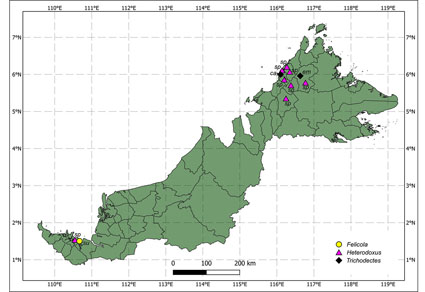
Abstract
Literature records of chewing lice (Phthiraptera) from mammals in Malaysia were checked and reviewed, resulting in a list of 13 confirmed species belonging to eight genera (Bovicola, Felicola, Gliricola, Gyropus, Haematomyzus, Heterodoxus, Lorisicola, Trichodectes) from four families (Boopiidae, Gyropidae, Haematomyzidae, Trichodectidae) in three suborders (Amblycera, Ischnocera, Rhynchophthirina). We present a checklist of those 13 chewing lice recorded from Peninsular Malaysia and Malaysian Borneo, including hosts, localities, and literature references. An additional 12 species are listed and discussed as possibly occurring in this country. A host-louse list is also given.
References
- Abdullah, M.T. & Mammalian Research Group (2013) List of 361 species of mammals in Malaysia. Available from: http://ir.unimas.my/id/eprint/1554 (Accessed 2 July 2022)
- Ahmad, N.I.I. (2013) A survey of ectoparasites on domestic cat (Felis catus Linnaeus, 1758) from rural and urban areas. Bachelor of Science Degree. Universiti Malaysia Sarawak, Kota Samarahan. 30 pp.
- Amin-Babjee, S.M. (1978) Parasites of the domestic cat in Selangor, Malaysia. Kajian Veterinaire, 10, 107–114.
- Bedford, G.A.H. (1929) Anoplura (Siphunculata and Mallophaga) from South African hosts. 15th Annual report of the Director of Veterinary Services, Union of South Africa, 501–549.
- Bedford, G.A.H. (1932a) Trichodectes (Mallophaga) found on African Carnivora. Parasitology, 24 (3), 350–364. https://doi.org/10.1017/S003118200002076X
- Bedford, G.A.H. (1932b) A synoptic check-list and host list of the ectoparasites found on South African Mammalia, Aves, Reptilia. Part II. Report of the Director of Veterinary Services and Animal Industry, Union of South Africa, 18, 223–523.
- Bedford, G.A.H. (1936) Notes on species of Trichodectidae with descriptions of new genera and species. Onderstepoort Journal Veterinary Science and Animal Industry, 7, 33–58.
- Burmeister, H. (1838) Mallophaga. In: Handbuch der Entomologie. Enslin, Berlin, 2 (1), 418–443.
- Changbunjong,T., Prompiram, P., Weluwanarak, T. & Buddhirongawatr, R. (2011) A redescription of Felicola (Paradoxuroecus) bengalensis (Werneck, 1948) (Phthiraptera: Trichodectidae) from a common palm civet (Paradoxurus hermaphroditus) in Thailand. Kasetsart Journal (Natural Science), 45, 1020–1027.
- Changbunjong, T., Jirapattharasate, C., Buddhirongawatr, R., Chewajon, K., Charoenyongyoo, P., Suwanapakdee, S., Waengsothorn, S., Triwitayakorn, K., Chaichoun, K. & Ratanakorn, P. (2010) Ectoparasitic fauna of birds, and volant and non-volant small mammals captured at Srinakarin Dam, Kanchanaburi, Thailand. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health, 41, 526–535.
- Che Kamaruddin, N., Adrus, M. & Ismail, W.N.M. (2020) Prevalence of ectoparasites on a stray cat population from “Town of Knowledge” Kota Samarahan, Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo. Turkish Journal of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, 44, 1212–1221. https://doi.org/10.3906/vet-2005-24
- Cheah, T.S. (1988) A record of the finding of the Mallophagan (biting louse) Gyropus ovalis on guinea pigs. Journal Sekolah Teknologi Makmal Veterinar (Malaysia), 5: 25–28.
- Colella, V., Nguyen, V.L., Tan, D.Y., Lu, N., Fang, F., Zhijuan, Y., Wang, J., Liu, X., Chen, X., Dong, J., Nurcahyo, W., Hadi, U.K., Venturina, V., Tong, K.B.Y., Tsai, Y.L., Taweethavonsawat, P., Tiwananthagorn, S., Le, T.Q., Bui, K.L., Watanabe, M., Rani, P.A.M.A., Annoscia, G., Beugnet, F., Otranto, D. & Halos, L. (2020) Zoonotic vectorborne pathogens and ectoparasites of dogs and cats in Eastern and Southeast Asia. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 26 (6), 1221–1233. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2606.191832
- Colless, D.H. (1959) Heterodoxus spiniger (Mallophaga: Boopiidae) from cats in Singapore. Journal of Parasitology, 45, 248. https://doi.org/10.2307/3274490
- Conci, C. (1942) Diagnosi preliminare di tre nuovi generi e di una nuova specie di Trichodectinae (Mallophaga). Bollettino della Societá Entomologica Italiana, 74, 140–142.
- De Geer, C. (1778) Des Ricins. Pp. 69–82, pl. 4. In: Mémoires pour servir à l’histoire des insectes. Volume 7. Pierre Hesselberg, Stockholm. xii + 950 pp., 49 pls.
- Denny, H. (1842) Monographia Anoplurorum Britanniae or, an essay on the British species of parasitic insects belonging to the order of Anoplura of Leach, with the modern divisions of the genera according to the views of Leach, Nitzsch, and Burmeister, with highly magnified figures of each species. Henry G. Bohn, London, xxiv + 262 pp., 26 pls. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.137104
- Denny, H. (1852) List of the specimens of British animals in the collection of the British Museum. Part XI. Anoplura, or parasitic insects. Trustees of the British Museum, London. iv + 51 pp.
- Deplazes, P., Eckert, J., Mathis, A., von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G. & Zahner, H. (2016) Parasitology in veterinary medicine. Wageningen Academic Publishers, Wageningen, 653 pp.
- Duckworth, J.W., Mathai, J., Chutipong, W., Brodie, J. & Wilting, A. (2016a) Prionodon linsang. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016. e.T41705A45219711. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41705A45219711.en
- Duckworth, J.W., Timmins, R. & Semiadi, G. (2015) Tragulus javanicus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015. e.T41780A61978138. (Accessed 23 August 2022) https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T41780A61978138.en.
- Duckworth, J.W., Timmins, R.J., Chutipong, W., Choudhury, A., Mathai, J., Willcox, D.H.A., Ghimirey, Y., Chan, B. & Ross, J. (2016b) Paguma larvata. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016. e.T41692A45217601. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41692A45217601.en
- Durden, L.A. (2019) Chapter 7. Lice (Phthiraptera). In: Mullen, G.R. & Durden, L.A. (Eds.), Medical and Veterinary Entomology. 3rd Edition. Academic Press Inc., Cambridge, Massachusetts, pp. 79–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814043-7.00007-8
- Eichler, W. (1940) Notulae Mallophagologicae. — I. Neue Gattungen und Subfamilien von Haarlingen. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 129 (5/6), 158–162.
- Emerson, K.C. (1940) Records of Mallophaga from Oklahoma hosts. Canadian Entomologist, 72, 104–108. https://doi.org/10.4039/Ent72104-5
- Emerson, K.C. (1964a) A new species of Mallophaga from Malaya. Journal of Kansas Entomological Society, 37, 4–5.
- Emerson, K.C. (1964b) Notes on some Mallophaga from Formosan mammals. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington, 77, 195–198.
- Emerson, K.C. & Price, R.D. (1975) Mallophaga of Venezuelan mammals. Brigham Young University Science Bulletin. Biological Series, 20 (3), 1–77. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.5667
- Emerson, K.C. & Price, R.D. (1981) A host-parasite list of the Mallophaga on mammals. Miscellaneous Publications of the Entomological Society of America, 12 (1), 1–72.
- Enderlein, G. (1904) Läusestudien. I. Über die Morphologie, Klassifikation und systematische Stellung der Anopluren nebst Bemerkungen zur Systematik der Insektenordnungen. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 28 (4), 121–147.
- Enderlein, G. (1909) Anopluren (Siphunculaten) und Mallophagen. In: Schultze, L. (Ed.) Zoologisch und Anthropologische Ergebnisse einer Forschungreise in Südafrika 2 (2). Denkschriften der medizinisch-naturwissenschaftlichen Gessellschaft, 14, 79–81, pl. 8.
- Ewing, H.E. (1924) On the taxonomy, biology, and distribution of the biting lice of the family Gyropidae. Proceedings of the United States National Museum, 63 (20), 1–42. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.00963801.63-2489.1
- Ewing, H.E. (1929) A manual of external parasites. Baillière Tindall & Cox, London. xvi + 225 pp. https://doi.org/10.2307/3271887
- Ewing, H.E. (1930) Six new species of Mallophaga. Proceedings of the Entomological Society of Washington, 32 (7), 117–121.
- Fabricius, O. (1780) Fauna Groenlandica systematice sistens animalia Groenlandiae occidentalis hactenus indagata. J.G. Rothe, Hafniae et Lipsiae. xvi + 452 pp., pl. 1.
- Fahrenholz, H. (1910) Diagnosen neuer Anopluren. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 35 (23), 714–715.
- Fahrenholz, H. (1919) Bemerkungen zu der Arbeit. In: Schwalbe, G. “Uber die Bedeutung der ausseren Parasiten fur die Phylogenie der Saugetiere und des Menschen”. Zeitschrift für Morphologie und Anthropologie, 21, 361–364.
- Ferris, G.F. (1922) The mallophagan family Trimenoponidae. Parasitology, 14 (1), 75–86. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182000009999
- Ferris, G.F. (1931) The louse of elephants, Haematomyzus elephantis Piaget (Mallophaga: Haematomyzidae). Parasitology, 23 (1), 112–127, 2 pls. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182000013494
- Gervais, F.L.P. (1844) Dicères épizoiques. Pp. 290–361, pls 48–49. In: Walckenaer, C.A. (Ed.) Histoire Naturelle des Insectes. Aptères. Tome 3. Librairie Encyclopédique de Roret, Paris. viii + 476 pp.
- Giebel, C.G.A. (1861a) Die Haarlinge der Gattungen Trichodectes und Gyropus nach Chr. L. Nitzsch’s Untersuchungen. Zeitschrift für die gesammten Naturwissenschaften (Halle), 18, 81–93, 2 pls.
- Giebel, C.G.A. (1861b) Die. Verzeichrniss der von Chr. L. Nitzsch untersuchten Epizoen nach den Wohnthieren geordnet. Zeitschrift für die gesammten Naturwissenschaften (Halle), 18, 289–
- Gurlt, E.F. (1843) Über die auf den Haus-Säugetieren und Haus-Vögeln lebenden Schmarotzer – Insekten und Arachniden. Magazin für die gesammte Thierheilkunde, 9, 1–24, 1 pl.
- Harrison, L. (1916) The genera and species of Mallophaga. Parasitology, 9 (1), 1–156. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.102856
- Hopkins, G.H.E. (1949) The host-associations of the lice of mammals. Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London, 119 (2), 387–604. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1949.tb00888.x
- Hopkins, G.H.E. (1960) Notes on some Mallophaga from mammals. Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History), Entomology, 10 (2), 77–95, 2 pls. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.16257
- Jeffery, J., Vellayan, S., Sulaiman, S., Oothuman, P., Zahedi, M. & Krishmasamy, M. (1999) The occurrence of Haematomyzus elephantis, Piaget (Mallophaga: Haematomyzidae) on the Asian elephant Elephas maximus indicus Cuvier. A new record for Peninsular Malaysia. Tropical Biomedicine, 16 (2), 51–52
- Kazim, A.-R., Houssaini, J., Tappe, D. & Heo, C.-C. (2022) An annotated checklist of sucking lice (Phthiraptera: Anoplura) from domestic and wild mammals in Malaysia, with lists of hosts and pathogens. Zootaxa, 5214 (3), 301–336. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5214.3.1
- Kéler, S. von (1937) Über einige neue und interessantere Mallophagen des Deutschen Entomologischen Instituts in Berlin-Dahlem. Arbeiten über Morphologische und Taxonomische Entomologie aus Berlin-Dahlem, 4 (4), 312–324.
- Kéler, S. von (1938) Baustoffe zu einer Monographie der Mallophagen. I. Teil: Überfamilie Trichodectoidea. Nova Acta Leopoldina Abhandlungen der Kaiserlich Leopoldinisch-Carolinisch Deutschen Akademie der Naturforscher (Neue Folge), 5 (32), 393–467.
- Kéler, S. von (1957) Der Haarling der Wildkatze (Felicola hercynianus n. sp.) (Mallophaga, Trichodectidae). Deutsche Entomologische Zeitschrift, N.F., 4, 172–178. https://doi.org/10.1002/mmnd.4800040306
- Kéler, S. von (1971) A revision of the Australasian Boopiidae (Insecta: Phthiraptera), with notes on the Trimenoponidae. Australian Journal of Zoology, Supplement, 6, 1–126. https://doi.org/10.1071/AJZS006
- Kellogg, V.L. (1896) New Mallophaga, I, — with special reference to a collection made from maritime birds of the Bay of Monterey, California. Proceedings of the California Academy of Sciences (Series 2), 6, 31–168, 14 pls.
- Kellogg, V.L. & Nakayama, S. (1914) A new Trichodectes from Baja California. Psyche, 21, 90–92. https://doi.org/10.1155/1914/56086
- Lahille, (1908) El piojo y la elefantita, Haematomyzus paradoxus Lahille. Revista del Jardín Zoológico de Buenos Aires (Series 2), 1, 187–189.
- Lee, H.L., Krishnasamy, M., Jeffery, J. & Paramasvaran, S. (2006) Notes on some ectoparasites received by the Medical Entomology Unit, Institute for Medical Research. Tropical Biomedicine, 23, 131–132.
- Le Souëf, S.A. & Bullen, H. (1902) Description of a mallophagous parasite from the kangaroo. The Victorian Naturalist, 18, 159. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.27549
- Linnaeus, C. (1758) Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Volume 1. 10th Edition. Laurentii Salvii, Holmiae, iv + 824 pp. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.542
- Linnaeus, C. (1761) Pediculi. In: Fauna Suecica Sistens Animalia Sueciae Regni: Mammalia, Aves, Amphibia, Pisces, Insecta, Vermes. Laurentii Salvii, Stockholmiae. Pp. 475–479.
- Low, V.L., Prakash, B.K., Tan, T.K., Sofian-Azirun, M., Anwar, F.H.K., Vinnie-Siow, W.Y. & Abu-Bakar, S. (2017) Pathogens in ectoparasites from free-ranging animals: infection with Rickettsia asembonensis in ticks, and a potentially new species of Dipylidium in fleas and lice. Veterinary Parasitology, 245, 102–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2017.08.015
- Lyal, C.H.C. (1985) A cladistic analysis and classification of trichodectid mammal lice (Phthiraptera: Ischnocera). Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History), 51 (3), 187–346.
- Macadam, I., Gudan, D., Timbs, D.V., Urquhart, H.R. & Sewell, M.M.H. (1984) Metazoan parasites of dogs in Sabah, Malaysia. Tropical Animal Health and Production, 16, 34–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02248927
- Madinah, A., Fatimah, A., Mariana, A. & Abdullah, M.T. (2011) Ectoparasites of small mammals in four localities of wildlife reserves in Peninsular Malaysia. The Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health, 42, 803–813.
- Madinah, A., Mariana, A., Fatimah, A. & Abdullah, M.T. (2013) A preliminary field survey of ectoparasites of rodents in urban park, Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo. Tropical Biomedicine, 30, 547–551.
- Madinah, A., Abang, F., Mariana, A., Abdullah, M.T. & Mohd-Azlan, J. (2014) Interaction of ectoparasites-small mammals in tropical rainforest of Malaysia. Community Ecology, 15, 113–120. https://doi.org/10.1556/ComEc.15.2014.1.12
- Mariana, A., Zuraidawati, Z., Ho, T.M., Mohd-Kulaimi, B., Saleh, I., Shukor, M.N. & Shahrul-Anuar, M.S. (2005) A survey of ectoparasites in Gunung Stong Forest Reserve, Kelantan, Malaysia. The Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health, 36 (5), 1125–1131.
- Mariana, A., Zuraidawati, Z., Ho, T.M., Mohd-Kulaimi, B., Saleh, I., Shukor, M.N. & Shahrul-Anuar, M.S. (2008) Ticks (Ixodidae) and other ectoparasites in Ulu Muda Forest Reserve, Kedah, Malaysia. The Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health, 39, 496–506.
- McGregor, E.A. (1917) Six new species of Mallophaga from North American mammals. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 10 (1), 167–175.
- https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/10.2.167
- Mey, E. (2021) Lorisicola mjobergi [sic] (Stobbe, 1913) sensu lato (Insecta, Psocodea, Phthiraptera, Ischnocera, Trichodectidae) from two Nycticebus species (Mammalia, Primates) from Vietnam, with notes on the genus Lorisicola Bedford. Vietnamese Journal of Primatology, 3, 179–201.
- Mjöberg, E. (1910) Studien über Mallophagen und Anopluren. Arkiv för Zoologi, 6 (13), 1–296, 5 pls. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.26907
- Mohd-Taib, F.S., Asyikha, R. & Md-Nor, S. (2021) Small mammal assemblages and their ectoparasite prevalence (Acarina) in mangrove forests of Peninsular Malaysia. Tropical Zoology, 34, 24–43. https://doi.org/10.4081/tz.2021.78
- Mohd-Zain S.N., Norhidayu, S., Pal, P. & Lewis, J.W. (2013) Macroparasite communities in stray cat populations from urban cities in Peninsular Malaysia. Veterinary Parasitology, 196, 469–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2013.03.030
- Mokhtar, A.S., Jeffery, J., Noraishah-Mydin, AA. & Tay, S.T. (2011) Molecular detection of Bartonella henselae and B. clarridgeiae (causative agents of cat scratch disease) from animal ectoparasites in Malaysia. 47th Annual Conference of the Malaysian Society of Parasitology and Tropical Medicine, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 3–4 March 2011. Malaysian Society of Parasitology and Tropical Medicine, Malaysia, p. 62.
- Mudappa, D. & Choudhury, A. (2016) Herpestes edwardsii. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016. e.T41611A45206787. (Accessed 23 August 2022) https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41611A45206787.en
- Mustaffa-Babjee, A. (1969) Lice and fleas of animals in Malaysia. Kajian Veterinaire, 2, 37.
- Nelson, G.S. (1962) Dipetalonema reconditum (Grassi, 1889) from the dog with a note on its development in the flea, Ctenocephalides felis, and the louse, Heterodoxus spiniger. Journal of Helminthology, 36, 297–308. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X00023968
- Neumann, L.G. (1912a) Notes sur les Mallophages. – II. I. – Sur le genre Menopon (sous-genre Menacanthus n. subgen.). Archives de Parasitologie, Paris, 15 (3) 353–368.
- Neumann, L.G. (1912b) Sur le genre Gyropus Nitzsch. Bulletin de la Société Zoologique de France, 37, 212–228.
- Neumann, L.G. (1913) Notes sur les Mallophages – III. Archives de Parasitologie, Paris, 15 (4), 608–634
- Nitzsch, C.L. (1818) Die Familien und Gattungen der Theierinsekten (Insecta epizoica); als ein Prodromus einer Naturgeschichte derselben. E.F. Germar’s Magazin der Entomologie, 3, 261–318.
- Norhidayu, S. (2012) Biodiversity and epidemiology study of macroparasites from stray cats in Peninsular Malaysia. Thesis, Master in Science. Universiti Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, 270 pp.
- Norhidayu, S., Mohd-Zain, S.N., Jeffery, J. & Lewis JW (2012) The dog louse Heterodoxus spiniger from stray cats in Penang, Malaysia. Tropical Biomedicine, 29, 301–303.
- Olfers, I.F.J.M. von (1816) De vegetativis et animatis corporibus in corporibus animatis reperiundis commentarius. Taberna Libraria Maureriana, Berolini. vi + 113 pp., 1 pl.
- Packard, A.S. (1870) Certain parasitic insects. American Naturalist, 4, 83–99, pl. 1. https://doi.org/10.1086/270541
- Paine, J.H. (1912a) The mallophagan genus Heterodoxus Le Souëf and Bullen. Entomological News, 23, 359–362.
- Paine, J.H. (1912b) Notes on a miscellaneous collection of Mallophaga from mammals. Entomological News, 23, 437–442.
- PERHILITAN – Jabatan Perlindungan Hidupan Liar dan Taman Negara Semenanjung Malaysia (2010) Red list of mammals for Peninsular Malaysia. Department of Wildlife and National Parks of Peninsular Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur. 150 pp.
- PERHILITAN – Jabatan Perlindungan Hidupan Liar dan Taman Negara Semenanjung Malaysia (2017) Red list of mammals for Peninsular Malaysia. Version 2.0. Department of Wildlife and National Parks of Peninsular Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur, 216 pp.
- Phan, T.D., Nijhawan, S., Li, S. & Xiao, L. (2020) Capricornis sumatraensis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020. e.T162916735A162916910. (Accessed 23 August 2022) https:// doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T162916735A162916910.en.
- Piaget, E. (1869) Description d’un parasite de l’elephant, Haematomyzus elephantis. Tijdschrift voor Entomologie, 12, 249–254.
- Piaget, E. (1880) Les Pédiculines. Essai Monographique. Volumes 1–2. E.J. Brill, Leide, xxxix + 714 pp., 56 pls.
- Piaget, E. (1885) Les Pédiculines. Essai Monographique. Supplément. E.J. Brill, Leide. xvi + 200 pp., 17 pls.
- Plomley, N.J.B. (1940) Notes on the systematics of two species of Heterodoxus (Mallophaga, Boopiidae). Papers and Proceedings of Royal Society of Tasmania, 1939, 19–36.
- Price, M.A. & Graham, O.H. (1997) Chewing and sucking lice as parasites of mammals and birds. United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Technical Bulletin, 1849, vi + 257 pp., 2 appendices.
- Price, R.D., Hellenthal, R.A. & Palma, R.L. (2003) World checklist of chewing lice with host associations and keys to families and genera. Pp. 1–448. In: Price, R.D., Hellenthal, R.A., Palma, R.L., Johnson, K.P. & Clayton, D.H. The chewing lice: world checklist and biological overview. Illinois Natural History Survey Special Publication 24. x + 501 pp.
- Ross, J., Wilting, A., Ngoprasert, D., Loken, B., Hedges, L., Duckworth, J.W., Cheyne, S., Brodie, J., Chutipong, W., Hearn, A., Linkie, M., McCarthy, J., Tantipisanuh, N. & Haidir, I.A. (2015) Cynogale bennettii. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015. e.T6082A45197343. (Accessed 23 August 2022) https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T6082A45197343.en.
- Rudow, F. (1866) Sechs neue Haarlinge. Zeitschrift für die gesammten Naturwissenschaften (Halle) (N.F. 2), 27 (2), 109–112, 3 pls.
- Schrank, F. von P. (1781) Enumeratio insectorum Austriae indigenorum. Eberhardi Klett et Franck, Viduam Augustae Vindelicorum. ix + 548 pp., 4 pls.
- Schrank, F. von P. (1803) Fauna Boica. Landshut, 3 (1), 186–194.
- Sebei, P.J., McCrindle, C.M.E., Green, E.D. & Turner, M.L. (2004) Use of scanning electron microscopy to confirm the identity of lice infesting communally grazed goat herds. Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 71, 87–92. https://doi.org/10.4102/ojvr.v71i2.269
- Séguy, E. (1948) Le trichodecte du muntjac (Mallophage). Musée Heude. Notes d’Entomologie Chinoise, 12 (13), 149–152.
- Shabrina, S.M. (1990) Ectoparasites of small mammals trapped at the Ulu Gombak Forest, Selangor Darul Ehsan. Journal of Wildlife and Parks, 9, 9–17.
- Shanta, C.S., Wan, S.P. & Kwong, K.H. (1980) A survey of the endo- and ectoparasites of cats in and around Ipoh, West Malaysia. Malaysian Veterinary Journal, 7, 17–27.
- Stobbe, R. (1913) Mallophagen. 3. Beitrag: Die Trichodectiden des Berliner Museums fur Naturkunde. Sitzungsberichte der Gesellschaft Naturforschender Freunde zu Berlin, 1913 (8), 365–383.
- Syamsul, V.S., Okene, I.A.A., Che-Yahya, S.N., Hamdan, R.H., Lee, S.H. & Tan, L.P. (2020) Prevalence of ectoparasitism on small ruminants in Kelantan, Malaysia. Tropical Life Sciences Research, 31, 45–56. https://doi.org/10.21315/tlsr2020.31.1.3
- Taschenberg, O. (1882) Die mallophagen mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der von Dr. Meyer gesammelten Arten systematisch bearbeitet. Nova Acta der Kaiserlich Leopoldinisch-Carolinisch Deutschen Akademie der Naturforscher, 44 (1), 1–244, 7 pls. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.82513
- Tay, S.T., Mokhtar, A.S., Low, K.C., Mohd-Zain, S.N., Jeffery, J., Abdul-Aziz, N.A. & Kho, K.L. (2014) Identification of rickettsiae from wild rats and cat fleas in Malaysia. Medical and Veterinary Entomology, 28, 104–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/mve.12075
- Timmins, R. & Duckworth, J.W. (2015) Tragulus napu. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015. e.T41781A61978315 (Accessed 23 August 2022) https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T41781A61978315.en.
- Torres, J. (1938) Sobre um parasito (Mallaphaga [sic!] – Gyropidae) de Cavia cobaya (Gyropus recifensis n. sp. ou G. ovalis N.2). Boletim da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Veterinaria, 8, 279–288.
- Walker, F. (1872) A new form of parasite. In: Richter, H.C. (Ed.) Hardwicke’s Science Gossip, 1871, 131–132, fig. 67.
- Wells, K., Beaucournu, J.C., Durden, L.A., Petney, T.N., Lakim, M.B. & O’Hara, R.B. (2012) Ectoparasite infestation patterns of domestic dogs in suburban and rural areas in Borneo. Parasitology Research, 111, 909–919. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-2917-7
- Werneck, F.L. (1936) Contribuição ao conhecimento dos mallophagos encontrados nos mammiferos sul-americanos. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, 31 (3), 391–590, 1 pl. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0074-02761936000300001
- Werneck, F.L. (1948) Os malófagos de mamíferos. Parte I: Amblycera e Ischnocera (Philopteridae e parte de Trichodectidae). Revista Brasileira de Biologia, Special Volume, 1–243 pp.
- Werneck, F.L. (1950) Os Malófagos de Mamíferos. Parte II: Ischnocera (continuação de Trichodectidae) e Rhyncophthirina. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, 207 pp.
- Werneck, F.L. (1956) A respeito de alguns Malófagos de mamíferos. Revista Brasileira de Biologia, 16, (1) 25–32.
- White, F.B. (1872) The new elephant parasite. In: Richter, H.C. (Ed.), Hardwicke’s Science Gossip, 1871, 234.
- Zavaleta, D. (1946) Dos nuevas especies de la familia Gyropidae encontradas en los cuyes de México. Anales del Instituto de Biología, Universidad Nacional de México, 16, 435–444.