Abstract
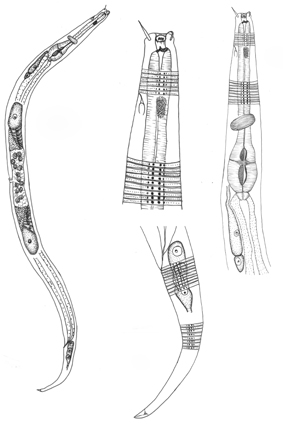
A study involving experiments on a natural Brazilian coral reef, with the aim of assessing the impacts that may be caused by an increase in sea level on benthic fauna, showed that Chromadoridae Filipjev, 1917 was the most abundant and diverse family of Nematoda. Our results also showed that Chromadora Bastian, 1865 was the most abundant and diverse genus, represented by three species: C. serrambi sp. nov., C. pernambucana sp. nov. and C. macrolaimoides Steiner, 1915. Chromadora serrambi sp. nov. is the only Chromadora species where pre-cloacal supplements are absent. Chromadora pernambucana sp. nov. is differentiated by gubernaculum shape and by three supplements, of which two are cup-shaped (small and slightly sclerotized) and a pre-cloacal papilla very close to the cloaca. Chromadora macrolaimoides is very similar to specimens described previously. Here, we propose a grouping of species based on features considered to be most relevant for species identification and present it as an illustrated guide. The diagnostic characteristics of all species were considered, and following discussions, C. micropapillata was revalidated. Finally, the most relevant diagnostic characteristics for the differentiation of Chromadora species were highlighted.
References
Barroso, M.S., da Silva, B.J., Montes, M.J.F. & Santos, P.J.P. (2018) Anthropogenic impacts on coral reef harpacticoid copepods. Diversity, 10 (2), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/d10020032
Bastian, H.C. (1865) Monograph of the Anguillulidae, or Free Nematoids, Marine, Land, and Freshwater; with Descriptions of 100 New Species. Transactions of the Linnean Society of London, 25 (2), 73–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1865.tb00179.x
Bezerra, T.N., Decraemer, W., Eisendle-Flöckner, U., Hodda, M., Holovachov, O., Leduc, D., Miljutin, D., Mokievsky, V., Peña Santiago, R., Sharma, J., Smol, N., Tchesunov, A., Venekey, V., Zhao, Z. & Vanreusel, A. (2020) Nemys: World Database of Nematodes. Available from: http://nemys.ugent.be (accessed 11 November 2020) https://doi.org/10.14284/366
Blome, D. (1982) Systematik der Nematoda eines Sandstrandes der Nordseeinsel Sylt. Mikrofauna des Meeresbodens, 86, 1–194.
Chitwood, B.G. (1933) A revised classification of the Nematoda. The Journal of Parasitology, Papers in Helminthology, Ninth Annual Meeting, 20 (2), 115–148.
Chitwood, B.G. (1951) North American marine nematodes. Texas Journal of Science, 3 (4), 617–672.
Cobb, N.A. (1914) Antarctic marine free-living nematodes of the Shackleton expedition. Contributions to a Science of Nematology, 1, 1–33.
Cobb, N.A. (1920) One hundred new nemas (type species of 100 new genera). Contributions to a Science of Nematology, 9, 217–343.
Da Rocha, C.M.C., Venekey, V., Bezerra, T.N.C. & Souza, J.R.B. (2006) Phytal marine nematode assemblages and their relation with the macrophytes structural complexity in a Brazilian tropical rocky beach. Hydrobiologia, 553, 219–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-0923-9
De Coninck, L.A. & Schuurmans-Stekhoven, J.H. (1933) The freeliving marine nemas of the Belgian Coast. II With general remarks on the structure and the system of nemas. Mémoires du Musée royal d’histoire naturelle de Belgique, 58, 3–163.
De Grisse, A.T. (1969) Redescription ou modification de quelques techniques utilisés dans l’étude des nématodes phytoparasitaires. Mededelingen van de Faculteit Landbouwwetenschappen, Rijksuniversiteit Gent, 34, 251–369.
De Ley, P., Decraemer, W. & Eyualem-Abebe (2006) Introduction: Summary of Present Knowledge and Research Addressing the Ecology and Taxonomy of Freshwater Nematodes. In: Eyualem-Abebe, Traunspurger, W. & Andrássy, I. (Eds.), Freshwater Nematodes: Ecology and Taxonomy. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, pp. 3–30.
De Man, J.G. (1889) Troisième note sur les nématodes libres de la mer du Nord et de la Manche. Mémoires de la Sociét zoologique de France, 2, 1–35 (182–216).
Decraemer, W. & Smol, N. (2006) Orders Chromadorida, Desmodorida and Desmoscolecida. In: Eyualem-Abebe, Traunspurger, W. & Andrássy, I. (Eds) Freshwater Nematodes: Ecology and Taxonomy. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, pp. 497–573. https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851990095.0497
Fabricius, K. & De’ath, G. (2001) Environmental factors associated with the spatial distribution of crustose coralline algae on the Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs, 19 (4), 303–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003380000120
Filipjev, I.N. (1917) Un Nematode libre nouveau de la mer Caspienue, Chromadorissa gen. nov. (Chromadoridae). Revue de Zooogie Russe, Moscow, 2, 29–30.
Filipjev, I.N. (1929) Classification of free-living Nematoda and relations to parasitic forms. Journal of Parasitology Urbana, 15, 281–282.
Gerlach, S.A. (1951) Nematoden aus der Famìlie der Chromadoridae von den deutschen Küsten De Ley. Kieler Meeresforschung, 8 (1), 106–132.
Gerlach, S.A. (1965) Freilebende Meersenematoden aus der Gezeitenzone von Spitzbergen. Veröffentlichungen des Instituts für Meeresforschung in Bremerhaven, Band IX, 109–172.
Gibbons, M.J. & Griffiths CL (1986) A comparison of macrofaunal and meiofaunal distribution and standing stock across a rocky shore, with an estimate of their productivities. Marine Biology, 3, 181–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508255
Heip, C., Vincx, M. & Vranken, G. (1985) The ecology of marine nematodes. Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review, 23, 399–489.
Hoey, A.S. & Bellwood, D.R. (2010) Cross-shelf variation in browsing intensity on the Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs, 29 (2), 499–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-010-0605-6
Hopper, B.E. & Meyers, S.P. (1967) Foliicolous marine nematodes on turtle grass, Thalassia testudinum König, in Biscayne Bay, Florida. Bulletin of Marine Science, 17 (2), 471–517.
Inglis, W.G. (1983) An outline classification of the phylum Nematoda. Australian Journal of Zoology, 31, 243–255. https://doi.org/10.1071/ZO9830243
Jensen, P. (1980). Description of the Marine Free-Living Nematode Chromadora lorenzeni n.sp. with notes on its Microhabitats. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 205 (3/4), 213–218.
Kelaher, B.P. (2003) Changes in habitat complexity negatively affect diverse gastropod assemblages in coralline algal turf. Oecologia, 135 (3), 431–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-003-1196-5
Kito, K. (1978a) Studies on the free-living marine nematodes from Hokkaido, III. Journal of the Faculty of Science, Hokkaido University, Series VI, Zoology , 21 (2), 248–261.
Kito, K. (1978b) Five Species of Marine Nematodes of the Genus Chromadora Bastian from Japan. Annotationes Zoologicae Japonenses, 51 (3), 164–178.
Koop, K., Steven, A., Mcgill, R., Drew, E. & Macdonal, B. (2001) Use of a telemetred dispensing system in controlling nutrient enrichment in the ENCORE at One Tree Island, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42, 121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00180-6
Kreis, H.A. (1924) Zur Kenntnis der freilebenden marinen Nematoden. Schriften für Süßwasser und Meereskunde, Büsum, 2, 157–170.
Lorenzen, S. (1994) The Phylogenetic Systematics of Freeliving Nematodes. The Ray Society, London, 167 pp.
Maida, M. & Ferreira, B.P. (1997) Coral reefs of Brazil: an overview. Proceedings 8th International Coral Reef Symposium, Panama, 1, 263–274.
Matias, M.G., Underwood, A.J. & Coleman, R.A. (2007) Interactions of components of habitat alter composition and variability of assemblages. Journal of Animal Ecology, 76, 986–994. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2656.2007.01277.x
Micoletzky, H. (1922) Freilebende Nematoden von den treibenden Tangen der Sargassosee. Mitteilungen aus dem Hamburgischen Zoologischen Museum und Institut, 39, 1–11.
Micoletzky, H. (1924) Weitere Beiträge zur Kenntnis freilebender Nematoden aus Suez. Sitzungsberichte der Kaiserlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften, (I) 132, 225–262.
Pearse, A.S. (1942) Introduction to parasitology. Bailliere, Tindall & Cox, London, 357 pp.
Pérez-García, J.A., Ruiz-Abierno, A. & Armenteros, M. (2015) Does Morphology of Host Marine Macroalgae Drive the Ecological Structure of Epiphytic Meiofauna? Journal of Marine Biology & Oceanography, 4, 1. https://doi.org/10.4172/2324-8661.1000139
Platt, H.M. & Warwick, R.M. (1988) Free-living Marine Nematodes Part II, British Chromadorids. Synopses of the British Fauna (New Series), D.M. Kermack and R.S.K. Barnes (Eds), 502 pp.
Sarmento, V.C., Pinheiro, B.R., Montes, M.J.F. & Santos, P.J.P. (2017) Impact of predicted climate change scenarios on a coral reef meiofauna community. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 74. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/fsw234
Schuurmans-Stekhoven, J.H.Jr. (1942) Nematoden und Spongien. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 137 (9/10), 169–174.
Schuurmans-Stekhoven J.H.Jr. (1943) Freilebende marine Nematoden des Mittelmeeres. IV. Freilebende marine Nematoden der Fischereigründe bei Alexandrien. Zool Jb (Syst), 76 (4), 323–378.
Steiner, G. (1915) Freilebende marine Nematoden von der Küste Sumatras. Zoologische Jahrbücher (Abteilung für Systematik), 38 (3–4), 223–24.
Timm, Z.W. (1978) Redescription of the marine nematodes of Shackleton’s British Antarctic Expedition of 1907–1909. Antarct Research Series, 26 (6), 237–255.
Venekey, V., Gheller, P.F., Kandratavicius, N., Cunha, B.P., Vilas-Boas, A.C., Fonseca, G. & Maria, T.F. (2019) The state of the art of Chromadoridae (Nematoda, Chromadorida): A historical review, diagnoses and comments about valid and dubious genera and a list of valid species (2019). Zootaxa, 4578 (1), 1–67. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4578.1.1
Wieser, W. (1954) Reports of the Lund University Chile Expedition 1948–49. 17. Free living marine nematodes II. Chromadoroidea. Lunds Universitets Arsskrift. Ny Foljd, Avdelningen, 50 (16), 148 pp.
Wieser, W. (1955) A collection of marine nematodes from Japan. Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory, IV (2-3), 159–181. https://doi.org/10.5134/174529
Wieser, W. (1959) Free-living nematodes and other small invertebrates of Puget Sound beaches. University of Washington Press, 19,1–179.
Wieser, W. & Hopper, B. (1967) Marine nematodes of the east coast of North America. I. Florida. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard College, 135, 239–344.
Wismer, S., Hoey, A.S. & Bellwood, D.R. (2009) Cross-shelf benthic community structure on the Great Barrier Reef: relationships between macroalgal cover and herbivore biomass. Marine Ecology, 376, 45–54. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps07790