Abstract
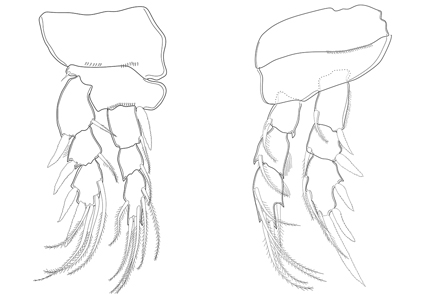
The siphonostomatoid copepod genus Scottocheres was established by Giesbrecht in 1897 and now includes nine species. Consequently, these new species introduced new characteristics that must be considered to define the genus. This study provides an emended diagnosis of the genus, describes a new species, discusses the geographic distribution and hosts of the genus, and includes a key to the species. The new species was found associated with the sponge Callyspongia in Todos-os-Santos Bay and can be distinguished from its congeners by a set of characters that includes the presence of a unique seta on the inner margin of the second endopodal segment of legs 1 to 4 and only two spines on the outer margin of third endopodal element of leg 1.
References
Giesbrecht, W. (1897) System der Ascomyzontiden, einer semiparasitischen Copepoden-Familie. Zoologisch Anzeiger, 20, 9–14.
Giesbrecht, W. (1899) Die Asterocheriden des Golfes von Neapel und angrenzenden Meeresabschinitte. Fauna und Flora des Golfes von Neapel, 25, 1–217. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.10537
Giesbrecht, W. (1902) Resultats du Voyage du S. Y. Belgica en 1897–1898–1899. Rapports Scientifiques, Zoologie, Copepoden, 1–46, pls. I–XIII. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.2170
Hansen, H.J. (1923) Crustacea Copepoda. II.Copepoda Parasita and Hemiparasita. The Danish Ingolf-Expedition, 3, 1–92. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.58675
Huys, R. & Boxshall, G.A. (1991) Copepod Evolution. The Ray Society, Londres, 468 pp.
Johnsson, R. (2002) Asterocherids (Copepoda: Siphonostomatoida) associated with invertebrates from California Reefs: Abrolhos (Brazil). Hydrobiologia, 470, 247–266. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015641516360
Johnsson, R. & Neves, E.G. (2012) Siphonostomatoid copepods (Crustacea) associated with marine invertebrates and algae in Brazil: a review and future considerations. Zoosymposia, 8 (4), 69–80. https://doi.org/10.11646/zoosymposia.8.1.10
Johnsson, R., Rocha, C.E.F. & Neves, E.G. (2001) Asterocherids (Copepoda: Siphonostomatoida) from Picinguaba, São Paulo State, Brazil. Nauplius, 9 (2), 75–95.
Kim, I.H. (2016) Siphonostomatoid copepods (Crustacea) mainly associated with marine invertebrates from Korean waters. Journal of Species Research, 5 (3), 393–442. https://doi.org/10.12651/JSR.2016.5.3.393
Malt, S.J. (1991) The copepod inhabitants of sponges and algae from Hong Kong. Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History), Zoology, 57 (2), 167–183.
Nicholls, A.G. (1944) Littoral Copepoda from South Australia (II) Calanoida, Cyclopoida, Notodelphyoida, Monstrilloida, and Caligoida. Records of the South Australia Museum, 8 (1), 1–62.
Stock, J.H. (1967) s.n. Copépodes associés aux invertrébrés des côtes du Roussillon VII. Sur deux espèces-jumelles de cyclopoïdes siphonostomes: Scottocheres elongatus (T. and A. Scott) et S. laubieri spec. nov. Vie et Milieu, XVIII (1A), 203–214.
Scott, T. & Scott, A. (1894) On some new and rare Crustacea from Scotland. Annals and Magazine of Natural History, Series 6, 13 (74), 137–149. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.39689