Abstract
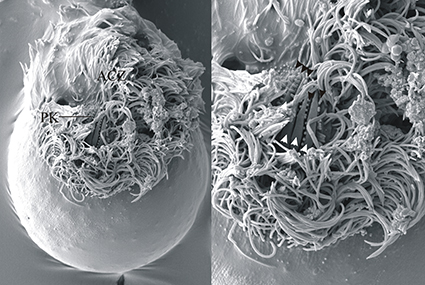
An investigation was carried out to identify the intestinal ciliated protozoa of the plains zebra known as Burchell’s zebra (Equus quagga burchellii Gray, 1824) living in Sasalı National Park (İzmir, Turkey) and Gaziantep Zoo (Gaziantep, Turkey) and of the plains zebra known as Grant’s zebra (Equus quagga boehmi Matschie, 1892) living in Darıca Faruk Yalçın Zoo (Darıca, Turkey). A total of 27 species and 1 morphotype belonging to 17 genera and 6 families were detected. Bundleia elongata was identified in all examined zebras, whereas Bundleia inflata, Blepharoconus benbrooki, Blepharocorys cardionucleata, Circodinium minimum, Cycloposthium bipalmatum, Ditoxum brevinucleatum, D. hamulus, and Arcosoma brevicorniger were identified only in one zebra. The average quantity of intestinal ciliates in the 9 zebras was 11.0 ± 17.0 × 104 cells mL−1. According to this study, the total number of ciliate species in the intestine of zebras increased to 51. This is the first time a report has been made on Paraisotricha colpoidea, Blepharoprosthium polytrichum, Bundleia elongata, B. triangularis, Paraisotrichopsis composita, Arcosoma brevicorniger, and A. dicorniger from zebra intestines. Moreover, A. brevicorniger was observed in binary fission for the first time.
References
Anderson, E. & Dumont, J. (1966) A comparative study of the concrement vacuole of certain endocommensal ciliates-a so-called mechanoreceptor. Journal of Ultrastructure Research, 15, 414–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5320(66)80117-X
Bundle, A. (1895) Ciliate infusorien im coecum des pferdes. Zeitschrift für Wissenschaftliche Zoologie, 60, 284–350.
Bush, A.O., Lafferty, K.D., Lotz, J.M. & Shostak, A.W. (1997) Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. Journal of Parasitology, 83, 575–583. https://doi.org/10.2307/3284227
Dehority, B.A. (1986) Protozoa of the digestive tract of herbivorous mammals. Insect Science and Its Application, 7, 279–296. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400009346
Dogiel, V.A. (1927) Monographie der Familie Ophryoscolecidae. Archiv für Protistenkunde, 59, 1–288.
Dogiel, V.A. (1929) Die sog. “Konkrementenvakuole” der infusoiren al eine statocyste betrachtet. Archiv für Protistenkunde, 63, 319–348.
Dovgal, I.V. (2002) Evolution, phylogeny and classification of Suctorea (Ciliophora). Protistology, 2, 194–270.
Egan, C.E., Snelling, T.J. & McEwan, N.R. (2010) The onset of ciliate populations in newborn foals. Acta Protozoologica, 49, 145–147.
Fantham, H.B. (1921) Some parasitic protozoa found in South Africa: IV. South African Journal of Science, 18, 164–170.
Gürelli, G. (2019) New entodiniomorphid ciliates, Buetschlia minuta n. sp., B. cirrata n. sp., Charonina elephanti n. sp., from Asian elephants of Turkey. Zootaxa, 4545 (3), 419–433. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4545.3.6
Gürelli, G. & Göçmen, B. (2010) Intestinal ciliate composition found in the feces of the Cypriot wild donkey, Equus asinus Linnaeus, 1758. European Journal of Protistology, 46, 38–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejop.2009.09.001
Gürelli, G. & Göçmen, B. (2011) Intestinal ciliate composition found in the feces of the Turk rahvan horse, Equus caballus Linnaeus, 1758. European Journal of Protistology, 47, 245–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejop.2011.04.005
Gürelli, G. & Göçmen, B. (2012) Intestinal ciliate composition found in the feces of racing horses from Izmir, Turkey. European Journal of Protistology, 48, 215–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejop.2012.01.002
Gürelli, G., Lyons, E.T. & Kesbiç, F.I. (2019) Hindgut ciliate composition of thoroughbred mares in Kentucky, USA, and binary fission in Polymorphella ampulla. Zootaxa, 4646 (2), 369–384. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4646.2.11
Gürelli, G. & Aydın, H. (2021) Hindgut ciliate diversity of domestic horses in Kastamonu, Turkey and scanning electron micrographs. Biharean Biologist, 15 (2), 91–101.
Harris, P.A. (1999) How understanding the digestive process can help minimise digestive disturbances due to diet and feeding practices. In: Harris, P.A., Gomarsall, G., Davidson, H.P.B. & Gren, R. (Eds.), Proceedings of the British Equine Veterinary Association Specialist Meeting on Nutrition and Behaviour. Proceedings of the British Equine Veterinary Association Specialist Meeting on Nutrition and Behaviour, UK, 1999, pp. 45–50.
Hsiung, T.-S. (1928) Suctoria of the large intestine of the horse: Allantosoma intestinalis Gassovsky, A. dicorniger sp. nov., and A. brevicorniger sp. nov. Iowa State College Journal of Science, 9, 101–103.
Hsiung, T.-S. (1930) A monograph on the protozoa of the large intestine of the horse. Iowa State College Journal of Science, 4, 359–423. https://doi.org/10.31274/rtd-180813-15927
Ike, K., Nuruki, R., Imai, S. & Ishii, T. (1981) Composition of intestinal ciliates excreted in feces of the light horse. Bulletin of the Nippon Veterinary and Zootechnical College, 30, 91–100.
Ike, K., Nuruki, R., Imai, S. & Ishii, T. (1983a) Composition of intestinal ciliates and bacteria excreted in feces of the race-horse. The Japanese Journal of Veterinary Science, 45, 157–163. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms1939.45.157
Ike, K., Nuruki, R., Nomoto, Y., Imai, S. & Ishii, T. (1983b) Comparative studies on the intestinal ciliate fauna excreted in the feces of yearlings, bloodmares, riding horses and racehorses. Bulletin of Equine Research Institute, 20, 63–70.
Ike, K., Imai, S. & Ishii, T. (1983c) A new ciliate, Spirodinium magnum sp. nov., from the light horse. The Japanese Journal of Veterinary Science, 45, 525–527. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms1939.45.525
Ike, K., Imai, S. & Ishii, T. (1985) Establishment of intestinal ciliates in new-born horses. The Japanese Journal of Veterinary Science, 47, 39–43. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms1939.47.39
Imai, S., Tsutsumi, Y., Yumura, S. & Mulenga, A. (1992) Ciliate protozoa in the rumen of Kafue lechwe, Kobus leche kafuensis, in Zambia, with the description of four new species. Journal of Protozoology, 39, 564–572. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1992.tb04852.x
Imai, S. Inami, K. Morita, T. Ike, K. & Ito, A. (1999) Intestinal ciliate composition found in the feces of Japanese native kiso horse. Bulletin of the Nippon Veterinary and Animal Science University, 48, 33–38.
Ito, A., Imai, S., Ogimito, K. & Nakahara, M. (1996) Intestinal ciliates found in the feces of Japanese native tokara pony, with the description of a new genus and a new species. The Japanese Journal of Veterinary Medical Science, 58, 103–108. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.58.103
Kornilova, O.A. (2003) The Fauna of Ciliates from the Intestine of Asiatic Wild Ass (Kulan). Tessa Press, St-Petersburg, 215 pp.
Kornilova, O.A. (2004) History of Study of Endobiotic Ciliates of Mammalia. Tessa Press, St-Petersburg, 349 pp.
Kornilova, O., Tsushko, K. & Chistyakova, L. (2020) The first record of intestinal ciliates from the mountain zebra (Equus zebra) in South Africa. Acta Protozoologica, 59, 149–155. https://doi.org/10.4467/16890027AP.20.012.13267
Kornilova, O.A., Radaev, A.V. & Chistyakova, L.V. (2021) Intestinal ciliates (Ciliophora) from the wild plains zebra (Equus quagga) in South Africa, with notes on the microtubule cytoskeleton organisation. European Journal of Protistology, 81, 125842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejop.2021.125842
Lynn, D.H. (2008) The Ciliated Protozoa, Characterization, Classification and Guide to the Literature. 3rd Edition. Springer, New York, New York, 605 pp.
Moehlman, P.D. (2002) Equids: Zebras, Asses and Horses. Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. IUCN, Gland and Cambridge, 190 pp.
Moon-van der Staay, S.Y., van der Staay, G.W.M., Michalowski, T., Jauany, J.-P., Pristas, P., Javorskı, P., Kišidayová, S., Varadyova, Z., McEwan, N.R., Newbold, C.J., van Alen, T., de Graaf, R., Schmid, M., Huynen, M.A. & Hackstein, J.H.P. (2014) The symbiotic intestinal ciliates and the evolution of their hosts. European Journal of Protistology, 50, 166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejop.2014.01.004
Moore, J.N., Melton, T., Carter, W.C., Wright, A.L. & Smith, M.L. (2001) I: A new look at equine gastrointestinal anatomy, function, and selected intestinal displacements. Aaep Proceedings, 47, 53–60.
Ogimoto, K. & Imai, S. (1981) Atlas of Rumen Microbiology. Japan Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo, 231 pp.
Schrenk, H.-G. & Bardele, C.F. (1987) The fine structure of the paralabial organelle in the rumen ciliate Ophryoscolex purkinjei Stein, 1858. Journal of Protozoology, 34, 97–104. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1987.tb03141.x
Strelkow, A. (1931) Über die fauna des colons beim zebra. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 94, 37–54.
Strelkow, A. (1939) Parasitical infusoria from the intestine of Ungulata belonging to the family Equidae. Uchenye Zapiski Leningrad Pedagog Institute Gertsena, 17, 1–262.
Tung, K.-C. (1992) Analysis of the composition and morphology of intestinal ciliates excreted in feces of the riding horses in Middle Taiwan. Bulletin of the Faculty of Agricultural and Natural Chung-Hsing University, 41, 53–56.
Vďačný, P. (2018) Evolutionary associations of endosymbiotic ciliates shed light on the timing of the marsupial-placental split. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35, 1757–1769. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy071
Wiedner, E.B., Lindsay, W.A. & Isaza, R. (2012) Management of zebras and zebra hybrids (zebroids). Compendium Continuing Education for Veterinarians, 34 (9), E1–E8.
Wolska, M. (1964) Infraciliature of Didesmis ovalis Fior. and Blepharozoum trizonum (Hsiung)-fam. Buetschliidae (Ciliata, Rhabdophorina). Acta Protozoologica, 2, 153–158.