Abstract
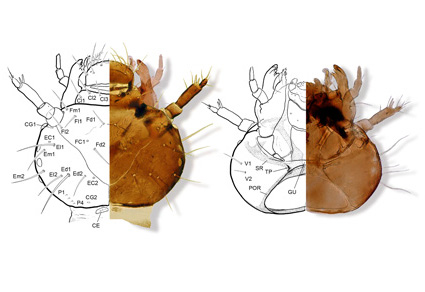
The larvae of three species of the South African endemic water beetle genus Prosthetops Waterhouse, 1879 are described and illustrated for the first time. The second and third instar larvae of Prosthetops nitens (Péringuey, 1892), as well as third instar larva of P. megacephalus (Boheman, 1851) and P. wolfbergensis Bilton, 2013, are treated here. These three species share a combination of morphological and chaetotaxic characters that can be used for positive identification of larvae of this genus: head capsule with pores FC1 present, second antennomeres with two well-developed distal sensory appendages, maxillary seta Cdo1 very reduced, thoracic subprimary setae Dd’ absent, subprimary setae Dc’ minute and inserted on the boundary between pretergal and tergal areas, urogomphi moderately separated at the base, anal lobe with well-developed dorsal, lateral and ventral plates, and a lack of anal hooks. Some insights on the gut-contents of the larva of P. wolfbergensis are offered and an unusual urogomphal malformation observed in a larva of P. nitens is also described and illustrated. These are the first described larvae of the subfamily Prosthetopinae, and their morphology is compared to that of other known hydraenid larvae.
References
- An, X. & Xie, B. (2022) Phytoliths from woody plants: A review. Diversity, 14 (339), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050339
- Bertrand, H. (1962) Contribution à l’étude des premiers états des Coléoptères aquatiques de la région éthiopienne (4e note). Bulletin de l’Institut fondamental d’Afrique noire, Sèrie A, 24 (4) 1065-1114.
- Bertrand, H. (1972) Larves et nymphes des coléoptères aquatiques du globe. F. Paillart, France, 804 pp.
- Beutel, R.G., Maddison, D.R. & Haas, A. (2003) Phylogenetic analysis of Myxophaga (Coleoptera) using larval characters. Systematic Entomology, 24, 171–192. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3113.1999.00075.x
- Bilton, D.T. (2013) Prosthetops wolfbergensis sp. nov.—a giant amongst the ‘minute moss beetles, with new data on other members of the genus (Coleoptera, Hydraenidae). Zootaxa, 3666 (3), 345–357. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3666.3.5
- Bilton, D.T. (2014) New species and new records of Pterosthetops: eumadicolous water beetles of the South African Cape (Coleoptera, Hydraenidae). Zootaxa, 3811(4), 438–462. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3811.4.2
- Bilton, D.T., Jäch, M.A., Ribera, I. & Toussaint, E.F.A. (2022) Minute moss beetles in the Southern Hemisphere: Molecular phylogeny, historical biogeography and habitat shifts (Coleoptera: Hydraenidae). Systematic Entomology, 48, 142–162. https://doi.org/10.1111/syen.12567
- Deler-Hernández, A. & Delgado, J.A. (2017) The Hydraenidae of Cuba (Insecta: Coleoptera) II: Morphology of preimaginal stages of six species and notes on their biology. Zootaxa, 4238 (4), 451–498. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4238.4.1
- Delgado, J.A. & Archangelsky, M. (2005) Description of the larval stages of Gymnochthebius jensenhaarupi and phylogenetic analysis of the relationships with other species of the subfamily Ochthebiinae (Coleoptera: Hydraenidae). European Journal of Entomology, 102 (2), 231–240. https://doi.org/10.14411/eje.2005.036
- Delgado, J.A. & Palma, R.L. (1998) Larval stages of three Meropathus species (Coleoptera: Hydraenidae: Ochthebiinae) from New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 25 (4), 409–419. https://doi.org/10.1080/03014223.1998.9518164
- Delgado, J.A. & Palma, R.L. (2004) Larval stages of Podaena latipalpis from New Zealand and phylogenetic relationships of the subfamily Orchymontiinae based on larval characters (Insecta: Coleoptera: Hydraenidae). New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 31: 327–242. https://doi.org/10.1080/03014223.2004.9518386
- Jäch, M.A., Beutel, R., Delgado, J.A. & Díaz, J.A. (2016) Hydraenidae. In: Beutel, R. & Leschen, R.A.B. (Eds.), Handbook of Zoology. Vol. 4. 2nd Edition. Arthropoda Insecta. Part. 38. Coleoptera, Beetles. Vol. 1. Morphology and Systematics (Archostemata, Adephaga, Myxophaga, Polyphaga partim). De Gruyter, Berlin, pp. 316–345.
- McLachlan, R.J. (1981) Food sources and foraging tactics in tropical rain pools. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 71, 265–277. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1981.tb01133.x
- Perkins, P.D. (1980) Aquatic beetles of the family Hydraenidae in the Western Hemisphere: classification, biogeography and inferred phylogeny (Insecta: Coleoptera). Quaestiones Entomologicae, 16, 3–554. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6184550
- Perkins, P.D. (2008) New species and new collection records of Prosthetopine water beetles from southern Africa (Coleoptera: Hydraenidae). Zootaxa, 1864, 1–124. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.1864.1.1
- Perkins, P.D. & Balfour-Browne, J. (1994) A contribution to the taxonomy of aquatic and humicolous beetles of the family Hydraenidae in southern Africa. Fieldiana Zoology, 77, 1–159. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.3533
- Turner, C.R. (2007) Water beetles associated with reservoirs on Table Mountain, Cape Town: implications for conservation. Journal of Insect Conservation, 11, 75–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10841-006-9020-2