Abstract
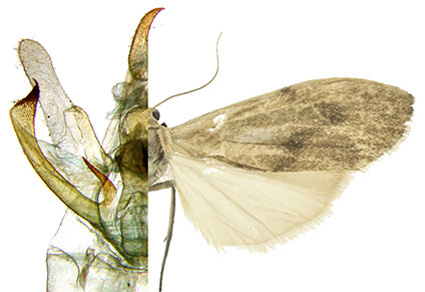
As part of a study of the genus Archithosia Birket-Smith as a whole, this article focuses on the subgenus Eurythosia Krüger, describing a new species from Uganda: Archithosia henricus Durante, Potenza, and Pellegrino n. sp. The authors compare this new species with the other five species previously included in the subgenus, basing their diagnosis primarily on the male genitalia.
References
- Bendib, A. & Minet, J. (1999) Lithosiine main lineages and their possible interrelationships. I. Definition of new or resurrected tribes (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). Annales de la Société Entomologique de France, 35 (3–4), 241–263.
- Birket-Smith, J. (1965) A revision of the West African Eilemic moths, based on the male genitalia (Lep., Arctiidae, Lithosinae; incl. gen. Crocosia, Eilema, Lithosia, Pelosia, Phryganopsis a. o.). Haile Sellassie I university. Papers from the Faculty of science, Series C (Zoology), 1, 1–161.
- Chapman, C.A., Struhsaker, T.T. & Lambert, J.E. (2005) Thirty years of research in Kibale National Park, Uganda, reveals a complex picture for conservation. International Journal of Primatology, 26, 539–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-005-4365-z
- Dang, P.T. (1993) Vesicas of selected Tortricid and small Lepidopterous species, with descriptions of new techniques of vesica eversion (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae, Oecophoridae, Gelechiidae, and Nepticulidae). The Canadian Entomologist, 125 (5), 785–799. https://doi.org/10.4039/Ent125785-5
- Debauche H.R. (1942) Lepidoptera, Heterocera. Exploration du Parc National Albert. Mission G. F. De Witte (1933–1935), 41, 17–18.
- Durante, A. & Apinda-Legnouo, E.A. (2022) Fifth contribution to the study of the Lithosiini of Gabon: two genera new for Gabon, with a description of two new species (Lepidoptera: Erebidae: Arctiinae). Zootaxa, 5091 (3), 416–428. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5091.3.2
- Durante, A. (2008) Asuroides, a new genus of lithosiine moths (Lepidoptera, Arctiidae, Lithosiinae). Zootaxa, 1713 (1), 53–68. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.1713.1.5
- Edwards, W.I., Popescu, V.D., Guma, N., Agaba, H., Balyesiima, G., Nakami, L. & Stevens, N.J. (2023) Living at the edge: home range patterns of the Buraiga Chimpanzee Community, Kibale National Park, Uganda. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 11, 1267688. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2023.1267688
- Holloway, J.D. (2001) The moths of Borneo [Part 7]: Arctiidae, Lithosiinae. Malayan Nature Journal, 55, 279–486.
- Holloway, J.D., Kibby, G. & Peggie, D. (2001) The Families of Malesian Moths and Butterflies. Fauna Malesiana Handbook. Brill, Leiden, xi + 455 pp. https://doi.org/10.1163/9789004475595
- Johns, B.G. (1996) Responses of chimpanzees to habituation and tourism in the Kibale Forest, Uganda. Biological Conservation, 78, 257–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3207(96)00044-4
- Klots, A.B. (1970) Lepidoptera. In: Tuxen, S.L. (Ed.), Taxonomist’s glossary of genitalia in insects. 2nd Edition. II. Munksgaard, Copenhagen, pp. 115–130.
- Kristensen, N.P. (2003) Skeleton and muscles: adults. In: Kristensen, N.P. (Ed.), Lepidoptera, Moths and Butterflies. Vol. 2. Morphology, Physiology, and development. Part 36. In: Fischer, M. (Ed.), Handbook of Zoology. Vol. IV. Anthropoda: Insecta. W. de Gruyter, Berlin and New York, pp. 39–131. https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110893724.39
- Krüger, M. (2015) Generic classification of Afrotropical footman moths sensu stricto (Lepidoptera: Erebidae: Arctiinae: Lithosiini (partim)). Transvaal Museum Monograph, 15, 1–176.
- Kühne, L. (2005) Neue Taxa und Synonyme afrikanischer Arctiidae (Lepidoptera). Lambillionea, 105 (3), 486–493.
- Kühne, L. (2007) Beschreibung neuer Flechtenbärenarten aus Afrika nebst taxonomischen Anmerkungen (Arctiidae: Lithosiinae). In: Hacker, H. (Ed.), Lepidoptera Africana Part 3. Esperiana Memoir, 3, pp. 353–394, pls. 44, 45.
- Mackenzie, C.A. (2012) Accruing benefit or loss from a protected area: Location matters. Ecological Economics, 76, 119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2012.02.013
- Opito, E.A., Alanko, T., Kalbitzer, U., Nummelin, M., Omeja, P., Valtonen, A. & Chapman, C.A. (2023) 30 years brings changes to the arthropod community of Kibale National Park, Uganda. Biotropica, 55, 529–539. https://doi.org/10.1111/btp.13206
- Osmaston, H.A. (1959) Working plan for the Kibale and Itwara forests. Ugandan Forest Department.
- Robinson, G.S. (1976) The preparation of slides of Lepidoptera genitalia with special reference to the microlepidoptera. Entomologist’s Gazette, 27, 127–132.
- Rode, K.D., Chapman, C.A., Mcdowell, L.R. & Stickler, C. (2006) Nutritional correlates of population density across habitats and logging intensities in redtail monkeys (Cercopithecus ascanius). Biotropica, 38, 625–634. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7429.2006.00183.x
- Scoble, M.J. (1992) The Lepidoptera. Form, function and diversity. The Natural History Museum in association with Oxford University Press, Oxford, XI + 404 pp.
- Strand, E. (1912a) Zur Kenntnis äthiopischer Lithosiinae. Archiv für Naturgeschichte, 78 (A: 7), 174–175. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.27906
- Strand, E. (1912b) Zoologische Ergebnisse der Expedition des Herrn G. Tessmann nach Süd-Kamerun und Spanisch-Guinea. Lepidoptera III. Archiv für Naturgeschichte, 78 (A: 9), 97–98.
- Strand, E. (1912c) Weitere Schmetterlinge aus Kamerun, gesammelt von Herrn Ingenieur E. Hintz. Archiv für Naturgeschichte, 78 (A: 12) 123.
- Struhsaker, T.T. (1997) Ecology of an African rain forest: Logging in Kibale and the conflict between conservation and exploitation. University Press of Florida, Gainesville, Florida, 456 pp.
- Struhsaker, T.T. (1999) Ecology of an African Rain Forest: Logging in Kibale and the Conflict Between Conservation and Exploitation. University Press of Florida, Gainesville, Florida, 434 pp.
- Uganda Wildlife Authority (2015) Kibale National Park - General Management Plan (2015–2025). Available from: https://www.ugandawildlife.org/wildlife-a-conservation-2/researchers-corner/general-managementplans?download=15:kibale national-park_gmp (accessed 26 June 2024)
- Winter, W.D. (2000) Basic techniques for observing and studying moths and butterflies. The Lepidopterists’ Society Memoir, 5, 1–XVIII + 1–444.
- Wootton, R.J. (1979) Function, homology and terminology in insect wings. Systematic Entomology, 4, 81–93. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3113.1979.tb00614.x