoda and Cladocera. Transactions of the Zoological Society of London, 13 (10), 46–53.
Galil, B., Spanier, E. & Ferguson, W.W. (1990). The Scyphomedusae of the Mediterranean coast of Israel, including two lessepsian migrants new to the Mediterranean. Zoologische Mededelingen, Leiden, 64, 95–106.
Garcia-Madrigal, M.S. (2007) Annotated checklist of the amphipods (Peracarida: Amphipoda) from the tropical eastern Pacific. In: Hendrickx, M.E. (Ed.), Contributions to the study of East Pacific Crustaceans, 4 (2), 63–195. Instituto de Ciencias del Mar y Limnologia, UNAM, 195 pp.
Gasca, R. (2003a) Hyperiid amphipods (Crustacea: Peracarida) and mesoscale features in the Gulf of Mexico. Marine Ecology, 24 (4), 303–317.
Gasca, R. (2003b) Hyperiid amphipods (Crustacea: Peracarida) in relation to a cold-core ring in the Gulf of Mexico. Hydrobiologia, 510, 115–124.
Gasca, R. (2004) Distribution and abundance of hyperiid amphipods in relation to summer mesoscale features in the southern Gulf of Mexico. Journal of Plankton Research, 26 (9), 993–1003. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbh091
Gasca, R. (2007) Hyperiid amphipods of the Sargasso Sea. Bulletin of Marine Science, 81 (1), 115–125.
Gasca, R. (2009a) Hyperiid amphipods (Crustacea: Peracarida) in Mexican waters of the Pacific Ocean. Pacific Science, 63 (1), 83–95. [2009] https://doi.org/10.2984/1534-6188(2009)63[83:HACPIM]2.0.CO;2
Gasca, R. (2009b) Diversity of Hyperiid Amphipods (Crustacea: Peracarida) in the Western Caribbean Sea: News from the Deep. Zoological Studies, 48 (1), 63–70.
Gasca, R. (2009c) Part 22. Hyperiid Amphipods. In: Wehrtmann, I.S. & Cortés, J. (Eds.), Marine Biodiversty of Costa Rica, Central America. Monographiae Biologicae 86. Springer & Business Media B.V., pp. 275–282, + tables. [pp. 217 & 218]
Gasca, R. & Browne, W.E. (2017) Symbiotic associations of crustaceans and a pycnogonid with gelatinous zooplankton in the Gulf of California. Marine Biodiversity, Online First, 9 pp. [Published online: 11 March 2017.] https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-017-0668-5
Gasca, R. & Franco-Gordo, C. (2008) Hyperiid amphipods (Peracarida) from Banderas Bay, Mexican tropical Pacific. Crustaceana, 81 (5), 563–575. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854008784092256
Gasca, R. & Franco-Gordo, C. (2014) Anfípodos Hyperiidea de la costa sur de Jalisco y Colima. Chapter 6. In: María del Carmen Franco-Gordo (Ed.), Inventario de biodiversidad de la costa sur de Jalisco y Colima, vol. 1, 78 pp. [Universidad de Guadalajara. January 2014.]
Gasca, R., Franco-Gordo, C., Godínez-Domínguez, E. & Suárez-Morales, E. (2012) Hyperiid amphipod community in the Eastern Tropical Pacific before, during, and after El Niño 1997–1998. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 455, 123–139. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps09571
Gasca, R. & Haddock, S.H.D. (2004) Associations between gelatinous zooplankton and hyperiid amphipods (Crustacea: Peracarida) in the Gulf of California. Hydrobiologia, 530/531, 529–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-004-2657-5
Gasca, R., Manzanilla, H. & Suárez-Morales, E. (2009) Distribution of hyperiid amphipods (Crustacea) of the southern Gulf of Mexico, summer and winter, 1991. Journal of Plankton Research, 31 (12), 1493–1504. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbp096
Gasca, R. & Morales-Ramírez, A. (2012) Anfípodos hiperídeos (Crustacea: Peracarida) del Parque Nacional Isla del Coco, Costa Rica, Pacífico Tropical Oriental. Revista de Biología Tropical, 60 (Suppl. 3), 223–233.
Gasca, R. & Shih, C.-T. (2001) Hyperiid amphipods from surface waters of the western Caribbean Sea (1991). Crustaceana, 74 (5), 489–499. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854001750243063
Gasca, R. & Shih, C-T. (2003) Hyperiid amphipods of Banco Chinchorro. Bulletin of Marine Science, 73 (1), 91–98.
Gasca, R. & Suárez-Morales, E. (2004) Distribution and abundance of hyperiid amphipods (Crustacea: Peracarida) of the Mexican Caribbean Sea, (August 1986). Caribbean Journal of Science, 40 (1), 23–30.
Gates, J.E., Stoddart, H.E. & Lowry, J.K. (2003) Hyperiidea. In: Lowry, J.K. & Stoddart, H.E. (Eds.), Crustacea: Malacostraca: Peracarida: Amphipoda, Cumacea, Mysidacea. In: Beesley, P.L. & Houston, W.W.K. (Eds.), Zoogical Catalogue of Australia. Vol. 19.2B. CSIRO Publishing, Melbourne, i–xii, pp. 298–369. [Total page number: 531 pp.]
Gerstaecker, A. (1886) Dr. H. G. Bronn’s Klassen und Ordnungen des Thierreichs, wissenschaftlich dargestellt in Wort und Bilt. 5(2). Gliederfüssler; Arthropoda. Leipzig und Heidelberg, 1886, pp. 417–512.
Grice, G.D. & Hart, A.D. (1962) The abundance, seasonal occurrence and distribution of the epizooplankton between New York and Bermuda. Ecological Monographs, 32, 287–307. https://doi.org/10.2307/1942377
Harbison, G.R. (1976) Development of Lycaea pulex Marion, 1874 and Lycaea vincentii Stebbing, 1888 (Amphipoda, Hyperiidea). Bulletin of Marine Science, 26 (2), 152–164.
Harbison, G.R., Biggs, D.C. & Madin, L.P. (1977) The associations of Amphipoda Hyperiidea with gelatinous zooplankton – II. Associations with Cnidaria, Ctenophora and Radiolaria. Deep-Sea Research, 24, 465–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-6291(77)90484-2
Hereu, C.M., Arteaga, M.C., Galindo-Sánchez, C.E., Herzka, S.Z., Batta-Lona, P.G. & Jiménez-Rosenberg, S.P.A. (2020) Zooplankton summer composition in the southern Gulf of Mexico with emphasis on salp and hyperiid amphipod assemblages. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0025315420000715
Holmes, S.J. (1908) The Amphipoda collected by the U.S. Bureau of Fisheries Steamer ‘Albatross’ off the West Coast of North America in 1903 and 1904, with descriptions of a new family and several new genera and species. Proceedings of the United States National Museum, 35, 489–543., figures 1–46.
Hope, F.W. (1851) Catalogo dei crostacei Italiani e di moltri altri del Mediterraneo. Napoli Stabilimento Tippografico di Fr’. Azzolino Vico Gerolomini, 10, 48 pp., 2 figs.
Hure, J., Scotto di Carlo, B. & Basile, A. (1969) Comparazione tra lo Zooplancton del Golfo di Napoli e dell’Adriatico Méridionale presso Dubrovnik, II: Amphipoda (Hyperiidea). Pubblicazioni della Stazione Zoologica di Napoli, 37, 599–609.
Hurley, D.E. (1955) Pelagic amphipods of the sub-order Hyperiidea in New Zealand waters. I. Systematics. Transactions of the Royal Society of New Zealand, 83 (1), 119–194.
Hurley, D.E. (1960) Pelagic Amphipoda of the N.Z.O.I. Pacific cruise, March 1958. New Zealand Journal of Science, 3 (2), 274–288.
Hurley, D.E. (1969) Amphipoda Hyperiidea. In: ‘Antarctic Map Folio Series’, Folio 11, Distribution of selected groups of marine invertebrates in waters south of 35°S Latitude. American Geographical Society, pp. 32–34, sheets 1–2.
Hurt. C., Haddock, S.H.D. & Browne, W.E. (2013) Molecular phylogenetic evidence for the reorganization of the Hyperiid amphipods, a diverse group of pelagic crustaceans. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 67, 28–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2012.12.021
International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (1999) International code of Zoological Nomenclature, 4th edition. The International Trust for Zoological Nomenclature and The Natural History Museum, London, 306 pp.
Irie, H. (1948) Preliminary Report on Pelagic Amphipods in the Adjacent Seas of Japan. Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University, 9 (1), 33–40. https://doi.org/10.5109/22606
Irie, H. (1957a) Pelagic Amphipods in the Western Seas of Kyûsyû. Bulletin of the Faculty of Fisheries, Nagasaki University, 5, 8–12.
Irie, H. (1957b) 25 species of Pelagic Amphipods, in the adjacent Seas of Japan. In: Suisan Gaku Syûsei (compilations of Fishery Science). Tokyo University Press, Tokyo, pp. 345–355. [In Japanese]
Irie, H. (1959) Studies on pelagic amphipods in the adjacent seas of Japan. Bulletin of the Faculty of Fisheries, Nagasaki University, 8, 20–42.
Jespersen, P. & Tåning, A.V. (1934) Introduction to the Reports from the Carlsberg Foundation’s Oceanographical Expedition Round the World 1928–30 and list of stations. Dana Report, 1, 7–130.
Kane, J.E. (1962) Amphipoda from waters south of New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Science, 5 (3), 295–315.
Land, M.F. (1989) The eyes of hyperiid amphipods: relations of optical structure to depth. Journal of Comparative Physiology A, 164, 751–762. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00616747
Land, M.F., Marshall, N.J. & Diebel, C. (1995) Tracking of blue lights by hyperiid amphipods. Journal of the Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 75, 71–81. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315400015204
Laval, P. (1980) Hyperiid amphipods as crustacean parasitoids associated with gelatinous plankton. Oceanography and Marine Biology, Annual Review, 18, 11–56.
Lavaniegos, B.E. & Hereu, C.M. (2009) Seasonal variation in hyperiid amphipod abundance and diversity and influence of mesoscale structures off Baja California. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 394, 137–152. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps08285
LeCroy, S.E., Gasca, R., Winfield, I., Ortiz, M. & Escobar-Briones, E. (2009) Amphipoda (Crustacea) of the Gulf of Mexico, Chapter 54. In: Felder, D.L. & Camp, D.K. (Eds.), Gulf of Mexico – origin, waters and biota. Volume 1. Biodiversity. Texas A & M University Press, Texas, pp. 941–972.
Lesueur, C.A. (1813) Mémoire sur quelques nouvelles espéces d’animaux mollusques et radiares recueillis dans la Méditerranée prés de Nice. Nouveau Bulletin des Sciences, par la Société Philomatique de Paris, (2), 3 (69), 281–285, plate 5.
Lima, M.C.G. & Valentin, J.L. (2001) Preliminary results to the holistic knowledge of the Amphipoda Hyperiidea faunal composition off the Brazilian coast. Journal of Plankton Research, 23 (5), 469–480. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/23.5.469
Lin, J. & Chen, R. (1988) Distribution of planktonic Amphipoda in the western Taiwan Strait. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 7 (4), 324–330. [In Chinese]
Lin, J. & Chen, R. (1994) Distribution of pelagic amphipods in the central part of the South Sea area. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 16 (4), 113–119. [In Chinese]
Lin, J., Chen, M. & Chen, R. (1995) The distribution pattern of planktonic Amphipoda in the southern Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 17 (5), 117–123. [In Chinese]
Lin, J., Chen, M. & Chen, R. (1996) The species diversity of planktonic Amphipoda in China Seas. Chinese Biodiversity, 4 (4), 228–234. [In Chinese]
Lo Bianco, S. (1902) Le pesche pelagiche abissali eseguite dal Maia nelle vicinanze di Capri. Mittheilungen aus der Zoologischen Station zu Neapel, 15, 413–482, plate 19.
Lo Bianco, S. (1903) Le pesche abyssali eseguite da F.A. Krupp col Yacht Puritan nelle adiacenze di Capri ed in Altre Località del Mediterraneo. Mittheilungen aus der Zoologischen Station zu Neapel, 16 (1–2), 109–278, plates 7–9, 1 table. [folded]
Lo Bianco, S. (1904) Hyperiden In: Pelagische tiefseefischerei der “Maja” in der umgebung von Capri. 41 plates, 1 map. Jena. pp. 41–45. [German translation of 1902]
Louw, E. (1977) The South African Museum’s Meiring Naude cruises. Part 1. Station data 1975, 1976. Annals of the South African Museum, 72 (8), 147–159.
Louw, E. (1980) The South African Museum’s Meiring Naude cruises. Part 10. Station data 1977, 1978, 1979. Annals off the South African Museum, 81 (5), 187–205.
Lowry, J.K. (2000) Taxonomic status of amphipod crustaceans in the South China Sea with a checklist of known species. Raffles Bulletin of Zoology, Supplement, No. 8, 309–342.
Madin, L.P. & Harbison G.R. (1977) The associations of Amphipoda Hyperiidea with gelatinous zooplankton – I. Associations with Salpidae. Deep-Sea Research, 24, 449–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-6291(77)90483-0
Milne-Edwards, H. (1830) Extrait de recherches pour servir à l’histoire naturelle des Crustacés Amphipodes. Annales des Sciences Naturelles, 20, 353–399, plates 10–11.
Montú, M. (1994) Northern Brazilian pelagic amphipods, suborder Hyperiidea (Crustacea). Nauplius, Rio Grande, 2, 131–134.
Montú, M. (1998) Malacostraca – Peracarida. Amphipoda –Hyperiidea. In: Young, P.S. (Ed.), Catalogue of Crustacea of Brazil. Série Livros 6. Museu Nacional, Rio de Janeiro, pp. 595–603.
Mori, M., Suzuki, Y., Yamaki, A. & Lindsay, D.J. (2010) A checklist of hyperiid amphipods (Amphipoda: Hyperiidea) from Japanese waters, including new records from 1996–2007 for Sagami Bay and outlying areas. Bulletin of the Plankton Society of Japan, 57 (1), 1–14. [In Japanese with English summary]
Műller, F. (1861) Polypen und Quallen von Santa Catharina. Olindias sambaquiensis n. sp. Archiv fűr Naturgeschichte, 27, 312–319, plate 9.
Nagata, K. (1986) Amphipod crustaceans from surface waters of the Southern Ocean during 1983–84 summer. Memoirs of National Institute of Polar Research, Special Issue, 40, 259–276.
Natale, G.De. (1850) Su pochi Crostacei del porto di Messina. Lettera del Dottor Giuseppe de Natale socio corrispondente dell’ Academia Gioenia di Catania al Sig. Achille Costa con una tavola in rame. Napoli, pp. 1–16.
Nayar, K.N. (1959) The Amphipoda of the Madras coast. Bulletin of the Madras Government Museum, New Series – Natural History Section, 4 (3), 1–59, plates 1–16.
Norman, A.M. (1900) British Amphipoda of the Tribe Hyperiidea and the Families Orchestiidae and some Lysianassidae. The Annals and Magazine of Natural History, series 7, number 5, 126–144, plate 6.
Nunes, T.R.S., Barreto, T.M.S.P. & Larrazábal, M.E.L.L. (2013) Macrozooplântcon das cadeias Norte/Rocus/Noronha e da plataforma/talude sul do nordeste do Brasil, com ênfase em Crustacea Amphipoda. Tropical Oceanography, Recife, 41 (1–2), 67–82. https://doi.org/10.5914/to.2013.0080
Pallas, P.S. (1774) Spicilegia zoologica, quibus novae imprimis et obscurae animalium species iconibus, descriptionibus atque commentariis illustrantur cura P.S. Pallas. Fasciculus, 10, 1–41, 4 plates.
Philippi, R.A. (1836) Enumeratio molluscorum Siciliae cum viventium tum in tellure tertiaria fossilium, quae in itinere suo observavit. Volume 1. Schropp, Berlin (Berolini), xiv + 267 pp., plates 1–12. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.100735
Pillai, N.K. (1966) Pelagic amphipods in the collections of the Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute, India: Part II. Excluding Oxycephalidae. Proceedings of the Symposium on Crustacea held at Ernakulam from January 12–15, 1965. Part I, 205–232. [Marine Biological Association of India]
Pirlot, J.M. (1929) Résultats zoologiques de la croisière atlantique de l’Armauer Hansen’ (Mai-Juin 1922). 1. Les Amphipodes Hypérides. Mémoires de la Société Royale des Sciences de Liège, série 3, 15 (2), 1–196.
Pirlot, J.M. (1930) Les Amphipodes de l’expédition du ‘Siboga’, Première Partie, Les Amphipodes Hypérides (à l’exception des Thaumatopsidae et des Oxycephalidae). Siboga-Expeditie, Monograph 33a, 1–54.
Pirlot, J.M. (1939a) Sur des Amphipodes Hypérides provenant des croisières du Prince Albert 1er de Monaco. Résultats des Campagnes Scientifiques accomplies sur son Yacht par Albert 1er Prince Souverain de Monaco, fascicule 102, 1–64.
Pirlot, J.M. (1939b) Résultats Scientifiques des croisières du Navire-école Belge <<Mercator>>. Vol. 3, part 3. Amphipoda. Mémoires du Musée royal d’Histoire naturelle de Belgique, série 2, fascicule 15, 47–80.
Potier, M., Marsac, F., Cherel, Y., Lucas, V., Sabatié, R., Maury, O. & Ménard, F. (2007) Forage fauna in the diet of three large pelagic fishes (lancetfish, swordfish and yellowfin tuna) in the western equatorial Indian Ocean. Fisheries Research, 83, 60–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fishres.2006.08.020
Puente-Tapia, F.A., Gasca, R., Genzano, G., Schiariti, A. & Morandini, A.C. (2018) New records of association between Brachyscelus cf. rapacoides (Arthropoda: Amphipoda) and medusae (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa and Hydrozoa) from São Sebastião Channel, southeast Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Oceanography, 66 (3), 301–306. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1679-87592018017806603
Quoy, J.R.C. & Gaimard, J.P. (1824–1826) Zoologie. In: de Freycinet, L. (Ed.), Voyage au tour du monde fait par ordre du roi, sur les corvettes de S.M. l’Uranie et la Physicienne pendant les années 1817 à 1820. iv + 712 pp. [pp. 1–328, 1824; 329–616, 1825; 617–664, 1826]
Reid, D.M. (1955) Amphipoda (Hyperiidea) off the coast of tropical West Africa. Atlantide Report 3, 7–40.
Schellenberg, A. (1927) Amphipoda des Nordischen Plankton. Nordisches Plankton, Zoologischer Teil. Vol. 3. Kiel, Leipzig. pp. 589–722.
Senna, A. (1903) Thaumonectes un nuovo genere di anfipodo iperide del Mare Caraibico. Bulletino della Societá Entomologica Italiana, (Firenze), 35, 93–95.
Sexton, E.W. (1911) The Amphipoda collected by the “Huxley” from the north side of the Bay of Biscay in August, 1906. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 9 (2), 199–227. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315400073379
Sheard, K. (1965) Species groups in the zooplankton of the eastern Australian slope waters, 1938–41. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 16, 219–254. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF9650219
Sheard, K. (1967) Temperature and chlorinity distributions, and species’ associations of some subtropical euphausiid and hyperiid Crustacea. Proceedings of the Symposium on Crustacea, Ernakulam, Marine Biological Association of India 1965, Part III, 976–986.
Shih, C.-T. & Chen, Q.-C. (1995) Zooplankton of China Seas (2)—The Hyperiidea (Crustacea: Amphipoda). China Ocean Press, Beijing, 295 pp.
Shoemaker, C.R. (1945) The Amphipoda of the Bermuda Oceanographic Expeditions, 1929–1931. Zoologica, New York, 30 (4), 185–266.
Shoemaker, C.R. (1948) The Amphipoda of the Smithsonian-Roebling Expedition to Cuba in 1937. Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collections, 110, 1–15.
Shulenberger, E. (1977) Hyperiid amphipods from the zooplankton community of the North Pacific Central Gyre. Marine Biology, 42, 375–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00402200
Shulenberger, E. (1980) Factor analysis of a Hyperiid Amphipod Assemblage from the North Pacific C Shulenberger, E. (1980) Factor analysis of a Hyperiid Amphipod Assemblage from the North Pacific Central Gyre. Marine Ecology, Progress Series, 2 (2), 109–120. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps002109
Siegfried, W.R. (1963) The Hyperiidea (Amphipoda) off the West coast of Southern Africa. Investigational Report No. 48. Commerce and Industry, December, 1963. Division of Sea Fisheries, Cape Town, 12 pp.
Souza, C.S., Conceição, L.R. & Mafalda JR, P.O. (2016) Hyperiid amphipods around the seamounts and Islands off northeastern Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Oceanography, 64 (4), 339–352. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1679-87592016123306404
Spandl, H. (1924) Expeditionen S.M. Schiff ‘Pola’ in das Rote Meer. Nördliche und Südliche Hälfte, 1895/96–1897/98. Zoologische Ergebnisse 35. Die Amphipoden des Roten Meeres. Denckschriften Akademie der Wissenschaften in Wien, Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftliche Klasse, 99, 19–73.
Spandl, H. (1927) Die Hyperiiden (exkl. Hyperiidea Gammaroidea und Phronimidae) der Deutschen Südpolar-Expedition 1901–1903. Deutsche Südpolar-Expedition 1901–1903, Band 19, Zoologie, 11, 145–287, plate 10.
Spence Bate, C. (1861) On the morphology of some Amphipoda of the Division Hyperina. The Annals and Magazine of Natural History, series 3, 8 (43), 1–16, plates 1–2.
Spence Bate, C. (1862) Catalogue of the specimens of Amphipodous Crustacea in the collection of the British Museum. British Museum, Natural History, London, 399 pp., plates 1–58.
Stebbing, T.R.R. (1888) Report on the Amphipoda collected by H.M.S. ‘Challenger’ during the years 1873–1876. Report on the Scientific Results of the Voyage of H.M.S. ‘Challenger’ during the years 1873–76. Zoology, 29, i–xxiv + 1–1737, plates 1–210.
Stephensen, K. (1923) Crustacea Malacostraca, V. (Amphipoda. 1) Danish Ingolf-Expedition, 3 (8), 1–100, + 2 tables, 1 map.
Stephensen, K. (1925) Hyperiidea-Amphipoda (Part 3: Lycaeopsidae, Pronoidae, Lycaeidae, Brachyscelidae, Oxycephalidae, Parascelidae, Platyscelidae). Report on the Danish Oceanographical Expeditions 1908–10 to the Mediterranean and Adjacent Seas, 2 (Biology-D5), 151–252.
Stewart, D.A. (1913) A report on the extra-Antarctic Amphipoda Hyperiidea collected by the ‘Discovery’. The Annals and Magazine of Natural History, series 8 (12), 245–264, plates 4–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222931308693395
Tarling, G.A., Ward, P., Sheader, M., Williams, J.A. & Symon, C. (1995) Distribution patterns of macrozooplankton assemblages in the southwest Atlantic. Marine Ecology in Progress Series, 120, 29–40. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps120029
Tashiro, J.E. & Jossi, J.W. (1972) Amphipoda (Hyperiidea) distribution and abundance off the coast of central West Africa. NOAA, National Marine Fisheries Service, Seattle, Washington, Data Report, 76, 38 pp.
Tattersall, W.M. (1906) Pelagic Amphipoda of the Irish Atlantic Slope. The Marine Fauna of the Coast of Ireland. Part VIII. Scientific Investigations of the Fisheries Branch of Ireland, 1905, 4 (8), 1–39, plates 1–5.
Thurston, M.H. (1976) The vertical distribution and diurnal migration of the Crustacea Amphipoda collected during the SOND Cruise, 1965. II. The Hyperiidea and general discussion. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 56, 383–470. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315400018981
Tranter, H.A. (1977) Further studies of plankton ecosystems in the eastern Indian Ocean VII. Ecology of the Amphipoda. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 28, 645–662. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF9770645
Valencia, B. & Giraldo, A. (2009) Hipéridos (Crustacea: Amphipoda) en el Sector norte del Pacífico oriental tropical colombiano. Latin American Journal of Aquatic Research, 37 (2), 265–273.
https://doi.org/10.3856/vol37-issue2-fulltext-14
Valencia, B. & Giraldo, A. (2012) Structure of hyperiid amphipod assemblages on Isla Gorgona, eastern tropical Pacific off Colombia. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 92 (7), 1489–1499.
https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315411001780
Valencia, B., Lavaniegos, B., Giraldo, A. & Rodríguez-Rubio, E. (2013) Temporal and spatial variation of hyperiid amphipod assemblages in response to hydrographic processes in the Panama Bight, eastern tropical Pacific. Deep-Sea Research I, 73, 46–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2012.11.009
Véliz, C., Mujica, A. & Nava, M.L. (2021) Hyperiid amphipods distribution between the central coast and oceanic islands off Chile, southeastern Pacific. Latin American Journal of Aquatic Research, 49 (1), 169–181. https://doi.org/10.3856/vol49-issue1-fulltext-2489
Vicencio-Aguilar, M.E. & Fernández-Alamo, M.A. (1996) Zooplancton del Domo de Costa Rica: taxonomia y biogeografia. Lab. Invertebrados, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad Nacional Autónomia de México, 31 pp.
Vinogradov, G.M. (1991) Hyperiid amphipods in the eastern part of the South Pacific gyre. Marine Biology, 109 (2), 259–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01319394
Vinogradov, G.M. (1993) Hyperiid amphipods from the Walters Shoal (south-western Indian Ocean). Arthropoda Selecta, 2 (1), 41–48.
Vinogradov, G.M. (1999) Amphipoda. In: Boltovskoy, D. (Ed.), South Atlantic Zooplankton. Vol. 2. Backhuys, Leiden, pp. 1141–1240.
Vinogradov, G.M., Hernández, F., Tejera, E. & León, M.E. (2004) Pelagic amphipods from the Cape Verde Islands (TFMCBM/98 cruise, Macaronesia 2000-project). Vieraea, 32, 7–27.
Vinogradov, M.E. (1962) Hyperiidea (Amphipoda) collected by the Soviet Antarctic Expedition on M/V ‘Ob’ south of 40°S. Issledovaniya Fauny Morei I (IX), Resultaty biologcheskikh issledovanii Sovetskoi antarkticheskoi ekspeditsii (1955–1958), 1, 1–35. [In Russian; English translation: Biological Reports of the Soviet Antarctic Expedition (1955–1958), 1, 1–32: Israel Program for Scientific Translations, Jerusalem, 1966]
Vinogradov, M.E. & Semenova, T.N. (1996) Supplement. In: Vinogradov, M.E., Volkov, A.F. & Semenova, T.N. Hyperiid Amphipods (Amphipoda, Hyperiidea) of the World Oceans. Pp. 609–621. Smithsonian Institution Libraries, D. Siegel-Causey, Scientific Editor, Washington D.C., Oxonian Press Pvy. Ltd., New Delhi, 632 pp.
Vinogradov, M.E., Volkov, A.F. & Semenova, T.N. (1982) Amfipody-Giperiidy (Amphipoda: Hyperiidea) Mirovogo Okeanea. Akademiya Nauk SSSR, Opredeliteli po Faune SSSR No. 132. Leningrad, 492 pp. [In Russian]
Vinogradov, M.E., Volkov, A.F. & Semenova, T.N. (1996) Hyperiid Amphipods (Amphipoda, Hyperiidea) of the World Oceans. Smithsonian Institution Libraries, D. Siegel-Causey, Scientific Editor, Washington D.C., Oxonian Press Pvy. Ltd., New Delhi, 632 pp. [English translation from 1982 Russian original]
Walker, A.O. (1909) Amphipoda Hyperiidea of the ‘Sealark’ Expedition to the Indian Ocean. The Transactions of the Linnean Society of London, Series-Zoology, 13, 49–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1909.tb00409.x
Yoo, K.I. (1971) Pelagic hyperiids (Amphipoda: Hyperiidea) of the western North Pacific Ocean. Journal of the National Academy of Sciences, Republic of Korea, Natural Science Series, 10, 39–89.
Young, J.W. (1989) The distribution of hyperiid amphipods (Crustacea: Peracarida) in relation to warm-core eddy J in the Tasman Sea. Journal of Plankton Research, 11 (4), 711–728. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/11.4.711
Young, J.W. & Anderson, D.T. (1987) Hyperiid amphipods (Crustacea: Peracarida) from a warm-core eddy in the Tasman Sea. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 38, 711–725. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF9870711
Zeidler, W. (1978) Hyperiidea (Crustacea: Amphipoda) from Queensland waters. Australian Journal of Zoology, Supplementary Series, No. 59, 1–93. https://doi.org/10.1071/ZO9780617 https://doi.org/10.1071/AJZS059
Zeidler, W. (1984) Distribution and abundance of some Hyperiidea (Crustacea: Amphipoda) in Northern Queensland waters. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 35, 285–305. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF9840285
Zeidler, W. (1991) Crustacea Amphipoda: Hyperiidea from MUSORSTOM cruises. In: Crosnier, A. (Ed.), Résultats des campagnes MUSORSTOM, 9. Mémoires du Muséum national d’Histoire naturelle, A (Zoologie), 152, 125–137.
Zeidler, W. (1992) Hyperiid amphipods (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Hyperiidea) collected recently from eastern Australian waters. Records of the Australian Museum, 44 (1), 85–133. https://doi.org/10.3853/j.0067-1975.44.1992.29
Zeidler, W. (1995) The drawings of hyperiid amphipods (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Hyperiidea) by Sydney Parkinson commissioned by Joseph Banks on the Endeavour Voyage 1768–1771 held in the Natural History Museum, London. Archives of Natural History, 22 (2), 267–281. https://doi.org/10.3366/anh.1995.22.2.267
Zeidler, W. (1998) Pelagic amphipods (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Hyperiidea) collected from eastern and south-eastern Australian waters by the C.S.I.R.O. research vessel ‘Warreen’ during the years 1938–41. Records of the South Australian Museum. Monograph Series, No. 4, 1–143.
Zeidler, W. (2016) A review of the families and genera of the superfamily PLATYSCELOIDEA Bowman & Gruner, 1973 (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Hyperiidea), together with keys to the families, genera and species. Zootaxa, 4192 (1), 1–136. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4192.1.1
Zeidler, W. & De Broyer, C. (2009) Catalogue of the Hyperiidean Amphipoda (Crustacea) of the Southern Ocean with distribution and ecological data. In: De Broyer, C. (Ed.), Census of Antarctic Marine Life: Synopsis of the Amphipoda of the Southern Ocean, Volume 3. Bulletin de l’Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de Belgique, Biologie, 79, supplement 1, 1–96, + 4 colour plates.
Zeidler, W., Douek, J., Rinkevich, B., Gevili, M.G. & Galil, B.S. (2018) Validation and resdescription of the hyperiidean amphipod Brachyscelus rapacoides Stephensen, 1925 (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Hyperiidea: Brachyscelidae), a new record of association with the scyphozoan jellyfish Rhopilema nomadica Galil, 1990 (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae: Rhizostomatidae) in the Mediterranean Sea. Zootaxa, 4471 (3), 523–534. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4471.3.5
Zelickman, E.A. (2005) Amphipoda: Hyperiidea of Israel. A morphological atlas. Fauna Palaestina. Crustacea 1. The Israel Academy of Sciences and Humanities, Jerusalem, 440 pp.
Zhang, W., Lin, Y., He, C., Cao, W., Huang, J., Zheng, L., Yang, W. & Wang, Y. (2014) Hyperiid amphipod communities and the seasonal distribution of water masses in eastern Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Aquatic Biology, 20, 209–217. https://doi.org/10.3354/ab00556