Abstract
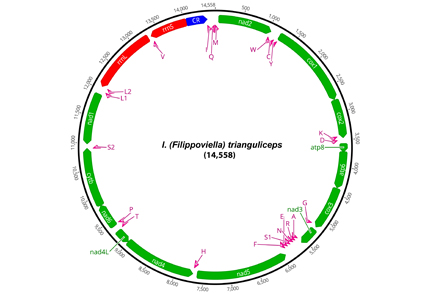
We establish a new subgenus, Filippoviella n. subgen. (Acari: Ixodidae) based on two species formerly assigned to the subgenus Exopalpiger Schulze, 1935 in the genus Ixodes Latreille, 1795. Ixodes (Filippoviella) trianguliceps Birula, 1895 is a tick species broadly distributed throughout Europe and western Siberia, the females, nymphs and larvae of which mostly feed on small mammals such as shrews and rodents. Ixodes (Filippoviella) ghilarovi Filippova & Panova, 1988 is found in the Caucasus region on rodents and shrews. The type species of this new subgenus is Ixodes trianguliceps. The major morphological differences allowing discrimination of the two species of Filippoviella n. subgen from members of the subgenus Exopalpiger are the shape of the idiosoma, shape of the basis capituli, development of palpal segment I, the suture between palpal segments II and III, development of syncoxae and chaetotaxy. We sequenced the entire mitochondrial genome of I. trianguliceps; according to our phylogeny from 10 protein-coding mitochondrial genes of 17 of the 23 Ixodes subgenera (34 spp.), I. (Filippoviella) trianguliceps is basal to the “other Ixodes” and polyphyletic with I. (Exopalpiger) fecialis Warburton & Nuttall, 1909.
References
- Apanaskevich, D.A. & Lemon, H.E. (2018) Description of a new species of Ixodes Latreille, 1795 (Acari: Ixodidae) and redescription of I. priscicollaris Schulze, 1932, parasites of New Guinea rodents (Rodentia: Muridae). Systematic Parasitology, 95, 373–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-018-9786-0
- Arthur, D.R. (1965) Ticks of the genus Ixodes in Africa. Athlone Press, University of London, London, 348 pp.
- Barker, D., Seeman, O.D. & Barker, S.C. (2021) The development of tick taxonomy and systematics in Australia and Papua New Guinea through the works of five late 20th century contributors and with comments on the place of Australasia in the study of the phylogeny and evolution of the ticks. Systematic & Applied Acarology, 26, 1793–1832. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.26.10.1
- Barker, S.C., Kelava, S., Heath, A.C.G., Seeman, O.D., Apanaskevich, D.A., Mans, B.J., Shao, R., Gofton, A.W., Teo, E.J.M., Byrne, A.F., Ito, T., Tan, C.J., Barker, D. & Nakao, R. (2023) A new subgenus, Australixodes n. subgen. (Acari: Ixodidae), for the kiwi tick, Ixodes anatis Chilton, 1904, and validation of the subgenus Coxixodes Schulze, 1941 with a phylogeny of 16 of the 22 subgenera of Ixodes Latreille, 1795 from entire mitochondrial genome sequences. Zootaxa, 5325 (4), 529–540. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5325.4.4
- Camicas, J.L., Hervy, J.P., Adam, F. & Morel, P.C. (1998) Les tiques du monde. Nomenclature, stades décrits, hôtes, repartition (Acarida, Ixodida). Orstom, Paris, 233 pp.
- Castresana, J. (2000) Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 17, 540–552.
- Chen, Y., Ye, W., Zhang, Y. & Xu, Y. (2015) High speed BLASTN: An accelerated MegaBLAST search tool. Nucleic Acids Research, 43, 7762–7768. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv784
- Clifford, C.M., Sonenshine, D.E., Keirans, J.E. & Kohls, G.M. (1973) Systematics of the subfamily Ixodinae (Acarina: Ixodidae). 1. The subgenera of Ixodes. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 66, 489–500. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/66.3.489
- Dierckxsens, N., Mardulyn, P. & Smits, G. (2017) NOVOPlasty: de novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Research, 45, e18. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw955
- Dobson, S.J. & Barker, S.C. (1999) Phylogeny of the hard ticks (Ixodidae) inferred from 18S rRNA indicates that the genus Aponomma is paraphyletic. Molecular Phylogenetics & Evolution, 11, 288–295. https://doi.org/10.1006/mpev.1998.0565
- Donath, A. Jühling, F., Al-Arab, M., Bernhart, S.H., Reinhardt, F., Stadler, P.F., Middendorf, M. & Bernt, M. (2019) Improved annotation of protein-coding genes boundaries in metazoan mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Research, 47, 10543–10552. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz833
- Filippova, N.A. (1977) Ixodid ticks of subfam. Ixodinae. Fauna of the USSR, 4 (4). Nauka Publishing House, Leningrad, 396 pp. [in Russian]
- Filippova, N.A. (2010) Uncommon zoogeographical connections in the subgenus Exopalpiger Schultze of the genus Ixodes Latreille (Acari, Ixodidae). Entomological Review, 90, 793–797. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0013873810060151
- Filippova, N.A. & Panova, I.V. (1988) Ixodes ghilarovi sp. n. – a new relic species of ixodid ticks (Ixodoidea, Ixodidae). Systematics of insects and acarines. Nauka, Leningrad, pp. 212–217. [in Russian]
- Filippova, N.A. & Panova, I.V. (1989) Description of female and larva of the relic species Ixodes ghilarovi (Ixodidae). Parazitologiya, 23, 419–422. [in Russian]
- Filippova, N.A. & Panova, I.V. (1996) Catalogue of type specimens in the collection of the Zoological Institute RAS, ixodoid ticks (Ixodoidea), argasids (Argasidae), ixodids (Ixodidae). Zoological Institute RAS, St. Petersburg, 28 pp. [in Russian]
- Guglielmone, A.A., Robbins, R.G., Apanaskevich, D.A., Petney, T.N., Estrada-Peña, A. & Horak, I.G. (2014) The hard ticks of the world (Acari: Ixodida: Ixodidae). Springer, Dordrecht, Heidelberg, New York and London, 738 pp. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7497-1
- Guglielmone, A.A., Petney, T.N. & Robbins, R.G. (2020) Ixodidae (Acari: Ixodoidea): descriptions and redescriptions of all known species from 1758 to December 31, 2019. Zootaxa, 4871 (1), 1–322. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4871.1.1
- Guglielmone, A.A., Nava, S. & Robbins, R.G. (2023) Geographic distribution of the hard ticks (Acari: Ixodida: Ixodidae) of the world by countries and territories. Zootaxa, 5251 (1), 1–274. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5251.1.1
- Hoang, D.T., Chernomor, O., Von Haeseler, Aa, Minh, B.Q. & Vinh, L.S. (2018) UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 35, 518–522. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx281
- Hornok, S., Kontschán, J., Takács, N., Heyne, H., Kovacs, A.B., Plantard, O., Keve, G., Fedorov, D., Gyuranecz, M. & Halajian, A. (2023) Molecular-phylogenetic analyses of Ixodes species from South Africa suggest an African origin of bird-associated exophilic ticks (subgenus Trichotoixodes). Parasites and Vectors, 16, 392. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-023-05998-5
- ICZN (2012) International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature: Amendment of articles 8, 9, 10, 21 and 78 of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature to expand and refine methods of publication. Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature, 69, 161–169. https://doi.org/10.21805/bzn.v69i3.a8.161
- Kelava, S., Mans, B.J., Shao, R., Moustafa, M.A.M., Matsuno, K., Takano, A., Kawabata, H., Sato, K., Fujita, H., Ze, C., Plantard, O., Hornok, S., Gao, S., Barker, D., Barker, S.C. & Nakao, R. (2021) Phylogenies from mitochondrial genomes of 120 species of ticks: Insights into the evolution of the families of ticks and of the genus Amblyomma. Ticks & Tick Borne Diseases, 12, 101577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2020.101577
- Kelava, S., Mans, B.J., Shao, R., Barker, D., Teo, E.J.M., Chatanga, E., Gofton, A.W., Moustafa, M.A.M., Nakao, R. & Barker, S.C. (2023) Seventy-eight entire mitochondrial genomes and nuclear rRNA genes provide insight into the phylogeny of the hard ticks, particularly the Haemaphysalis species, Africaniella transversale and Robertsicus elaphensis. Ticks & Tick Borne Diseases, 14, 102070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2022.102070
- Kohls, G.M. (1956) Eight new species of Ixodes from Central and South America (Acarina: Ixodidae). Journal of Parasitology, 42, 636–649. https://doi.org/10.2307/3274884
- Kohls, G.M., Sonenshine, D.E. & Clifford, C.M. (1969) Ixodes (Exopalpiger) jonesae sp. n. (Acarina: Ixodidae), a parasite of rodents in Venezuela. Journal of Parasitology, 55, 447–452. https://doi.org/10.2307/3277433
- Nuttall, G.H.F. & Warburton, C. (1911) Ticks. A monograph of the Ixodoidea. Part II. The Ixodidae. Section II. Genus I. Ixodes Latreille 1795. Cambridge University Press, London, pp. 133–293. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.24075
- Lanfear, R., Frandsen, P.B., Wright, A.M., Senfeld, T. & Calcott, B. (2017) PartitionFinder 2: New Methods for Selecting Partitioned Models of Evolution for Molecular and Morphological Phylogenetic Analyses. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 34, 772–773. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw260
- Lowe, T.M. & Chan, P.P. (2016) tRNAscan-SE On-line: integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Research, 44, W54–W57. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw413
- Rambaut, A. (2009) TRACER. Version 1.7.1. 1 May 2018. Available from: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/tracer/ (accessed 9 November 2023)
- Rambaut, A. (2012) FigTree. Version 1.4.4. 25 November 2018. Available from: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/FigTree/ (accessed 9 November 2023)
- Roberts, F.H.S. (1970) Australian ticks. CSIRO, Melbourne, 267 pp.
- Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., van der Mark, P., Ayres, D.L., Darling, A., Höhna, S., Larget, B., Liu, L., Suchard, M.A. & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2012) MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology, 61, 539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
- Schulze, P. (1935) Zur vergleichenden Anatomie der Zecken. Das Sternale, die Mundwerkzeuge, Analfurchen und Analbeschilderung und ihre Bedeutung, Ursprünglichkeit und Luxurieren. Zeitschrift für Morphologie und Ökologie der Tiere, 30, 1–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00418067
- Stamatakis, A. (2014) RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics, 30, 1312–1313. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033