Abstract
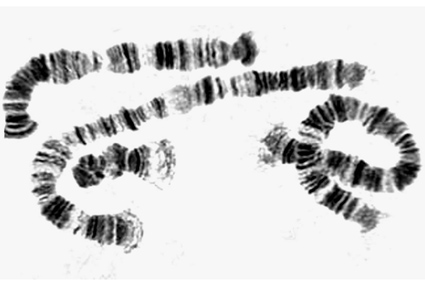
Based on the morphology of the polytene chromosomes, 21 species of the genus Chironomus Meigen from Bulgaria have been identified. Original pictures of the polytene chromosomes are presented for each species. “Basic” sequences were determined for each arm of the polytene chromosomes which are used to determine the corresponding arms of the chromosomes, and the cytocomplex to which the species belongs. The species are distributed in five cytocomplexes: thummi, pseudothummi, parathummi, lacunarius and modified thummi cytocomplexes. Marker sequences have been revealed on chromosome G that are proposed as a species identifier. Cytogenetic characters by which homosequential species of the genus Chironomus can be distinguished are discussed. This study emphasizes the importance of polytene chromosomes for the taxonomy of the species of Chironomus.
References
- Barna, I., Michailova, P. & Kownacki, A. (2010) The Karyotype of Chironomus acerbiphilus Tokunaga, 1939 (Diptera: Chironomidae) from Poland. Zootaxa, 2359 (1), 65–67. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.2359.1.6
- Bovero, S., Hankeln, T., Michailova, P., Schmidt, E. & Sella, G. (2002) Nonrandom chromosomal distribution of spontaneous breakpoints and satellite DNA clusters in two geographically distant populations of Chironomus riparius (Diptera, Chironomidae). Genetica, Hague, 115 (3), 273–281. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020697228525
- De Pauw, N.P., Ghetti, P., Manzeni, F. & Saggiari, R. (1992) Biological assessment methods for running water. In: River water quality, Ecological assessment and control. European Communities, Brussels, pp. 217–248.
- Duran, M., Michailova, P., Sari, A., Ilkova, J., Sen, A. & Karadurmus, E. (2012) Assessment of the sediment toxicity in Bulgarian and Turkish Rivers using the biomarkers in Chironomus riparius Mg. (Diptera, Chironomidae). Acta Zoologica Bulgarica, Supplement 4, 167–173.
- Faria, M.S., Lopes, R.J., Malcato, J., Nogueira, A.J.A. & Soares, A.M. (2008) In situ bioassays with Chironomus riparius larvae to biomonitor metal pollution in rivers and to evaluate the efficiency of restoration measures in mine areas. Environmental Pollution, 151 (1), 213–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.01.050
- Hägele, K. (1977) Differential staining of polytene chromosome bands in Chironomus by Giemsa banding methods. Chromosoma, 59, 207–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292778
- Ilkova, J., Hankeln, T., Schmidt, E., Michailova, P., Petrova, N., Sella, G. & White K. (2007) Genome instability of Chironomus riparius Mg. and Chironomus piger Strenzke (Diptera, Chironomidae). Caryologia, 60 (4), 299–308. https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.2007.10797951
- Ilkova, J., Michailova, P., Sella, G., Zampicinini, G., Cervella, P., Bovero, S. & Brunetti, S. (2004) Satellite DNA clusters, transposable elements and chromosome rearrangements in the salivary gland chromosomes of Chironomus riparius Mg (Diptera, Chironomidae) chronically treated with Al ions. Proceedings in Evolution and Ecology, 2004, 23–50.
- Jannssen De Bistoven, L.G., Timmermans, K.R. & Ollevier, F. (1992) The Concentration of cadmium, lead, copper and zinc in Chironomus riparius larvae with deformed versus normal menta. Hydrobiologia, 239, 141–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007671
- Keyl, H. (1962) Chromosomen evolution bei Chiuronomus II. Chromosomenumbauten und Phylogenetische Beziehungen der Arten. Chromosoma, 13, 464–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327342
- Kiknadze, I.I. (1978) Comparative puffing characteristics in salivary gland chromosomes in larval development and metamorphosis. Puffing in Ist, IInd and IIIrd chromosomes. Cytologia, 20, 514–521. [in Russian]
- Kiknadze, I.I., Michailova, P., Istomina, A., Golygina, V. & Krastanov, B. (2006) Chromosome polymorphism and populations divergency of Chironomus nuditarsis Str. (Diptera, Chironomidae). Tsitologia, St. Petersburg, 48 (7), 595–609. [in Russian]
- Kiknadze, I., Shilova, A., Kerkis, I., Shobanov, N., Zelenzov, N., Grebenjuk, L., Istomina, A. & Prasolov, B. (1991) Karyotype and Morphology of Larvae in Chironomus. Atlas, Novosibirsk, 112 pp.
- Kiknadze, I.I., Istomina, A., Golygina, V. & Gunderina, L. (2016) Karyotypes of Palearctic and Holarctic species of the genus Chironomus. Academic Publishing House, “Geo”, Novosibirsk, 489 pp.
- Krastanov, B. (2007) Cytotaconomy and chromosome polymorphism of species from family Chironomidae (Diptera) from fish pool in Bulgaria. PhD Thesis, Institute of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Research, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Sofia, 182 pp.
- Martin, J. (1979) Chromosomes as tool in taxonomy and phylogeny of Chironomidae (Diptera). Entomologica Scandinavia Supplement, 10, 67–74.
- Martin, J., Wülker, W. & Sublette, J. (1974) Evolutionary cytology of the genus Chironomus Meigen (Diptera: Chironomidae). Studies in Natural Science Portales, New Mexico, 1 (12), 1–12.
- Michailova, P. (1989) The polytene chromosomes and their significance for the systematics of family Chironomidae, Diptera. In: Acta Zoooologic. Fennica, Helsinki, pp. 1–107.
- Michailova, P. (1994) Chironomus bonus Shilova et Dyvarsheishvili (Diptera, Chironomidae) from Bulgaria; karyotype and morphology. Studia Dipterologica, Halle, 1 (h.2), 186–194.
- Michailova, P. (2014) Chapter 14. Polytene chromosomes and their significance for taxonomy, speciation and genotoxicology. In: Chandrasekar, R., Tyagi, B.K., Gui, Z.Z. & Reeck, G. (Eds.), Short View on Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Printed in the K-State Union. Copy and Printing services, Kansas State University, Manhattan Kansas, pp. 331–353. [ISBN: 978-1-63315-205-2]
- Michailova, P., Ilkova, J., Kerr, R. & White, K. (2009) Chromosome variability in Chironomus acidophilus Keyl from the Afon Goach, UK—a river subject to long-term metal pollution. Aquatic Insects, 31 (3), 213–225. https://doi.org/10.1080/01650420903113711
- Michailova, P., Ilkova J., Mariyanska-Nadachowska, A. & Warchalowska-Sliwa, E. (2015) Characterization of Heterochromatin in the salivary gland chromosomes of Chironomus riparius Meigen and Chironomus piger Strenzke (Diptera, Chironomidae) by Differential and Fluorochrome Staining. Folia Biologica, 63 (2), 108–117. https://doi.org/10.3409/fb63_2.107
- Michailova, P., Ilkova, J. & White, K. (2016) Implications of Genome alterations in Chironomus bernensis Klȍtzli (Diptera) for assessment of trace metal pollution in two Bulgarian rivers. River Research and Applications, 32, 914–924. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.2927
- Michailova, P., Ilkova, J., Szarek-Gwiazda, E., Kownacki, A. & Ciszewski, D. (2018) Genome instability in Chironomus annularius sensu Strenzke (Diptera, Chironomidae): A biomarker for assessment of the heavy metal contaminants in Poland. Journl of Limnology, 77 (1), 15–24. https://doi.org/10.4081/jlimnol.2018.1710
- Michailova, P., Ilkova, J. & White, K. (2022) New genomic approach for assessing pollution of aquatic ecosystems (Review). Quest Journals, Journal of Research in Environmental and Earth Sciences, 8 (2), 43–49. [https://www.questjournals.org/jrees/archive.html]
- Michailova, P. & Petrova, N. (1994) Cytogenetic characteristics of Chironomus balatonicus Devai, Wülker, Scholl (Chironomidae, Diptera). Cytobios, Cambridge, 79, 15–29.
- Michailova, P., Petrova, N., Ilkova, J., Bovero S., Brunetti, S., White, K. & Sella, G. (2006) Genotoxic effect of cooper on salivary gland chromosomes of Chironomus riparius Meigen 1804 (Diрtera, Chironomidae). Environmental Pollution, USA, 144 (2), 647–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.12.041
- Michailova, P., Sella, G. & Petrova, N. (2012) Chironomids (Diptera) and their salivary gland chromosomes as indicators of trace metal genotoxicology. Italian Journal of Zoology, 79, 218–230. https://doi.org/10.1080/11250003.2011.622084
- Petrova, N. & Michailova, P. (1996) Cytogenetic monitoring of Chironomus balatonicus Devai, Wűlker, Scholl (Diptera, Chironomidae) from the Chernobyl Region. Internationl.Journal of Dipterological Research, St. Petersburg, 7 (2), 79–86.
- Petrova, N. & Zhirov, S. (2022) Structure of polytene chromosomes and larval morphology of chironomids (Diptera, Chironomidae) Atlas. KMK Scientific Press, Saint Peterburg- Moscow, 114 pp., 155 pics. [in Russian]
- Saether, O.A. (1979) Chironomid communities as water quality indicators. Holarctic Ecology, 2, 65–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0587.1979.tb00683.x
- Schmidt, E. (1984) Cluster and interspersed repetative DNA sequence family of Chironomus. The nucleotide sequence of the Cla-elements and various flanking sequences. Journal of Molecular.Biology, 178, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(84)90227-4
- Stoichev, S. (1996) On the Chironomid fauna from Bulgarian inland waters. Lauterbornia, 25, 117–123.
- Wülker, W. (1980) Basic patterns in the chromosome evolution of the genus Chironomus (Diptera). Zeitschrift fur zoologische Systematik and Evolutionforschung, 18 (2), 122–123. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0469.1980.tb00733.x
- Wülker, W. (2010) The role of chromosomes in chironomid systematics, ecology and phylogeny. In: Ferrington, L.C. (Ed.), Proceeding in the XV International Symposium on Chironomidae. Minnesota Press, Minnesota, pp. 385.