Abstract
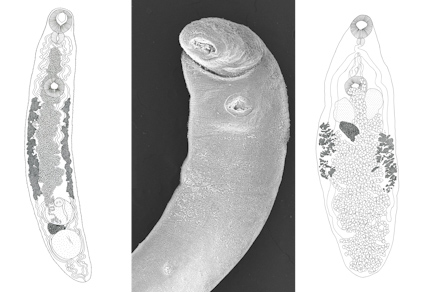
In the present study, helminths from six Didelphis virginiana and one Philander vossi are reported using morphological techniques (clearing, staining, and scanning electron microscopy). Additionally, the 28S rRNA sequences of individuals from nine helminth taxa are provided. Phylogenetic analyses were performed with the new 28S rRNA sequences to confirm the identification and the genealogical relationships of the parasites. Thirteen helminth taxa were identified, comprising the trematodes Brachylaima sp. and Platynosomum illiciens, the cestode Mathevotaenia sp., the nematodes Cruzia americana, Cruzia tentaculata, Viannaia arriaguensis, Viannaia sp., Travassostrongylus sp., Strongyloides sp., Turgida turgida, Trichuris minuta, and Trichuris sp., and the acanthocephalan Oligacanthorhynchus microcephalus. All opossums were infected with at least four helminth taxa. In total, 17 new 28S rRNA sequences from nine helminth taxa were provided. These data, combined with previous records in Mexico, increase the number of helminth taxa parasitizing D. virginiana and P. vossi to 41 and 29, respectively. However, these reports are incompletes and concentered in localities of some states. It is possible that new surveys in the Nearctic and even Neotropical regions will reveal a higher helminth diversity in these mammals in the country.
References
- Acosta-Virgen, K., López-Caballero, J., García-Prieto, L. & Mata-López, R. (2015) Helminths of three species of opossums (Mammalia, Didelphidae) from Mexico. ZooKeys, 511, 131–152. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.511.9571
- Adnet, F.A.O., Anjos, D.H.S., Menezes-Oliveira, A. & Lanfredi, R.M. (2009) Further description of Cruzia tentaculata (Rudolphi, 1819) Travassos, 1917 (Nematoda: Cruzidae) by light and scanning electron microscopy. Parasitology Research, 104, 1207–1211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1316-6
- Albino Miranda, S., López-Tello, E. & González-Romero, A. (2022) El tlacuache y sus primos mexicanos. Therya ixmana, 1, 89–91. https://doi.org/10.12933/therya_ixmana-22-241
- Amin, O.M. (1987) Key to the families and subfamilies of Acanthocephala, with the erection of a new class (Polyacanthocephala) and a new order (Polyacanthorhynchida). Journal of Parasitology, 73, 1216–1219. https://doi.org/10.2307/3282307
- Amin, O.M. (2013) Classification of the Acanthocephala. Folia Parasitologica, 60, 273–305. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2013.031
- Anderson, R.C., Chabaud, A.G. & Willmott, S. (2009) Keys to the nematode parasites of vertebrates: archival volume. CAB International, Oxfordshire, 463 pp.
- Aragón-Pech, R.A., Ruiz-Piña, H.A., Rodríguez-Vivas, R.I., Cuxim-Koyoc, A.D. & Reyes-Novelo, E. (2018) Prevalence, abundance and intensity of eggs and oocysts of gastrointestinal parasites in the opossum Didelphis virginiana Kerr, 1792 in Yucatan, Mexico. Helminthologia, 55, 119–126. https://doi.org/10.2478/helm-2018-0008
- Arcangeli, J., Light, J.E. & Cervantes, F.A. (2018). Molecular and morphological evidence of the diversification in the gray mouse opossum, Tlacuatzin canescens (Didelphimorphia), with description of a new species. Journal of Mammalogy, 99, 138–158. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmammal/gyx173
- Babero, B.B. (1960) Further studies on helminths of the opossum, Didelphis virginiana, with a description of a new species from this host. Journal of Parasitology, 46, 455–463. https://doi.org/10.2307/3275138
- Beddard, M.A. (1914) On two new species belonging to the genera Oochoristica and Linstowia, with remarks upon those genera. Proceedings of the General Meetings for the Scientici Business of the Zoological Society of London, 4, 263–283.
- Bray, R.A., Gibson, D.I. & Jones, A. (2008) Keys to the Trematoda. Vol. 3. CABI Publishing and The Natural History Museum, London, 824 pp. https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851995885.0000
- Buchanan, G.D. (1956) Occurrence of the cestode Mathevotaenia surinamensis (Cohn, 1902) Spasskii, 1951 in a North American armadillo. Journal of Parasitology, 42, 34–38. https://doi.org/10.2307/3274617
- Caira, J.N. & Jensen, K. (2017) Planetary biodiversity inventory (2008-2017): tapeworms from vertebrate bowels of the Earth. Natural History Museum, The University of Kansas, Lawrence, 463 pp.
- Campbell, M.L., Gardner, S.L. & Navone, G.T. (2003) A new species of Mathevotaenia (Cestoda: Anoplocephalidae) and other tapeworms from marsupials in Argentina. Journal of Parasitology, 89, 1181–1185. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-1778
- Cañeda Guzman, I.C. (1997) Parasitos de tres especies de marsupiales de la estación “Los Tuxtlas” y algunas zonas cercanas, Veracruz, México. B.S. Thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Ciudad de México, 193 pp.
- Crites, J.L. (1956) A redescription of Cruzia americana, a nematode parasitic in the opossum, Didelphis marsupialis virginiana. Journal of Parasitology 42, 68–72. https://doi.org/10.2307/3274625
- Cruz-Salazar, B., Ruiz-Montoya, L., Navarrete-Gutiérrez, D., Espinoza-Medinilla, E.E., Vázquez-Domínguez, E. & Vázquez, L.B. (2014) Diversidad genética y abundancia relativa de Didelphis marsupialis y Didelphis virginiana en Chiapas, México. Revista Mexicana de Biodiversidad 85, 251–261. https://doi.org/10.7550/rmb.36116
- Darriba, D., Taboada, G.L., Doallo, R. & Posada, D. (2012) jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nature Methods, 9, 772–772. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2109
- Diaw, O.T. (1976) Contribuition à l’étude de nématodes Trichostrongyloidea parasites de xenarthre, marsupiaux et rongeurs néotropicaux. Bulletin du Museum National d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris, 405, 1065–1089.
- Durette-Desset, M.-C. (2009) Strongylida. Trichostrongyloidea. In: Anderson, R.C., Chabaud, A.G. & Willmott, S. (Eds.), Keys to the nematodes parasites of vertebrates. CAB International, Wallingford, pp. 110–177. https://doi.org/10.1079/9781845935726.0110
- Durette-Desset, M.-C., Digiani, M.C., Kilani, M. & Geffard-Kuriyama, D. (2017) Critical revision of the Heligmonellidae (Nematoda: Trichostrongylina: Heligmosomoidea). Publications Scientifiques du Muséum National d’Historie Naturelle, Paris, 290 pp.
- Eckerlin, R.P. & Leigh, W.H. (1962) Platynosomum fastosum Kossack, 1910 (Trematoda: Dicrocoeliidae) in South Florida. Journal of Parasitology, 48, 49.
- Eslava-Araujo, A.G. (2005) Helmintos en la mastofauna silvestre de la Sierra de Monte Negro, Morelos, México. B.S. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Morelos, Morelos, 80 pp.
- García-Prieto, L., Falcón-Ordaz, J. & Guzmán-Cornejo, C. (2012) Helminth parasites of wild Mexican mammals: list of species, hosts and geographical distribution. Zootaxa, 3290 (1), 1–92. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3290.1.1
- García-Valle, J.L., Ramírez, J.A.R., García-Prieto, L., Ramírez-Hernández, C., Ramírez-Romero, R., Macedo-Barragán, R.J., López-Mayagoitia, A., Martínez-Burnes, J. & García-Márquez, L.J. (2023) Metazoan and protozoan pathology of wild opossums (Didelphis virginiana) in Mexico. Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira, 43, e07282. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-5150-pvb-7282
- García-Varela, M. & Nadler, S.A. (2005) Phylogenetic relationships of Palaeacanthocephala (Acanthocephala) inferred from SSU and LSU rDNA gene sequences. Journal of Parasitology, 91, 1401–1409. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-523R.1.
- Gibson, D.I., Jones, A. & Bray, R.A. (2002) Keys to the Trematoda. Vol. 1. CABI Publishing, The Natural History Museum, London, 521 pp. https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851995472.0000
- Gray, J.B. & Anderson, R.C. (1982) Development of Turgida turgida (Rudolphi, 1819) (Nematoda: Physalopteroidea) in the opossum (Didelphis virginiana). Canadian Journal of Zoology, 60, 1265–1274. https://doi.org/10.1139/z82-170
- Guerrero, R. (1985) Nematoda:Trichostrongyloidea parásitos de mamíferos silvestres de Venezuela. II. Revisión del género Viannaia Travassos, 1914. Memoria de la Sociedad de Ciencias Naturales La Salle, 44, 9–47.
- Hernández-Mena, D.I., García-Varela, M. & Pérez-Ponce de León, G. (2017) Filling the gaps in the classification of the Digenea Carus, 1863: systematic position of the Proterodiplostomidae Dubois, 1936 within the superfamily Diplostomoidea Poirier, 1886, inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial DNA sequences. Systematic Parasitology, 94, 833–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-017-9745-1
- Hodda, M. (2022) Phylum Nematoda: a classification, catalogue and index of valid genera, with a census of valid species. Zootaxa, 5114 (1), 1–289. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5114.1.1
- Hughes, R.C. (1940) The genus Oochoristica Luhe 1898. American Midland Naturalist, 23, 368–381. https://doi.org/10.2307/2420669
- Jiménez, F.A., Braun, J.K., Campbell, M.L. & Gardner, S.L. (2008) Endoparasites of fat-tailed mouse opossums (Thylamys: Didelphidae) from Northwestern Argentina and Southern Bolivia, with the description of a new species of tapeworm. Journal of Parasitology, 94, 1098–1102. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-1424.1
- Kearse, M., Moir, R., Wilson, A., Stones-Havas, S., Cheung, M., Sturrock, S., Buxton, S., Cooper, A., Markowitz, S., Duran, C., Thierer, T., Ashton, B., Meintjes, P. & Drummond, A. (2012) Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics, 28, 1647–1649. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts199
- Khalil, L.F., Jones, A. & Bray, R.A. (1994) Key to cestode parasites of vertebrates. CAB International, Wallingford, 746 pp. https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851988795.0000
- Kingston, N. & Tay, J. (1968) Rhopalias macracanthus y Rhopalias coronatus en Didelphis marsupialis. Anales del Instituto de Biología UNAM, Serie Zoología, 39, 167–168.
- Lee, S.-U., Huh, S., Sohn, W.-M. & Chai, J.-Y. (2004) Sequence comparisons of 28S ribosomal DNA and mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I of Metagonimus yokogawai, M. takahashii and M. miyatai. Korean Journal of Parasitology, 42, 129–135. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2004.42.3.129
- Li, L. (2019) Redescription of Cruzia americana Maplestone, 1930 (Nematoda: Kathlaniidae) a parasite of Didelphis virginiana (Kerr) (Mammalia: Didelphidae) in the USA. Systematic Parasitology, 96, 433–440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-019-09853-z
- Liu, D. (2013) Molecular detection of human parasitic pathogens. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 854 pp. https://doi.org/10.1201/b12264
- Lopes de Jesus, S. (2020) Diversidade da helmintofauna e sua relação com a biologia de Didelphis albiventris Lund, 1840 (Mammalia, Didelphimorphia). MSc. Thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Rio Grande do Sul, 133 pp.
- López-Caballero, J., Mata-López, R., García-Varela, M. & Pérez-Ponce de León, G. (2015) Genetic divergence of Oligacanthorhynchus microcephalus (Acanthocephala: Archiacanthocephala: Oligacanthorhynchidae), parasite of three species of opossum (Mammalia: Didelphidae) across Central and Southeastern Mexico. Comparative Parasitology, 82, 175–186. https://doi.org/10.1654/4742.1
- López-Caballero, J., Mata-López, R. & de León, G.P.P. (2019) Molecular data reveal a new species of Rhopalias Stiles & Hassall, 1898 (Digenea, echinostomatidae) in the common opossum, Didelphis marsupialis L. (Mammalia, Didelphidae) in the Yucatán peninsula, Mexico. ZooKeys, 2019, 145–163. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.854.34549
- Martínez-Flores, W. & Martínez-Salazar, E.A. (2016) Helmintos de Didelphis virginiana (Mammalia: Didelphidae) en Zacatecas. Ciencias Naturales y Exactas, 4, 305–310.
- Matey, V.E., Kuperman, B.I. & Kinsella, J.M. (2001) Scanning electron microscopy of Turgida turgida (Nematoda: Spiruroidea), parasite of the Virginia opossum, Didelphis virginiana, from Southern California. Journal of Parasitology, 87, 1199–1202. https://doi.org/10.2307/3285267
- Monet-Mendoza, A., Osorio-Sarabia, D. & García-Prieto, L. (2005) Helminths of the Virginia opossum Didelphis virginiana (Mammalia: Didelphidae) in Mexico. Journal of Parasitology, 91, 213–219. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-273R
- Nadler, S.A., Carreno, R.A., Adams, B.J., Kinde, H., Baldwin, J.G. & Mundo-Ocampo, M. (2003) Molecular phylogenetics and diagnosis of soil and clinical isolates of Halicephalobus gingivalis (Nematoda: Cephalobina: Panagrolaimoidea), an opportunistic pathogen of horses. International Journal for Parasitology, 33, 1115–1125. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7519(03)00134-6
- Nguyen, H.M., Van Hoang, H. & Ho, L.T. (2017) Platynosomum fastosum (Trematoda: Dicrocoeliidae) from cats in Vietnam: morphological redescription and molecular phylogenetics. Korean Journal of Parasitology, 55, 39. https://doi.org/10.3347/KJP.2017.55.1.39
- Ortíz-Villaseñor, A. (2000) Fauna parasitaria de Didelphis virginiana (Marsupialia: Didelphidae) y su importancia zoonótica en el oeste del estado de Morelos. MSc. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Morelos, Morelos, 61 pp.
- Pinto, H.A., Mati, V.L.T., Pujoni, D.G.F. & Melo, A.L. (2017) Platynosomum illiciens (Trematoda: Dicrocoeliidae) in captive black-tufted marmoset Callithrix penicillata (Primates: Cebidae) from Brazil: a morphometric analyses with taxonomic comments on species of Platynosomum from nonhuman primates. Journal of Parasitology, 103, 14–21. https://doi.org/10.1645/16-1
- Pinto, H.A., Melo, A.L. & Mati, V.L.T. (2022) Platynosomum illiciens. Trends in Parasitology, 38, 188–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2021.08.004
- Poulin, R., Hay, E. & Jorge, F. (2019) Taxonomic and geographic bias in the genetic study of helminth parasites. International Journal for Parasitology, 49, 429–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2018.12.005
- Premvati, G. & Bair, T.D. (1979) Trematode parasites of the opossum, Didelphis virginiana, from Florida. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 46, 207–212.
- Ramírez-Cañas, S.A., George-Nascimento, M., García-Prieto, L. & Mata-López, R. (2019) Helminth community structure of the gray four-eyed opossum Philander opossum (Mammalia: Didelphidae) in the neotropical portion of Mexico. Journal of Parasitology, 105, 624–629. https://doi.org/10.1645/18-195
- Ramírez-Cañas, S.A., López-Caballero, J.D. & Mata-López, R. (2021) Morphological and molecular data reveal two new species of Viannaia (Nematoda: Viannaiidae), parasitizing opossums (Mammalia: Didelphidae) in Mexico. Journal of Parasitology, 107, 388–403. https://doi.org/10.1645/18-199
- Ramírez-Pulido, J., González-Ruiz, N., Gardner, A.L. & Arroyo-Cabrales, J. (2014) List of recent land mammals of Mexico, 2014. Special Publications Museum of Texas Tech University 63. Museum of Texas Tech University, Lubbock, Texas, 76 pp. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.142891
- Řežábková, L., Brabec, J., Jirků, M., Dellerba, M., Kuchta, R., Modrý, D., Parker, W. & Jirků Pomajbíková, K. (2019) Genetic diversity of the potentially therapeutic tapeworm Hymenolepis diminuta (Cestoda: Cyclophyllidea). Parasitology International, 71, 121–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2019.04.009
- Richardson, D.J., Gardner, S.L. & Allen, J.W. (2014) Redescription of Oligacanthorhynchus microcephalus (Rudolphi, 1819) Schmidt 1972 (syn. Oligacanthorhynchus tortuosa (Leidy, 1850) Schmidt 1972) (Acanthocephala: Oligacanthorhynchidae). Comparative Parasitology, 81, 53–60. https://doi.org/10.1654/4673.1
- dos Santos, K.R., Carlos, B.C., Paduan, K.S., Kadri, S.M., Barrella, T.H., Amarante, M.R.V., Ribolla, P.E.M. & da Silva, R.J. (2010) Morphological and molecular characterization of Strongyloides ophidiae (Nematoda, Strongyloididae). Journal of Helminthology, 84, 136–142. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X09990381
- Scheibel, R., Catzeflis, F. & Jiménez, F. (2014) The relationships of marsupial-dwelling Viannaiidae and description of Travassostrongylus scheibelorum sp. n. (Trichostrongylina: Heligmosomoidea) from mouse opossums (Didelphidae) from French Guiana. Folia Parasitologica, 61, 242–254. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2014.032
- Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. (2014) Handbook of zoology. Vol. 2. Nematoda. De Gruyter, Berlin, 759 pp. https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110274257
- Shylla, J.A., Ghatani, S. & Tandon, V. (2013) Utility of divergent domains of 28S ribosomal RNA in species discrimination of paramphistomes (Trematoda: Digenea: Paramphistomoidea). Parasitology Research, 112, 4239–4253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3616-8
- Sikes, R.S. & the Animal Care and Use Committee of the American Society of Mammalogists (2016) 2016 Guidelines of the American Society of Mammalogists for the use of wild mammals in research and education. Journal of Mammalogy, 97, 663–688. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmammal/gyw078
- Speare, R. (1989) Identification of species of Strongyloides. In: Grove, D.I. (Ed.), Strongyloidiasis: a major roundworm infection of man. Taylor and Francis, London, pp. 11–83.
- Stamatakis, A. (2006) RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics, 22, 2688–2690. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btl446
- Tamura, K., Stecher, G. & Kumar, S. (2021) MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 38, 3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120
- Thaenkham, U., Chaisiri, K. & Hui En Chan, A. (2022) Molecular systematics of parasitic helminths. Springer, Singapore, 396 pp. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-1786-8
- Thompson, J.D., Higgins, D.G. & Gibson, T.J. (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic acids Research, 22, 4673–4680. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/22.22.4673
- Vicente, J.J., Rodrigues, H.O., Gomes, D.C. & Pinto, R.M. (1997) Nematóides do Brasil. Parte V: nematóides de mamíferos. Revista Brasileira de Zoologia, 14, 1–452. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-81751997000500001
- Viney, M.E., Ashford, R.W. & Barnish, G. (1991) A taxonomic study of Strongyloides Grassi, 1879 (Nematoda) with special reference to Strongyloides fuelleborni von Linstow, 1905 in man in Papua New Guinea and the description of a new subspecies. Systematic Parasitology, 18, 95–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00017661
- Wolfgang, R.W. (1951) Studies on the endoparasitic fauna of Trinidad mammals. VIII. Parasites of marsupials. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 29, 352–373. https://doi.org/10.1139/z51-031