Abstract
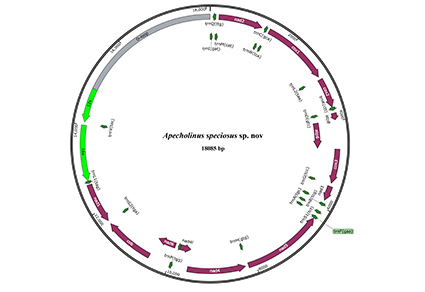
A new species, Apecholinus speciosus Sun & Liu, sp. nov. collected from Mangshan, Hunan Province, China, is described. Illustrations of taxonomically important characters and photographs of the habitus are provided. The new species is compared to Apecholinus imitator Smetana & Hu, 2019. The complete mitochondrial genome of A. speciosus was sequenced, assembled, and annotated. Phylogenetic analysis based on mitochondrial genomes showed that two Apecholinus species form a clade sister to Ocypus and Dinothenarus, and they all belong to the Ocypus lineage.
References
- Allio, R., Schomaker-Bastos, A., Romiguier, J., Prosdocimi. F., Nabholz, B. & Delsuc, F. (2020) Mitofinder: efficient automated large-scale extraction of mitogenomic data in target enrichment phylogenomics. Molecular Ecology Resources, 20 (4), 892–905. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.13160
- Bernhauer, M. (1933) Neuheiten der chinesischen Staphylinidenfauna. Wiener Entomologische Zeitung, 50, 25–48.
- Bernt, M., Donath, A., Jühling, F., Externbrink, F., Florentz, C., Fritzsch, G., Pütz, J., Middendorf, M. & Stadler, P.F. (2013) MITOS: improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 69 (2), 313–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2012.08.023
- Brunke, A.J. & Smetana, A. (2019) A new genus of Staphylinina and a review of major lineages (Staphylinidae: Staphylininae: Staphylinini). Systematics and Biodiversity, 17 (8), 745–758. https://doi.org/10.1080/14772000.2019.1691082
- Hernando, C. & Andújar, C. (2021) Mitogenomic phylogenetics of Diochus occultus n. sp., a palaeoendemic endogean species within the tribe Diochini (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae: Staphylininae). Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research, 59 (1), 78–93. https://doi.org/10.1111/jzs.12425
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S., Minh, B.Q., Wong, T.K., Von Haeseler, A. & Jermiin, L.S. (2017). ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nature Methods, 14 (6), 587–589. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4285
- Katoh, K. & Standley, D.M. (2013) MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30 (4), 772–780. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst010
- Kearse, M., Moir, R., Wilson, A., Stones-Havas, S., Cheung, M., Sturrock, S., Buxton, S., Cooper, A., Markowitz, S., Duran, C., Thierer, T., Ashton, B., Meintjes, P. & Drummond, A. (2012) Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics, 28 (12), 1647–1649. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts199
- Nguyen, L.T., Schmidt, H.A., Von Haeseler, A. & Minh, B.Q. (2015) IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Molecular Biology Evolution, 32 (1), 268–274. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu300
- Ranwez, V., Harispe, S., Delsuc, F. & Douzery, E.J. (2011) MACSE: Multiple Alignment of Coding SEquences Accounting for Frameshifts and Stop Codons. PloS one, 6 (9), e22594. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0022594
- Senda, Y. & Han, C. (2023) Apecholinus septentrionalis sp. n. from North Korea. Koleopterologische Rundschau, 93, 181–185. [https://www.researchgate.net/publication/375360822]
- Smetana, A. (2003) Contributions to the knowledge of the genera of the “Staphylinus-complex” (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae) of China. Part 4. Key to Chinese genera, treatment of the genera Collocypus gen. n., Ocychinus gen. n., Sphaerobulbus gen. n., Aulacocypus and Apecholinus, and comments on the genus Protocypus. Folia Heyrovskyana, 11, 57–135.
- Smetana, A. (2018) Review of the genera Agelosus Sharp, 1889, Apostenolinus Bernhauer, 1934 and Apecholinus Bernhauer, 1933 (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae: Staphylinini: Staphylinina). Zootaxa, 4471 (2), 201–224. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4471.2.1
- Smetana, A. & Davies, A. (2000) Reclassification of the north temperate taxa associated with Staphylinus sensu lato, including comments on relevant subtribes of Staphylinini (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae). American Museum Novitates, 3287, 1–88. https://doi.org/10.1206/0003-0082(2000)287%3C0001:ROTNTT%3E2.0.CO;2
- Smetana, A. & Hu, F.S. (2019) The genera Agelosus Sharp, 1889 and Apecholinus Bernhauer, 1933 in Taiwan (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae: Staphylinini: Staphylinina). Zootaxa, 4638 (3), 181–185. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4638.3.4
- Talavera, G. & Castresana, J. (2007) Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Systematic Biology, 56 (4), 564–577. https://doi.org/10.1080/10635150701472164
- Zhang, D., Gao, F.L., Jakovlić, I., Zou, H., Zhang, J., Li, W.X. & Wang, G.T. (2020) PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Molecular Ecology Resources, 20 (1), 348–355. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.13096