Abstract
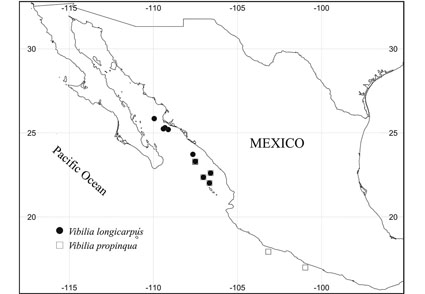
Ten species belonging to the families Paraphronimidae and Vibiliidae were collected during a deep-water survey off western Mexico: two species of Paraphronima and eight species of Vibilia. This represents about 40% of all known species of these two genera world-wide. A total of 419 males and 607 females were obtained in 39 samples from localities in the Gulf of California (33) and off southwestern Mexico (6). Vibilia armata was by far the most frequently (32 localities) and most abundantly (687 specimens, 67% of the total) collected species, followed by V. longicarpus (231 specimens in nine localities) and P. crassipes (35 specimens in 9 localities). Co-ocurrence of species of Vibilioidea in our samples was very low, with maxima of seven and five species collected in the same sample, once each. Considering previous records, a total of 16 species of Vibilioidea (almost 70% of all known species) have now been reported from western Mexico: two species of Paraphronima and 14 species of Vibilia, including V. australis occasionally reported in the area as its junior synonym, V. wolterecki.
References
Barkhatov, V.A., Vinogradov, M.E. & Vinogradov, G.M. (1999) Boundaries of the areals of hyperiid amphipods in the epipelagic part of the Southern Subtropical Frontal Zone of the Pacific Ocean. Oceanology, 39 (6), 805‒812.
Behning, A. (1913) Die Vibiliden (Amphipoda, Hyperiidea) der Deutschen Sudpolar-, Schwedischen Südpolar-, ‘Albatross’- und ‘Michael Sars’- Expeditionen. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 41 (12), 529‒534.
Behning. A & Woltereck, R. (1912) Achte Mitteilung über die Hyperiden der “Valdivia” Expedition, insbesondere über die Vibiliden. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 41 (1), 1‒11.
Bovallius, C. (1885) On some forgotten genera among the amphipodous Crustacea. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskaps-Akademiens Handlingar, 10 (14), 1‒17.
Bovallius, C. (1887) Systematical list of the Amphipoda Hyperiidea. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar, 11 (16), 1‒50. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.5127
Brusca, G.J. (1967) The ecology of pelagic Amphipoda, I. species accounts, vertical zonation and migration of Amphipoda from the waters off southern California. Pacific Science, 21 (3), 382‒393.
Brusca, G.J. (1981) Annotated keys to the Hyperiidea (Crustacea: Amphipoda) of North American coastal waters. Allan Hancock Foundation Technical Reports, 5, 1‒76. https://doi.org/10.2307/1547968
Brusca, R.C. & Hendrickx, M.E. (2005) Cap. 12. Crustacea 4. Lophogastrida, Mysida, Amphipoda Tanaidacea & Cumacea. In: Hendrickx, M.E., Brusca, R.C. & Findley, L.T. (Eds.), A Distributional Checklist of the Macrofauna of the Gulf of California, Mexico. Part I. Invertebrates. [Listado y Distribución de la Macrofauna del Golfo de California, México, Parte I. Invertebrados]. Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum, Tucson, Arizona, pp. 139‒154.
Bulycheva, A.I. (1955) Hyperiids (Amphipoda: Hyperiidea) of the north-west Pacific Ocean. Akademiya Nauk SSSR, Doklady, 102 (5), 1047–1050. [in Russian]
Cartes, J.E. (1993) Diets of two deep-sea decapods: Nematocarcinus exilis (Caridea: Nematocarcinidae) and Munida tenuimana (Anomura: Galatheidae) on the western Mediterranean slope. Ophelia, 37 (3), 213‒229. https://doi.org/10.1080/00785326.1993.10429919
Chevreux, E. (1892) Vibilia erratica, amphipode pélagique nouveau, du littoral des Alpes-Maritimes. Bulletin de la Société Zoologique de France, 17, 32‒35. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.15968
Chevreux, E. (1900) Amphipodes provenant des campagnes de «l’Hirondelle» 1885‒1888. Résultats des campagnes scientifiques accomplies sur son Yacht, par le Prince Albert Ier Prince Souverain de Monaco, 16, 1‒195.
Claus, C. (1879) Der Organismus der Phronimiden. Arbeiten aus dem Zoologischen Institute der Universität Wien und der Zoologischen Station in Triest, 2, 59‒146, pls. 1‒8.
Espinosa-Leal, L.L. & Lavaniegos, B.E. (2016) Seasonal variability of pelagic amphipods off Baja California during la Niña 2011 and comparison with a “neutral year” (2005). California Cooperative Oceanic Fisheries Investigations Report, 57, 132–150
García-Madrigal, M.S. (2007) Annotated checklist of the amphipods (Peracarida: Amphipoda) from the tropical eastern Pacific. Contributions to the study of East Pacific Crustaceans, 4 (2), 63‒195.
Gasca, R. (2009) Hyperiid Amphipods. In: Wehrtman, I.S. & Cortés, J. (Eds.), Marine biodiversity of Costa Rica. Central America. Monographiae Biologicae 86. Springer Verlag Publishing, New York, pp. 275‒282. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8278-8_25
Gasca, R. & Browne, W.E. (2018) Symbiotic associations of crustaceans and a pycnogonid with gelatinous zooplankton in the Gulf of California. Marine Biodiversity, 48 (4), 1767‒1775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-017-0668-5
Gasca, R. & Haddock, S.H.D. (2004) Associations between gelatinous zooplankton and hyperiid amphipods (Crustacea: Peracarida) in the Gulf of California. Hydrobiologia, 530/531 (Developments in Hydrobiology), 529‒535. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-2762-8_60
Gasca, R. & Haddock, S.H.D. (2016) The rare deep-living hyperiid amphipod Megalanceoloides remipes (Barnard, 1932): complementary description and symbiosis. Zootaxa, 4178 (1), 138–144. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4178.1.7
Gasca, R & Hendrickx. M.E. (2020) Species of Scina Prestandrea, 1833 (Amphipoda, Hyperiidea, Scinidae) from western Mexico with the description of a new species from the Gulf of California. Zootaxa, 4803 (2), 329–344. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4803.2.5
Gasca, R. & Hendrickx, M.E. (2021a) Hyperiids (Amphipoda, Hyperiidea) collected during the TALUD cruises in western Mexico. 2. Family Eupronoidae. Zootaxa, 4948 (3), 419‒430. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4948.3.6
Gasca, R. & Hendrickx, M.E. (2021b) Pelagic amphipods (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Hyperiidea) in western Mexico. 3. Family Lestrigonidae. Zootaxa, 4974 (1), 169‒187. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4974.1.8
Gasca, R. & Hendrickx, M.E. (2021c) Pelagic amphipods (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Hyperiidea) in western Mexico. 4. Superfamily Lanceoloidea Bovallius, 1887: families Chuneolidae Woltereck, 1909 and Lanceolidae Bovallius, 1887. Geomare Zoologica, 3 (1), 3‒13.
Gasca, R., Suárez-Morales, E. & Hendrickx, M.E. (2021) Pelagic amphipods (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Hyperiidea) in western Mexico. 5. Family Amphithyridae, with the description of a new species of Amphithyropsis Zeidler. Zootaxa, 5039 (4), 479–494. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5039.4.2
Gasca, R., Suárez-Morales, E. & Haddock, S.H.D. (2007) Symbiotic associations between crustaceans and gelatinous Zooplankton in deep and surface waters off California. Marine Biology, Berlin, 151, 233‒242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-006-0478-y
Gasca, R., Suárez-Morales, E. & Franco-Gordo, C. (2010) New records of hyperiids (Amphipoda, Hyperiidea) from surface waters of the central Mexican Pacific. Crustaceana, 83 (8), 927‒940. https://doi.org/10.1163/001121610X504298
Gasca, R., Franco-Gordo, C., Godínez-Domínguez, E. & Suárez-Morales, E. (2012) Hyperiid amphipod community in the Eastern Tropical Pacific before, during, and after El Niño 1997−1998. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 455, 123‒139. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps09571
Guérin-Méneville, F.E. (1836) Planches des Animaux Invertébrés (Crustacés). Iconographie du Règne Animal de G. Cuvier. Vol. 2. Bailliere, Paris and London, 35 pls.
Guillén Pozo, W. (2007) Composición y distribución de Amphipoda (Hyperiidae) en aguas ecuatorianas durante el evento de La Niña 2005. Graduate Thesis, Facultad de Ciencias Naturales, University of Guayaquil, Guayaquil, 198 pp.
Hendrickx, M.E. (2012) Operaciones oceanográficas en aguas profundas: los retos del pasado, del presente y del proyecto TALUD en el Pacífico mexicano (1989‒2009). In: Zamorano, P., Hendrickx, M.E. & Caso, M. (Eds.), Biodiversidad y comunidades del talud continental del Pacífico mexicano. Secretaría del Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (SEMARNAT), Instituto Nacional de Ecología (INE), México, D.F., pp. 23‒104.
Hendrickx, M.E. & Serrano, D. (2010) Impacto de la zona de mínimo de oxígeno sobre los corredores pesqueros en el Pacífico mexicano. Interciencia, 35 (1), 12‒18.
Horton, T., Lowry, J., De Broyer, C., Bellan-Santini, D., Coleman, C.O., Corbari, L., Costello, M.J., Daneliya, M., Dauvin, J.-C., Fišer, C., Gasca, R., Grabowski, M., Guerra-García, J.M., Hendrycks, E., Hughes, L., Jaume, D., Jazdzewski, K., Kim, Y.-H., King, R., Krapp-Schickel, T., LeCroy, S., Lörz, A.-N., Mamos, T., Senna, A.R., Serejo, C., Sket, B., Souza-Filho, J.F., Tandberg, A.H., Thomas, J.D., Thurston, M., Vader, W., Väinölä, R., Vonk, R., White, K. & Zeidler, W. (2020) World Amphipoda Database. Lanceola Say, 1818. World Register of Marine Species. Available from: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=101801 (accessed 31 October 2020)
Hurley, D.E. (1956) Bathypelagic and other Hyperiidea from California waters. Allan Hancock Foundation Publications, Occasional Paper, 18, 1‒25.
Lavaniegos, B.E. (2014) Pelagic amphipod assemblage associated with subarctic water off the West Coast of the Baja California Peninsula. Journal of Marine Systems, 132, 1‒12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2013.12.012
Lavaniegos, B.E. (2017) Changes in composition of summer hyperiid amphipods from a subtropical region of the California Current during 2002-2008. Journal of Marine Systems, 165, 13‒26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2016.09.001
Lavaniegos, B.E. (2020) Hyperiid amphipods from the Gulf of Ulloa and offshore region, Baja California: The possible role of gelatinous zooplankton as a transport vector into the coastal shelf waters. PLoS ONE, 15 (11), e0233071 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone. 0233071
Lavaniegos, B.E. & Hereu, C. (2009) Seasonal variation in hyperiid amphipod abundance and diversity and influence of mesoscale structures off Baja California. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 394, 137−152. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps08285
Lavaniegos, B.E. & Ohman, M.D. (1999) Hyperiid amphipods as indicators of climate change in the California Current. In: Schram, F.R. & von Vaupel Klein, J.C. (Eds.), Crustaceans and the biodiversity crisis. Proceedings of the Fourth International Crustacean Congress, Amsterdam, 1998, 489‒509.
Ohman, M.D. & Lavaniegos, B.E. (2002) Comparative zooplankton sampling efficiency of a ring net and Bongo net with comments on pooling of subsamples. CalCOFI Reports, 42, 162–173.
Padovani, L.N., Viñas, M.D., Sánchez, F. & Mianzan, H. (2012) Amphipod-supported food web: Themisto gaudichaudii, a key food resource for fishes in the southern Patagonian Shelf. Journal of Sea Research, 67 (1), 85‒90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2011.10.007
Papiol, V., Hendrickx, M.E. & Serrano, D. (2016) Effects of latitudinal changes in the oxygen minimum zone of the northeast Pacific on the distribution of bathyal benthic decapod crustaceans. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 137, 113‒130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2016.04.023
Provencher, J.F., Gaston, A.J., O’Hara, P.D. & Gilchrist, H.G. (2012) Seabird diet indicates changing Arctic marine communities in eastern Canada. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 454, 171‒182. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps09299
Shih, C.-T. & Hendrycks, E.A. (2003) A new species and new records of the genus Vibilia Milne Edwards, 1830 (Amphipoda: Hyperiidea: Vibiliidae) occurring in the eastern Pacific Ocean. Journal of Natural History, 37, 253‒296. https://doi.org/10.1080/713834685
Shoemaker, C.R. (1925) The Amphipoda collected by the United States Fisheries Steamer “Albatross” in 1911, chiefly in the Gulf of California. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History, 52, 21‒61.
Siegel-Causey, D. (1982) Factors determining the distribution of hyperiid Amphipoda in the Gulf of California. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, 535 pp.
Stebbing, T.R.R. (1888) Report on the Amphipoda collected by H.M.S. Challenger during the years 1873‒1876. Report on the Scientific Results of the Voyage of H.M.S. Challenger during the years 1873–76, Zoology, 29 (part 67), i‒xxiv + 1‒1737, pls. 1‒210.
Stenvers, V.I., Gonzalez, B.C., Goetz, F.E., Hemmi, J.M., Jessop, A.-L., Lin, C., Hoving, H.-J.T. & Osborn, K.J. (2021) Extraordinary eyes reveal hidden diversity within the holopelagic genus Paraphronima (Amphipoda: Hyperiidea). Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 177, 103610 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2021.103610
Stewart, D.A. (1913) A report on the extra-Antarctic Amphipoda Hyperiidea collected by the “Discovery”. Annals and Magazine of Natural History, Series 8, 12 (69), 245‒264. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222931308693395
Vacchi, M. & La Mesa, M. (1995) The diet of the Antarctic fish Trematomus newnesi Boulenger, 1902 (Nototheniidae) from Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea. Antarctic Science, 7 (1), 37‒38. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954102095000071
Valencia, B. & Giraldo, A. (2009) Hipéridos (Crustacea: Amphipoda) en el sector norte del Pacífico oriental tropical colombiano. Latin American Journal of Aquatic Research, 37, 265‒273. https://doi.org/10.3856/vol37-issue2-fulltext-14
Valencia, B. & Giraldo, A. (2012) Structure of hyperiid amphipod assemblages on Isla Gorgona, eastern tropical Pacific off Colombia. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 92 (7), 1489‒1499. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315411001780
Valencia, B, Lavaniegos, B., Giraldo, A. & Rodriguéz-Rubio, E. (2013) Temporal and spatial variation of hyperiid amphipod assemblages in response to hydrographic processes in the Panama Bight, eastern tropical Pacific. Deep-Sea Reseach, I (73), 46–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2012.11.009
Vinogradov, G.M. (1990) Rare and new Hyperiidea for the Indian Ocean (Amphipoda Hyperiidea, Crustacea). Transactions of the P.P. Shirshov Institute of Oceanology, 124, 105–111. [in Russian]
Vinogradov, M.E., Volkov, A.F. & Semenova, T.N. (1996) Hyperiid amphipods (Amphipoda, Hyperiidea) of the world oceans. Smithsonian Institution Libraries, Siegel-Causey, D., Scientific Editor, Washington D.C. and Oxonian Press Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 632 pp. [English translation of the 1982 Russian original]
Zeidler, W. (1995) Paraphronima crassipes Claus, 1879 (Crustacea, Amphipoda): proposed conservation of the specific name. Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature, 52 (4), 310‒311. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.6805
Zeidler, W. (2003) A review of the Hyperiidean amphipod superfamily Vibilioidea Bowman & Gruner, 1973 (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Hyperiidea). Zootaxa, 280, 1–104. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.280.1.1