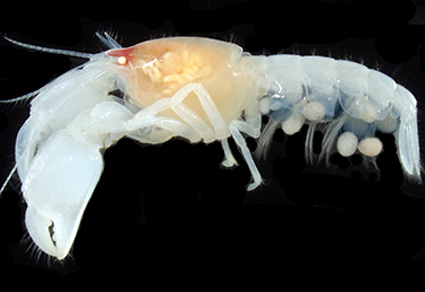
Abstract
Two new species of the axiid shrimp genus Eiconaxius Bate, 1888, are described from seamounts in the Nishi-Shichito Ridge, northwestern Pacific off Japan, during recent cruises of R/V Kaimei of the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology, exploring the marine protected area (MPA). Eiconaxius latirostrum sp. nov. is described on the basis of three specimens from Shoho Seamount at depths of 402–456 m; and E. kaimei sp. nov. is described on the basis of a single ovigerous female from An’ei Seamount at a depth of 888 m. The status of the two new taxa was assessed by phylogenetic analyses employing two mitochondrial markers (16S rRNA and COI genes) and morphological comparison. Specimens of the two new species lived in colonies of unidentified farreid sponges. This study contributes to documenting the benthic invertebrate fauna of the Japanese MPA as a baseline data for conservation.
References
- Bate, C.S. (1888) Report on the Crustacea Macrura collected by H. M. S. Challenger during the years 1873–76. Report on the Scientific Results of the Voyage of H. M. S. Challenger during the years 1873–76. Zoology, 24, 1–942. [http://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/2020399]
- Borradaile, L.A. (1916) Crustacea. Part I. Decapoda. British Antarctic (‘Terra Nova’) Expedition, 1910, Natural History Reports, Zoology, 3, 75–110. [http://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/31659725]
- Bouvier, E.L. (1905) Sur les Thalassinidés recueillis par le Blake dans la mer des Antilles et le golfe du Mexique. Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires de Séances de l’Académie des Sciences, Paris, 141, 802–806. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.28552
- Castresana, J. (2000) Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 17, 540–552. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026334
- Crandall, K.A. & Fitzpatrick, J.F. (1996) Crayfish molecular systematics: using a combination of procedures to estimate phylogeny. Systematic Biology, 45, 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/45.1.1
- Darriba, D., Posada, D., Kozlov, A. M., Stamatakis, A., Morel, B. & Flouri, T. (2019) ModelTest-NG: A new and scalable tool for the selection of DNA and protein evolutionary models. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 37, 291–294. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msz189
- DecaNet eds. (2024) Eiconaxius Spence Bate, 1888. Available from: https://www.decanet.info/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=390862 (accessed 30 June 2024)
- Edgar, R.C. (2004) MUSCLE: a multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinformatics, 5, 113. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-5-113
- Edler, D., Klein, J., Antonelli, A. & Silvestro, D. (2021) raxmlGUI 2.0: A graphical interface and toolkit for phylogenetic analyses using RAxML. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 12, 373–377. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.13512
- Faxon, W. (1896) Reports on the results of dredging, under the supervision of Alexander Agassiz, in the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, and on the east coast of the United States, 1877 to 1880, by the U. S. Coast Survey Steamer “Blake”, Lieut.-Commander C. D. Sigsbee, U. S. N. , and Commander J. R. Bartlett, U. S. N. , commanding. XXXVII: Supplementary notes on the Crustacea. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology, 30, 153–166, pls. 1 + 2.
- Felsenstein, J. (1985) Confidence-limits on phylogenies—an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution, 39 (4), 783–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
- Folmer, O., Black, M., Hoeh, W., Lutz, R. & Vrijenhoek, R. (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology, 3, 294–299.
- Huxley, T.H. (1879). On the classification and the distribution of the crayfishes. Proceedings of the Scientific Meetings of the Zoological Society of London, 1878 (3), 752–788. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7998.1878.tb08020.x
- Kensley, B. (1996) New thalassinidean shrimp from the Pacific Ocean (Crustacea: Decapoda: Axiidae and Calocarididae). Bulletin of Marine Science, 59, 469–489.
- Komai, T. (2024) Reappraisal of Eiconaxius farreae Ortmann, 1891 and Eiconaxius mortenseni Sakai, 1992 (Decapoda: Axiidea: Axiidae), with description of a new species from Japan. Zootaxa, 5419 (4), 495–524. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5419.4.2
- Komai, T. & Matsuzaki, K. (2022) Three new species of the thorid shrimp genus Lebbeus White, 1847 (Decapoda: Caridea) from Nemuro Strait, Hokkaido, Japan, with supplemental note on L. fujimotoi Matsuzaki, Hibino & Komai, 2015. Zootaxa, 5133 (2), 151–181. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5133.2.1
- Komai, T. & Tsuchida, S. (2012) Rediscovery and redescription of a sponge-associated axiid shrimp, Eiconaxius acutifrons Bate, 1888 (Crustacea: Decapoda: Axiidea). Zootaxa, 3393 (1), 27–40. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3393.1.2
- Komai, T., Tsuchida, S & Fujiwara, Y. (2022) New record of a rarely collected caridean shrimp Bathypalaemonella pandaloides (Rathbun, 1906) (Decapoda: Bathypalaemonellidae) from the West Mariana Ridge, northwestern Pacific. Zootaxa, 5129 (2), 272–284. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5129.2.7
- Komai, T., Tsuchida, S. & Fujiwara, Y. (2023a) A new deep-sea palaemonid shrimp assigned to Periclimenes Costa, 1844 (Decapoda: Caridea) from the West Mariana Ridge, northwestern Pacific. Zootaxa, 5231 (4), 376–392. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5231.4.2
- Komai, T., Tsuchida, S & Fujiwara, Y. (2023b) Squat lobsters of the superfamily Chirostyloidea (Decapoda: Anomura) from seamounts on the Nishi-Shichito and Mariana ridges, North-West Pacific off Japan, with descriptions of two new species. Zootaxa, 5293 (1), 45–73. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5293.1.2
- Komai, T., Tsuchida, S. & Fujiwara, Y. (2023c) New record of two species of munidid squat lobster (Decapoda: Anomura) from the North-West Pacific off Japan. Zootaxa, 5369 (2), 239–254. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5369.2.4
- Kou, Q., Xu, P., Poore, G.C.B., Li, X. & Wang, C (2020) A new species of the deep-sea sponge-associated genus Eiconaxius (Crustacea: Decapoda: Axiidae), with new insights into the distribution, speciation, and mitogenomic phylogeny of axiidean shrimps. Frontiers in Marine Science, 7, 469. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2020.00469
- Man, J.G. de (1907) Diagnoses of new species of macrurous decapod Crustacea from the ‘Siboga-Expedition’. II. Notes from the Leyden Museum, 29, 127–147. [http://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/10817187]
- Man, J.G. de (1925) Axiopsis (Eiconaxius) sibogae n. sp. Zoologische Mededeelingen, Leiden, 8, 218–219.
- Ministry of the Environment (2020a) Mid-Ocean Ridge/West Mariana Ridge Northern Offshore Seafloor Natural Environment Conservation Area Designation and Conservation Plan. Ministry of the Environment, Tokyo, 8 pp. [in Japanese]
- Ministry of the Environment (2020b) West Seven Island Ridge Offshore Submarine Natural Environment Conservation Area Designation and Conservation Plan. Ministry of the Environment, Tokyo, 8 pp. [in Japanese]
- Ortmann, A.E. (1891) Die Decapoden-Krebse des Strassburger Museums mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der von Herrn Dr. Döderlein dei Japan und bei den Liu-Kiu-Inseln gesammelten und z. Z. im Strassburger Museum aufbewahrten Formen. III. Theil. Die Abtheilungen der Reptantia Boas: Homaridae, Loricata und Thalassinidea. Zoologische Jahrbücher. Abteilung für Systematik, 6, 1–58. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.26455
- Poore, G.C.B. (2017) Synonymy and problematic species of Eiconaxius Spence Bate, 1888, with descriptions of new species (Crustacea: Decapoda: Axiidea: Axiidae). Zootaxa, 4231 (3), 364–376. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4231.3.4
- Poore, G.C.B. (2018) Caribbean species of Eiconaxius (Decapoda: Axiidea: Axiidae). Zootaxa, 4524 (1), 139–146. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4524.1.11
- Poore, G.C.B. (2020) Axiid and micheleid lobsters from Indo-West Pacific deep-sea environments (Crustacea: Decapoda: Axiidea: Axiidae, Micheleidae). In: Corbari, L., Ahyong, S.T. & Chan, T.-Y. (Eds.), Deep-Sea Crustaceans from Papua New Guinea. Tropical Deep-Sea Benthos Vol. 31. Mémoires du Muséum national d’Histoire naturelle, Paris, 213, pp. 259–367.
- Poore, G.C.B. & Dworschak, P.C. (2018) The Eiconaxius cristagalli species complex (Decapoda, Axiidea, Axiidae). Memoirs of Museum Victoria, 77, 105–120. https://doi.org/10.24199/j.mmv.2018.77.06
- Rambaut, A. (2016) FigTree. Version 1.4.1. Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh. Available from: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed 14 January 2023)
- Sakai, K. (1992) Axiid collections of the Zoological Museum, Copenhagen, with the description of one new genus and six new species (Axiidae, Thalassinidea, Crustacea). Zoologica Scripta, 21, 157–180. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-6409.1992.tb00318.x
- Sakai, K. (2014) Axioidea material collected by the Japanese R/V-s “Hakuhou-Maru” and “Nagasaki-Maru” in the east China Sea with a revised key to the families of the superfamily Axioidea Huxley, 1879 (Decapoda, Callianassidea). Crustaceana, 87, 609–626. https://doi.org/10.1163/15685403-00003302
- Schubart, C.D., Cuesta, J.A. & Felder, D.L. (2002) Glyptograpsidae, a new brachyuran family from Central America: larval and adult morphology, and a molecular phylogeny of the Grapsoidea. Journal of Crustacean Biology, 22 (1), 28–44. https://doi.org/10.1163/20021975-99990206
- Tamura, K., Stecher, G. & Kumar, S. (2021) MEGA 11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 38 (7), 3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120