Abstract
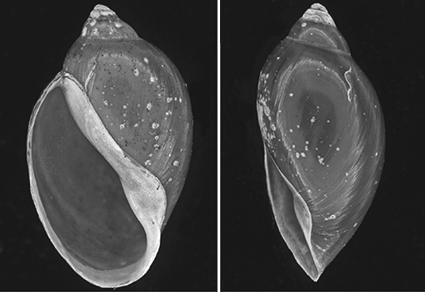
This is the first comparative study on alien and native Physidae (Gastropoda: Heterobranchia) from Western and Central Europe. Morphology, ecological features and distribution are presented for each physid species. We analysed taxonomical features of physid snails from Europe in great detail. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) methods were used to elucidate the external morphology of the shells of physid gastropods that occur in Western and Central Europe. On comparison we found significant differences in the external morphology among the species. Morphological analyses facilitate the recognition of variations of physid shells. An interspecific similarities were noted within Physidae while interspecific differences were identified in the morphology of apex and spires. The lowest intraspecific variability in shells was noted between particular individuals of P. fontinalis and A. hypnorum. The most characteristic features and differences of representatives of Physidae are presented and discussed. This is especially important for the identification of Physa gyrina and the worldwide invasive species Physa acuta which resemble each other in shape and are difficult to distinguish. We also present a new identification key for physid species, including the results of ecological assessment and discuss current distribution of these species in Europe.
References
Adam, W. (1960) Mollusques. I. Mollusques terrestres et dulcicoles. Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de Belgique, Brussels, 402 pp.
Anderson, R. (1996) Physa gyrina (Say), a North American freshwater gastropod new to Ireland, with a key to the British Isles Physidae. The Irish Naturalists' Journal, 25, 248–253.
Anderson, R. (1997) An annotated list of the land and freshwater Mollusca of Northern Ireland. Environment and Heritage Service Research & Development Series, 1997. [unknown pagination]
Anderson, R. (2003) Physella (Costatella) acuta (Draparnaud) in Britain and Ireland, its taxonomy, origins and relationship to other introduced Physidae. Journal of Conchology, 38, 7–21.
Appleton, C.C. (2003) Alien and invasive fresh water Gastropoda in South Africa. African Journal of Aquatic Science, 28, 69–81. https://doi.org/10.2989/16085914.2003.9626602
Aziz, S., Altaf, J., Ramzan, A., Ahmed, Z., Qamar, S.U.R., Awan, S.A., Khalil, S., Jehangir, K., Khalid, R., Ansari, B., Sultana, T., Sultana, S., Alsamadany, H., Alshamrani, R. & Awan, F.S. (2021) Characterization of the species of genus Physa on the basis of typological species concept from Central Punjab. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 83, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.246934
Backhuys, W. (1975) Land and freshwater molluscs of the Azores. Backhuys & Meesters, Amsterdam, 475 pp.
Balashov, I.A., Son, M.O., Coada, V. & Welter-Schultes, F. (2013) An updated annotated checklist of the molluscs of the Republic of Moldova. Folia Malacologica, 21, 175–181. https://doi.org/10.12657/folmal.021.021
Bank, R. (2006) Towards a catalogue and bibliography of the freshwater Mollusca of Greece. Heldia, 6, 51–86.
Beran, L. (2002) Vodní měkkýši národní přírodní rezervace Novozámecký rybník. Příroda, Praha, 20, 137–140.
Beran, L. (2004) Which Physella (Mollusca: Gastropoda) lives in the Czech Republic? Acta Societatis Zoologicae Bohemicae, 68, 241–243.
Beriozkina, G.V. & Starobogatov, Y.I. (1988) Reproductive ecology and egg clusters of freshwater Pulmonata. Trudy zoologichieskii Institute, 174, 1–306.
Bódis, E., Borza, P., Potyó, I., Puky, M., Weiperth, A. & Guti, G. (2012) Invasive mollusc, crustacean, fish and reptile species along the Hungarian stretch of the river Danube and some connected waters. Acta Zoologica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae, 58, 29–45.
Bolton, M.S. & Beaudoin, A.B. (2017) Recognizing macrofossils: A pictorial guide to some common seeds and shells from alluvial deposits in southern Alberta. After the flood: Investigations of impacts to archaeological resources from the 2013 flood in southern Alberta. Archaeological Survey of Alberta Occasional Paper, 37, 156–168.
Bondesen, P.A. (1950) Comparative Morphological-biological Analysis of the Egg Capsules of Freshwater Pulmonate Gastropods. Hygrophila. Basommatophora, Pulmonata. Natura Jutlandica, 3, 1–209.
Bourguignat, J.-R. (1860) Malacologie terrestre et fluviatile de la Bretagne. J.-B. Baillière, Paris, pp. I–XXIV + 25–178 + 1 (errata), pls 1–2. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.10634
Bousset, L., Henry, P.Y., Sourrouille, P. & Jarne, P. (2004) Population biology of the invasive freshwater snail Physa acuta approached through genetic markers, ecological characterization and demography. Mollecular Ecology, 13, 2023–2036. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2004.02200.x
Bousset, L., Pointier, J.P., David, P. & Jarne, P. (2014) Neither variation loss, nor change in selfing rate is associated with the worldwide invasion of Physa acuta from its native North America. Biological Invasions, 16, 1769–1783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-013-0626-5
Burch, J.B. (1989) North American freshwater snails. Malacological Publication, Hamburg, Michigan, pp. 1–365.
Byrne, A., Moorkens, E.A., Anderson, R., Killeen, I.J. & Regan, E.C. (2009) Ireland Red List No. 2. Non-Marine Molluscs. National Parks and Wildlife Service, Department of the Environment, Heritage and Local Government, Dublin, 49 pp.
CABI Data Mining (2021) Available from: http://www.cabi.org (accessed 29 October 2021)
Cieplok, A. & Spyra, A. (2020) The roles of spatial and environmental variables in the appearance of a globally invasive Physa acuta in water bodies created due to human activity. Science of The Total Environment, 744, 140928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140928
Cossignani, T. & Cossignani, V. (1995) Atlante delle conchiglie terrestri e dulciacquicole italiane. [Published for] Mostra mondiale malacologia by L'Informatore Piceno, Ancona, 208 pp.
Da Costa, E.M. (1778) Historia naturalis testaceorum Britanniae, or, the British Conchology; containing the descriptions and other particulars of natural history of the shells of Great Britain and Ireland; illustrated with figures. London: Millan, White, Elmsley & Robson, printed for the author, XII + 254 + VII pp
Den Hartog, C. (1963a) The distribution of the snail Aplexa hypnorum in Zuid-Beveland in relation to soil and salinity. Basteria, 27, 8–17.
Den Hartog, C. (1963b) The Aplexa hypnorum coenosis in Zuid-Beveland. Basteria, 27, 49–63.
Den Hartog, C. & De Wolf, L. (1962) The life cycle of the water snail Aplexa hypnorum. Basteria, 26, 61–72.
Devi, P., Islam, S. & Das, M. (2006) Prevalence of freshwater snails in Assam. Journal of Veterinary Parasitology, 20, 81–84.
DeWitt, R.M. (1954a) Reproduction, embryonic development, and growth in the pond snail, Physa gyrina say. Transactions of the American Microscopical Society, 73, 124–137. https://doi.org/10.2307/3223750
DeWitt, R.M. (1954b) Reproductive capacity in a pulmonate snail (Physa gyrina Say). The American Naturalist, 88, 159–164. https://doi.org/10.1086/281826
DeWitt, T.J., Robinson, B.W. & Wilson, D.S. (2000) Functional diversity among predators of a freshwater snail imposes an adaptive trade-off for shell morphology. Evolutionary Ecology Research, 2, 129–148.
Dillon, R.T. Jr. (2000) The Ecology of Freshwater Molluscs. Cambridge University Press, New York, New York, 509 pp. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511542008
Dillon, R.T. Jr. & Wethington, A.R. (2004) No-choice mating experiments among six nominal taxa of the subgenus Physella (Basommatophora: Physidae). Heldia, 6, 69–78.
Dillon, R.T., Wethington, A.R., Rhett, J.M. & Smith, T.P. (2002) Populations of the European freshwater pulmonate Physa acuta are not reproductively isolated from American Physa heterostropha or Physa integra. Invertebrate Biology, 12, 226–234. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7410.2002.tb00062.x
Draparnaud, J.P.R. (1805) Histoire naturelle des mollusques terrestres et fluviatiles de la France. Levrault & Schoell, Paris, 2 (Avertissement a sa Majesté l'Impératrice) + 2 (Rapport) + VII (Préface), 164 pp., 13 pls, 1 pp. (errata). [< 22 September] https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.12856
Duncan, C.J. (1959) The life cycle and ecology of the freshwater snail Physa fontinalis (L). Journal of Animal Ecology, 28, 97–117. https://doi.org/10.2307/2017
Dutkiewicz, J. (1959) Interesujące stanowisko ślimaka Physa acuta Drap. w Kombinacie Nowa Huta. Przegląd Zoologiczny, 3, 185–187.
Feliksiak, S. (1939) Physa acuta Draparnaud in den Fabrikteichen von Łódź und ihre allgemeine Verbreitung. Fragmenta Faunistica Musei Zoologici Polonici, 4, 243–258. https://doi.org/10.3161/15053970FF1939.4.15.243
Früh, D., Haase, P. & Stoll, S. (2017) Temperature drives asymmetric competition between alien and indigenous freshwater snail species, Physa acuta and Physa fontinalis. Aquatic Sciences, 79, 187–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-016-0489-9
Frömming, E. (1956) Biologie der mitteleuropäischen Süßwasserschnecken. Dunkler & Humbolt, Berlin, 313 pp.
Glöer, P. (2015) Süsswassermollusken. 14. Auflage. Deutscher Jugendbund für Naturbeobachtung, Hamburg, 135 pp.
Glöer, P. (2002) Die Süsswassergastropoden Nord- und Mitteleuropas, Bestimmungschlüssel, Lebenweise, Verbreitung, Die Tierwelt Deutschlands Begründet 1925 von Friedrich Dahl. 73. ConchBooks Publishing, Hackenheim BRD, 327 pp.
Glöer, P. & Diercking, R. (2010) Atlas der Süßwassermollusken Hamburgs. Rote Liste, Verbreitung, Ökologie. Umweltbehörde, Hamburg, 182 pp.
Glöer, P. (2019) The freshwater gastropods of the West-Palaearctis. Vol. 1. Fresh- and brakish waters except spring and subterranean snails. Identification key, anatomy, ecology, distribution. Published by the author, Biodiversity Research Lab, Hetlingen, 399 pp.
Gould, A.A. (1855) New species of land and fresh-water shells from Western (N.) America. Proceedings of the Boston Society of Natural History, 5, 127–130
Gustafson, K.D., Kensinger, B.J., Bolek, M.G. & Luttbeg, B. (2014) Distinct snail (Physa) morphotypes from different habitats converge in shell shape and size under common garden conditions. Evolutionary Ecology Research, 16, 77–89.
Haldeman, S.S. (1841) A monograph of the Limniades or freshwater univalve shells of North America. Vol. 3. J. Dobson, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 16 pp. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.11226
Harman, W.N. (2000) Diminishing species richness of mollusks in Oneida Lake, New York State, USA. Nautilus, 114, 120–126.
Horsák, M., Juřičková, L., Beran, L., Čejka, T. & Dvořák L. (2010) Komentovaný seznam měkkýšů zjištěných ve volné přírodě České a Slovenské republiky. [Annotated list of mollusc species recorded outdoors in the Czech and Slovak Republics]. Malacologica Bohemoslovaca, 1, 1–37. [http://www.animalbase.uni-goettingen.de (25 June 2021), http://www.faunaeur.org (25 June 2021)] https://doi.org/10.5817/MaB2010-9-s1-v2
Kerney, M.P. (1999) Atlas of land and freshwater molluscs of Britain and Ireland. Harley, Brill, Colchester, 264 pp.
Khokhutkin, I.M. & Vinarski, M.V. (2013) Molluscs of the Urals and the adjacent areas. The families Acroloxidae, Physidae, Planorbidae (Gastropoda, Pulmonata, Lymnaeiformes). Fasc. 2. Goshchitskiy Publishers, Yekaterinburg, 184 pp.
Laenko, T.M. (2012) The freshwater malacofauna of Byelorussia. Belaruskaya navuka, Minsk, 128 pp.
Lam, P.K.S. & Calow, P. (1989) Intraspecific life-history variation in Lymnaea peregra (Gastropoda: Pulmonata). I. Field study. The Journal of Animal Ecology, 58, 571–588. https://doi.org/10.2307/4849
Linnaeus, C. (1758) Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Vol. 1. Editio Decima, Reformata [10th Revised Edition]. Laurentius Salvius, Holmiae, 824 pp. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.542
Lisický, M.J. (1991) Mollusca Slovenska. VEDA, Bratislava, 44 pp.
Lydeard, C., Campbell, D. & Golz, M. (2016) Physa acuta Draparnaud, 1805 should be treated as a native of North America, not Europe. Malacologia, 59, 347–350. https://doi.org/10.4002/040.059.0213
Maansi R.J. & Wats, M. (2018) First Report of Family Physidae (Gastropoda) with Physa acuta as its Representative from Freshwaters of Chandigarh (U.T.), India. Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: C, Biological Science, 18 (1), 42–50.
Massot P. (1845) Description d'une espéce nouvelle de Physe. Bulletin de la Société agricole, scientifique & littéraire des Pyrénées, 6, 1–236.
Moroz, M., Baitchorov, V. & Giginiak, J.G. (2017) Fauna of aquatic invertebrate water currents of national park Beloviezskaja Pustchia». Редакционная Коллегия, 3, 1–69.
Neves, R.J., Bogan, A.E., Williams, J.D., Ahlstedt, S.A. & Hartfield, P.W. (1997) Status of aquatic mollusks in the southeastern United States: a downward spiral of diversity. In: Benz, G.W. & Collins, D.E. (Eds.), Aquatic fauna in peril: the southeastern perspective. Southeastern Aquatic Research Institute, Lenz Design and Communications, Decatur, Georgia, pp. 43–85.
Newman, R.M., Kerfoot, W.C. & Hanscom, Z. (1996) Watercress allelochemical defends high-nitrogen foliage against consumption: effects on freshwater invertebrate herbivores. Ecology, 77, 2312–2323. https://doi.org/10.2307/2265733
Ng, T.H., Limpanont, Y., Chusongsang, Y., Chusongsang, P. & Panha, S. (2018) Correcting misidentifications and first confirmation of the globally-invasive Physa acuta Draparnaud, 1805 (Gastropoda: Physidae) in Thailand and Laos. BioInvasions Records, 7, 15–19. https://doi.org/10.3391/bir.2018.7.1.03
Økland, J. (1990) Lakes and snails. Universal Book Services, Oegstgeest, 516 pp.
Paraense, W.L. & Pointier, J.P. (2003) Physa acuta Draparnaud, 1805 (Gastropoda: Physidae): a study of topotypic specimens. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, 98, 513–517. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0074-02762003000400016
Paul, P. & Aditya, G. (2021) Invasion of the freshwater snail Physella acuta (Draparnaud, 1805) in selected ponds of North Dinajpur, India. Journal of Environmental Biology, 42, 577–581. https://doi.org/10.22438/jeb/42/3/MRN-1628
Pfeiffer, L. (1839) Bericht über die Ergebnisse meiner Reise nach Cuba im Winter 1838–1839. Archiv für Naturgeschichte, 1, 346–358.
Pfennig, D.W., Wund, M.A., Snell-Rood, E.C., Cruickshank, T., Schlichting, C.D. & Moczek, A.P. (2010) Phenotypic plasticity's impacts on diversification and speciation. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 25, 459–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2010.05.006
Piechocki, A. (1975) Beobachtungen über den Bau von Laichen und die Fortpflanzung von Süßwasserschnecken aus den Familien: Physidae, Lymnaeidae und Planorbidae. Fragmenta Faunistica 20, 223–232. https://doi.org/10.3161/00159301FF1975.20.14.223
Piechocki, A. (1979) Mięczaki (Mollusca). Ślimaki (Gastropoda). In: Fauna słodkowodna Polski 7. PWN, Warszawa, Poznań, pp. 1–187.
Piechocki, A. & Wawrzyniak-Wydrowska, B. (2016) Guide to freshwater and marine Mollusca of Poland. Bogucki Wydawnictwo Naukowe, Poznań, 280 pp.
Pip, E. (2000) The decline of freshwater molluscs in southern Manitoba. Canadian Field-Naturalist, 114, 555–560.
Pip, E. & Franck, J.P.C. (2008) Molecular phylogenetics of central Canadian Physidae (Pulmonata: Basommatophora). Canadian Journal of Zoology, 86, 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1139/Z07-112
Raković, M J., Raković, M.B., Petrović, A.M., Popović, N.Z., Duknić, J.A., Naunovic, Z.Z. & Paunović, M.M. (2016) Haplotype variation in the Physa acuta group (Basommatophora): genetic diversity and distribution in Serbia. Mediterranean Marine Science, 17, 292–301. https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.1453
Reavell, P. (1980) A study of the diets of some British freshwater gastropods. Journal of Conchology, 30, 253–271.
Robertson, R. (1971) Scanning electron microscopy of planktonic larval marine gastropod shells. The Veliger, 14, 1–12.
Rondelaud, D., Vignoles, P. & Dreyfuss, G. (2016) Aplexa hypnorum (Gastropoda: Physidae) exerts competition on two lymnaeid species in periodically dried ditches. Annales de Limnologie-International Journal of Limnology, 52, 379–386. https://doi.org/10.1051/limn/2016022
Saha, C., Pramanik, S., Chakraborty, J., Parveen, S. & Aditya, G. (2016) Abundance and body size of the invasive snail Physa acuta occurring in Burdwan, West Bengal, India. Journal of Entomology and Zoology Studies, 4, 490–497.
Sankurathri, C.S. & Holmes, J.C. (1976) Effects of thermal effluents on the population dynamics of Physa gyrina Say (Mollusca: Gastropoda) at Lake Wabamun, Alberta. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 54, 582–590. https://doi.org/10.1139/z76-068
Say, T. (1817) Conchology. In: Nicholson, W., American edition of the British Encyclopedia, or, dictionary of arts and sciences comprising an accurate and popular view of the present improved state of human knowledge, First Edition, 3, pp. 1–4.
Say, T. (1821) Description of univalve shells of the United States. Journal of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, 2, 149–179.
Serafiński, W., Rembecka, I. & Strzelec, M. (1989) Biometrics and life cycle of Physa acuta Draparnaud, 1805 (Gastropoda: Basommatophora: Physidae) under human impact. Folia Malacologica, 3, 139–147. https://doi.org/10.12657/folmal.003.011
Son, M.O. (2007) Invasive species of Mollusca in fresh- and brackish waterbodies of the northern part of the Black Sea region. Druk, Odessa, 132 pp. [in Russian]
Spyra, A. (2010) Environmental factors influencing the occurrence of freshwater snails in woodland water bodies. Biologia, 65, 697–703. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-010-0063-1
Spyra, A. (2017) Acidic, neutral and alkaline forest ponds as a landscape element affecting the biodiversity of freshwater snails. The Science of Nature, 104, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-017-1495-z
Spyra, A., Cieplok, A., Strzelec, M. & Babczyńska, A. (2019) Freshwater alien species Physella acuta (Draparnaud, 1805)-A possible model for bioaccumulation of heavy metals. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 185, 109703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109703
Starobogatov, Y.I., Prozorova, L.A., Zatravkin, M.N. (1989) Species composition of the family Physidae (Gastropoda Pulmonata Lymnaeiformes) of Siberia and Far East of the USSR (with notes on European physids). Byulleten' Moskovskogo Obshchestva Ispytateley Pripody, otdel biologicheskiy, 94 (1), 62–78. [in Russian]
Starobogatov, Y.I., Prozorova, L.A., Bogatov, V.V. & Saenko, E.M. (2004) Molluscs. Key to freshwater invertebrates of Russia and adjacent lands, 6, 9–492.
Sitnikova, T.Y., Sysoev, A.V. & Kijashko, P.V. (2014) Freshwater gastropods described by Ya. I. Starobogatov, with additional data on the species: family Physidae. Zoologicheskie Issledovania, 16, 39–54.
Stewart, T.W. (2006) The freshwater gastropods of Iowa (1821–1998): species composition, geographic distributions, 76. and conservation concerns. American Malacological Bulletin, 21, 59–75.
Taylor, D.W. (2003) Introduction to Physidae (Gastropoda: Hygrophila). Biology, classification, morphology. Revista de Biología Tropical, 51, 1–299.
Ter Braak, C.J. & Smilauer, P. (2002) CANOCO reference manual and CanoDraw for Windows user's guide: software for canonical community ordination. Version 4.5. Available from: http://www.canoco.com (accessed 4 July 2022)
Thorson, J.L., Smithson, M., Beck, D., Sadler-Riggleman, I., Nilsson, E., Dybdahl, M. & Skinner, M.K. (2017) Epigenetics and adaptive phenotypic variation between habitats in an asexual snail. Scientific Reports, 7, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14673-6
Turner, A.M. & Montgomery, S.L. (2009) Hydroperiod, predators and the distribution of physid snails across the freshwater habitat gradient. Freshwater Biology, 54, 1189–1201. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2009.02168.x
Turner, H., Kuiper, J.G.J., Thew, N., Bernasconi, R., Ruetschi, J., Wuthrich, M. & Gosteli, M. (1998) Atlas der Mollusken der Schweiz und Liechtensteins. Fauna Helvetica, 2, 1–527.
Van Damme, D., Ghamizi, M., Seddon, M., Kristensen, T.K., Stensgaard, A.S., Budha, P.B. & Dutta, J. (2012) Haitia acuta. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. https://doi.org/10. 2305/IUCN.UK.2012.RLTS.T155538 A732330.en
Van den Brink, P.J., Van Den Brink, N.W. & Ter Braak, C.J. (2003) Multivariate analysis of ecotoxicological data using ordination: demonstrations of utility on the basis of various examples. Australasian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 9, 141–156.
Vidal Abarca, C. & Suarez, M.L. (1986) Lista faunistica y bibliografica de los moluscos (Gastropoda & Bivalvia) de las aguas continentales de la Peninsula Iberica e islas Balares. Listas de la flora y fauna de las aguas continentales de la Península Ibérica. Associación Española de Limnologia, Madrit, pp. 1–193.
Vinarski, M.V. (2017) The history of an invasion: phases of the explosive spread of the physid snail Physella acuta through Europe, Transcaucasia and Central Asia. Biological Invasions, 19, 1273–1288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-016-1339-3
Vinarski, M.V., Grebennikov, M E. & Shishkoedova, O.S. (2013) Past and present distribution of Myxas glutinosa (OF Müller, 1774) in the waterbodies of the Urals and Siberia. Journal of Limnology, 72, 336–342. https://doi.org/10.4081/jlimnol.2013.e27
Vinarski, M.V., Andreev, N.I., Andreeva, S.I., Kazantsev, I.E., Karimov, A.V. & Lazutkina, E.A. (2015) Alien mollusk species in the aquatic ecosystems of Western Siberia: a review. Russian Journal of Biological Invasions, 6, 137–147. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075111715030078
Welter-Schultes, F.W. (2012) European non-marine molluscs, a guide for species identification. Planet Poster Editions. Bestimmungsbuch für europäische Land-und Süsswassermollusken, Planet Poster Editions, Göttingen, 679, 1–78.
Wethington, A.R. (2004) Family Physidae. A supplement to the workbook accompanying the FMCS Freshwater Identification Workshop. University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, Alabama, 24 pp.
Wethington, A.R. & Guralnik R. (2004) Are populations of physids from different hot-springs distinctive lineages? American Malacological Bulletin, 19, 132–144.
Wethington, A.R. & Lydeard, C. (2007) A molecular phylogeny of Physidae (Gastropoda: Basommatophora) based on mitochondrial DNA sequences. Journal of Molluscan Studies, 73, 241–257. https://doi.org/10.1093/mollus/eym021
Wethington, A.R., Wise, J. & Dillon, R.T. Jr. (2009) Genetic and morphological characterization of the Physidae of South Carolina (Gastropoda: Pulmonata: Basommatophora), with description of a new species. Nautilus, 123, 1–282.
Winterbourn, M.J. (1973) A guide to the freshwater Mollusca of New Zealand. Tuatara, 20, 141–159.
Yildirim, M.Z., Kebapc, U., Gümüs, B.A. & Koca, S.V. (2006) The basommatophoran pulmonate species (Mollusca: Gastropoda) of Turkey. Turkish Journal of Zoology, 30, 445–458.