Abstract
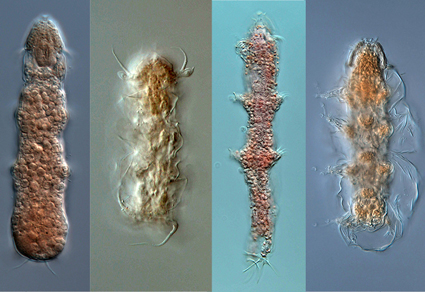
To date, only eight species of marine tardigrades have been recorded from the Southern Ocean. A total of 1210 tardigrade specimens were collected during various marine expeditions with R/V POLARSTERN: ANDEEP-1, ANDEEP-2, ANDEEP-3 and ANDEEP-SYSTCO. The sampled tardigrades belong to five families (Batillipedidae, Coronarctidae, Halechiniscidae, Styraconyxidae and Echiniscoididae), seven genera (Batillipes, Coronarctus, Moebjergarctus, Angursa, Styraconyx, Tholoarctus, Isoechiniscoides) and 15 species (Batillipes wyedeleinorum, Coronarctus dissimilis, Coronarctus tenellus, Coronarctus cf. tenellus, Moebjergarctus clarionclippertonensis, Angursa sp., A. abyssalis, A. antarctica, A. capsula, A. lanceolata, A. lingua, Styraconyx qivitoq, S. takeshii, Tholoarctus oleseni, Isoechiniscoides aff. sifae sp. can.). For the genera Batillipes, Coronarctus, Moebjergarctus, Tholoarctus and Isoechiniscoides, these new distribution data are the southernmost records and first reports from the Southern Ocean. Furthermore, the genera Styraconyx, Batillipes and Isoechiniscoides are reported from the abyssal zone for the first time. These new findings significantly expand our previous knowledge of both geographic and bathymetric distribution of marine Tardigrada.
References
- Accogli, G., Gallo, M., D’Addabbo, R. & Hansen, J.G. (2011) Diversity and ecology of the marine tardigrades along the Apulian Coast. Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research, 49 (S1), 53–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0469.2010.00598.x
- Arenas, C.T.P. & Fahrbach, E. (2005) ANT-XXII/3. s.n., s.l. [unknown pagination]
- Artois, T., Fontaneto, D., Hummon, W.D., McInnes, S.J., Todaro, M.A., Sørensen, M.V. & Zullini, A. (2011) Ubiquity of microscopic animals? Evidence from the morphological approach in species identification. In: Fontaneto, D. (Ed.), Biogeography of microscopic organisms. Is everything small everywhere? Systematics Association & Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 252–254. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511974878.014
- Bai, L., Wang, X., Zhou, Y., Lin, S., Meng, F. & Fontoura, P. (2020) Moebjergarctus clarionclippertonensis, a new abyssal tardigrade (Arthrotardigrada, Halechiniscidae, Euclavarctinae) from the Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone, North-East Pacific. Zootaxa, 4755 (3), 561–575. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4755.3.8
- Barnett, P.R.O., Watson, J. & Connelly, D. (1984) A multiple corer for taking virtually undisturbed samples from shelf, bathyal and abyssal sediments. Oceanologica Acta, 7 (4), 399–408.
- Bartels, P.J., Kaczmarek, Ł., Roszkowska, M. & Nelson, D.R. (2015) Interactive map of marine tardigrades of the world. Available from: https://paul-bartels.shinyapps.io/marine-tardigrades (accessed 22 October 2024)
- Bartels, P.J., Fontoura, P. & Nelson, D.R. (2018) Marine tardigrades of the Bahamas with the description of two new species and updated keys to the species of Anisonyches and Archechiniscus. Zootaxa, 4420 (1), 43–70. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4420.1.3
- Bartels, P.J., Fontoura, P., Nelson, D.R. & Kaczmarek, Ł. (2024) Intertidal and shallow subtidal marine tardigrades from the British Virgin Islands with a description of a new Batillipes (Heterotardigrada: Batillipedidae). Marine Biodiversity, 54 (4), 60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-024-01450-8
- Bathmann, U. (2010) The expedition of the research vessel" Polarstern" to the Antarctic in 2007/2008 (ANT-XXIV/2). Berichte zur Polar-und Meeresforschung (Reports on Polar and Marine Research), 2010, 604.
- Bathymetric Data Viewer (2024) Available from: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/maps/bathymetry/ (accessed 22 October 2024)
- Bellido, A. & Bertrand, M. (1981) Echiniscoides travei n. sp., un tardigrade marin des îles
- Kerguelen (Heterotardigrada). Bulletin du Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle, 3 (3), 789–798. https://doi.org/10.5962/p.285852
- Bengtson, P. (1988) Open nomenclature. Palaeontology, 31 (1), 223–227.
- Bogorov, W.G. (1927) Zur Methodik der Bearbeitung des Planktons. (Eine neue Kammer zur Bearbeitung des Zooplanktons). Russian Hydrobiological Zhurnal, 6, 193–198.
- Brandt, A., De Broyer, C., De Mesel, I., Ellingsen, K.E., Gooday, A.J., Hilbig, B., Linse, K., Thomson, M.R.A. & Tyler, P.A. (2007) The biodiversity of the deep Southern Ocean benthos. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 362 (1477), 39–66. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2006.1952
- Bussau, C. (1992) New deep-sea Tardigrada (Arthrotardigrada, Halechiniscidae) from manganese nodule area of the eastern South Pacific. Zoologica Scripta, 21 (1), 79–91. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-6409.1992.tb00311.x
- Danovaro, R. & Gambi, C. (2022) Cosmopolitism, rareness and endemism in deep-sea marine nematodes. The European Zoological Journal, 89 (1), 653–665. https://doi.org/10.1080/24750263.2022.2040621
- Darling, J.A. & Carlton, J.T. (2018) A framework for understanding marine cosmopolitanism in the Anthropocene. Frontiers in Marine Science, 5, 293. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2018.00293
- Da Rocha, C.M.C., Santos, E.C.L., Gomes Jr., E.L., Moura, J.D.R., Silva, L.G.S. & Barbosa, D.F. (2013) New records of marine tardigrades from Brazil. Journal of Limnology, 72 (S1), 102–107. https://doi.org/10.4081/jlimnol.2013.s1.e12
- D’Addabbo, M.G., de Zio Grimaldi, S. & Sandulli, R. (2001) Heterotardigrada of two submarine caves in S. Domino Island (Tremiti Islands) in the Mediterranean Sea with the description of two new species of Stygarctidae. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 240 (3–4), 361–369. https://doi.org/10.1078/0044-5231-00043
- D'Addabbo Gallo, M., Grimaldi de Zio, S., Morone de Lucia, M.R. & Troccoli, A. (1992) Halechiniscidae and Echiniscoididae from Western Mediterranean Sea (Tardigrada: Heterotardigrada). Cahiers de Biologie Marine, 33, 299–318.
- D'Addabbo, R., Gallo, M., De Leonardis, C., Sandulli, R. & Grimaldi, S.D.Z. (2007) Further studies on the marine tardigrade fauna from Sardinia (Italy). Journal of Limnology, 66 (Supplement 1), 56–59. https://doi.org/10.4081/jlimnol.2007.s1.56
- De Zio Grimaldi, S., Gallo D’Addabbo, M. & Pietanza, R. (2000) Two new sub-Antarctic Echiniscoididae from Marion Island (Heterotardigrada, Echiniscoidea). Italian Journal Zoology, 67 (2), 221–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/11250000009356315
- de Zio Grimaldi, S. & D'Addabbo, M.G. (2001) Further data on the Mediterranean Sea tardigrade fauna. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 240 (3–4), 345–360. https://doi.org/10.1078/0044-5231-00042
- Degma, P. & Guidetti, R. (2023) Actual checklist of Tardigrada species. 2009–2023. 42nd Edition. 09 January 2023. https://doi.org/10.25431/11380_1178608
- Dey, P.K., Gąsiorek, P. & Michalczyk, Ł. (2024) Convergent evolution of dark, ultraviolet-absorbing cuticular pigmentation in a new Afro-Oriental Echiniscus brunus species complex (Heterotardigrada: Echiniscidae). Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 200 (1), 34–59. https://doi.org/10.1093/zoolinnean/zlad132
- Doyère, L. (1840) Mémoire sur les Tardigrades. Annales des sciences naturelles, Series 2, Paris, 14, 269–361.
- Dunn, C.W., Giribet, G., Edgecombe, G.D. & Hejnol, A. (2014) Animal phylogeny and its evolutionary implications. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 45 (1), 371–395. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-120213-091627
- Faurby, S., Jørgensen, A., Kristensen, R.M. & Funch, P. (2012) Distribution and speciation in marine intertidal tardigrades: testing the roles of climatic and geographical isolation. Journal of Biogeography, 39 (9), 1596–1607. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2699.2012.02720.x
- Faurby, S. & Barber, P.H. (2015) Extreme population subdivision despite high colonisation ability: contrasting regional patterns in intertidal tardigrades from the west coast of North America. Journal of Biogeography, 42 (6), 1006–1017. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.12500
- Flores, H., van Franeker, J.A., Cisewski, B., Leach, H., Van de Putte, A.P., Meesters, E.H., Bathmann, U. & Wolff, W.J. (2011) Macrofauna under sea ice and in the open surface layer of the Lazarev Sea, Southern Ocean. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 58 (19–20), 1948–1961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2011.01.010
- Fontoura, P., Bartels, P.J., Jørgensen, A., Kristensen, R.M. & Hansen, J.G. (2017) A dichotomous key to the genera of the marine heterotardigrades (Tardigrada). Zootaxa, 4294 (1), 1–45. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4294.1.1
- Fujimoto, S. & Hansen, J.G. (2019) Revision of Angursa (Arthrotardigrada: Styraconyxidae) with the description of a new species from Japan. European Journal of Taxonomy, 510, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.5852/ejt.2019.510
- Fujimoto, S., Suzuki, A.C., Ito, M., Tamura, T. & Tsujimoto, M. (2020) Marine tardigrades from Lützow-Holm Bay, East Antarctica with the description of a new species. Polar Biology, 43, 679–693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-020-02671-w
- Fütterer, D.K., Brandt, A. & Poore, G.C.B. (2003) The Expedition ANTARKTIS XIX/3-4 of the Research Vessel Polarstern in 2002. Berichte zur Polar-und Meeresforschung, 470, 1–174.
- Gallo, M., D'Addabbo, R., De Leonardis, C., Sandulli, R. & Grimaldi de Zio, S. (2007) The diversity of Indian Ocean Heterotardigrada. Journal of Limnology, 66 (Supplement 1), 60–64. https://doi.org/10.4081/jlimnol.2007.s1.60
- Garraffoni, A.R.S. & Balsamo, M. (2017) Is the ubiquitous distribution real for marine gastrotrichs? Detection of areas of endemism using Parsimony Analysis of Endemicity (PAE). Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington, 130 (1), 197–210. https://doi.org/10.2988/17-00011
- Gąsiorek, P. & Kristensen, R.M. (2022) New marine heterotardigrade lineages (Echiniscoididae) from the tropics. The European Zoological Journal, 89 (1), 719–754. https://doi.org/10.1080/24750263.2022.2079737
- Gąsiorek, P. (2023) Catch me if you can, or how paradigms of tardigrade biogeography evolved from cosmopolitism to ‘localism’. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, zlad191. https://doi.org/10.1093/zoolinnean/zlad191
- Giere, O. (2009) Meiobenthology. The Microscopic Motile Fauna of Aquatic Sediments. 2nd Edition. Springer-Verlag, Berlin and Heidelberg, XVII + 527 pp.
- Gomes-Júnior, E., Santos, É., da Rocha, C.M., Santos, P.J. & Fontoura, P. (2020) The deep-sea genus Coronarctus (Tardigrada, Arthrotardigrada) in Brazil, south-western Atlantic Ocean, with the description of three new species. Diversity, 12 (2), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12020063
- Grimaldi de Zio, S.D., Gallo D’Addabbo, M., Sandulli, R. & D’Addabbo, R. (2003) Checklist of the Italian marine Tardigrada. Meiofauna Marina, 12, 97–135.
- Grimaldi de Zio, S.D. & D'Addabbo Gallo, M. (2001) Further data on the Mediterranean Sea tardigrade fauna. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 240 (3–4), 345–360. https://doi.org/10.1078/0044-5231-00042
- Gutzmann, E., Arbizu, P.M., Rose, A. & Veit-Köhler, G. (2004) Meiofauna communities along an abyssal depth gradient in the Drake Passage. Deep Sea Research, Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 51 (14–16), 1617–1628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2004.06.026
- Hallas, T.E. & Kristensen, R.M. (1982) Two new species of the tidal genus Echiniscoides from Rhode Island, USA (Echiniscoididae, Heterotardigrada). In: Nelson, D.R. (Ed.), Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on the Tardigrada. East Tennessee State University Press, Johnson City, Tennessee, pp. 179–192.
- Hansen J.G. (2005) The ongoing investigation of the Faroe Bank tardigrade fauna. Frodskaparrit supplementum: Proceedings from the BIOFAR Symposium, Tórshavn, Faroe Islands, 24–26 April 2003, North-East Atlantic marine benthic organisms in the Faroes - taxonomy, distribution and ecology, pp. 220–223.
- Hansen, J.G., Jørgensen, A. & Kristensen, R.M. (2001) Preliminary studies of the tardigrade fauna of the Faroe Bank. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 240 (3–4), 385–393. https://doi.org/10.1078/0044-5231-00046
- Hansen, J.G. & Kristensen, R.M. (2020) Tardigrada. In: Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. (Ed.), Guide to the identification of marine meiofauna. Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil, München, pp. 428–444.
- Higgins, R.P. & Thiel, H. (1988) Introduction to the study of meiofauna. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, D.C., 488 pp.
- IHO [International Hydrographic Organization] (1953) Limits of Oceans and Seas 3rd Edition. Special Publication No. 23 (S-23). International Hydrographic Organization, Monaco. [unknown pagination]
- IHO [International Hydrographic Organization] (2000) Report of the International Hydrographic Organisation. Working Paper No. 57 (WP 57). 20th Session of the United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names, New York, 17–28 January 2000. [unknown pagination]
- Jørgensen, A., Boesgaard, T. M., Møbjerg, N. & Kristensen, R.M. (2014) The tardigrade fauna of Australian marine caves: With descriptions of nine new species of Arthrotardigrada. Zootaxa, 3802 (4), 401–433. https://doi.org/10.1078/0044-5231-00033
- Jørgensen, A. & Møbjerg, N. (2015) Notes on the cryptobiotic capability of the marine arthrotardigrades Styraconyx haploceros (Halechiniscidae) and Batillipes pennaki (Batillipedidae) from the tidal zone in Roscoff, France. Marine Biology Research, 11 (2), 214–217. https://doi.org/10.1080/17451000.2014.904883
- Jørgensen, A., Faurby, S., Hansen, J.G., Møbjerg, N. & Kristensen, R.M. (2010) Molecular phylogeny of Arthrotardigrada (Tardigrada). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 54 (3), 1006–1015.
- Kaczmarek, Ł., Bartels, P.J., Roszkowska, M. & Nelson, D.R. (2015) The zoogeography of marine Tardigrada. Zootaxa, 4037 (1), 1–189. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4037.1.1
- Kharkevych, K. (2012) The first investigation of fauna and ecology of tardigrades (Tardigrada) of Karkinitsky Bay (Crimea, Black Sea). In: Optimization and Protection of Ecosystems. Vol. 7. TNU, Simferopol, pp. 45–54.
- Kieneke, A. & Zekely, J. (2008) Desmodasys abyssalis sp. nov.—first record of a deep-sea gastrotrich from hydrothermal vents. Marine Biodiversity Records, 1, e88. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1755267207008950
- Kieneke, A., Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. & Hochberg, R. (2015) A new species of Cephalodasys (Gastrotricha, Macrodasyida) from the Caribbean Sea with a determination key to species of the genus. Zootaxa, 3947 (3), 367–385. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3947.3.4
- Kristensen, R.M. & Higgins, R.P. (1984) Revision of Styraconyx (Tardigrada: Halechiniscidae) with descriptions of two new species from Disko Bay, West Greenland. Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology, 391, 1–40. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.00810282.391
- Kristensen, R.M. & Mackness, B.S. (2000) First record of the marine tardigrade genus Batillipes (Arthrotardigrada: Batillipedidae) from South Australia with a description of a new species. Records of the South Australian Museum, 33 (2), 73–87.
- Kristensen, R.M. & Hallas, T.E. (1980) The tidal genus Echiniscoides and its variability, with erection of Echiniscoididae fam. n. (Tardigrada). Zoologica Scripta, 9 (1–4), 113–127. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-6409.1980.tb00657.x
- Kristensen, R.M. & Renaud-Mornant, J. (1983) Existence d'Arthrotardigrades semi-benthiques de genres nouveaux de la sousfamille des Styraconyxinae subfam. nov. Cahiers de Biologie Marine, 24, 337–353.
- Kuklinski, P. & Barnes, D.K. (2010) First bipolar benthic brooder. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 401, 15–20. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps08446
- Liu, K.K., Atkinson, L., Quiñones, R.A. & Talaue-McManus, L. (2010) Biogeochemistry of continental margins in a global context. In: Carbon and nutrient fluxes in continental margins: A global synthesis. Springer, Berlin and Heidelberg, pp. 3–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-92735-8_1
- Marcus, E. (1927) Zur Anatomie und Ökologie mariner Tardigraden. Zoologische Jahrbücher. Abteilung für Systematik, 53, 487–558.
- Menechella, A.G., Bulnes, V.N. & Cazzaniga, N. (2015) A new Batillipedidae (Tardigrada, Arthrotardigrada) from Argentina. Zootaxa, 4032 (3), 339–344. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4032.3.11
- Menechella, A.G., Bulnes, V.N. & Cazzaniga, N.J. (2017) Two new species of Batillipes (Tardigrada, Arthrotardigrada, Batillipedidae) from the Argentinean Atlantic coast, and a key to all known species. Marine Biodiversity, 48, 239–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-017-0640-4
- Miller, R.M. & Kristensen, R.M. (1999) Tardigrades of the Australian Antarctic: a new species of the marine genus Echiniscoides from Macquarie Island, Subantarctica. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 238, 289–294.
- Miller, K.A., Thompson, K.F., Johnston, P. & Santillo, D. (2018) An overview of seabed mining including the current state of development, environmental impacts, and knowledge gaps. Frontiers in Marine Science, 4, 312755. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2017.00418
- Møbjerg, N., Kristensen, R.M. & Jørgensen, A. (2016) Data from new taxa infer Isoechiniscoides gen. nov. and increase the phylogenetic and evolutionary understanding of echiniscoidid tardigrades (Echiniscoidea: Tardigrada). Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 178 (4), 804–818. https://doi.org/10.1111/zoj.12500
- Morek, W., Surmacz, B., López‐López, A. & Michalczyk, Ł. (2021) “Everything is not everywhere”: Time‐calibrated phylogeography of the genus Milnesium (Tardigrada). Molecular Ecology, 30 (14), 3590–3609. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.15951
- Nelson, D.R., Guidetti, R. & Rebecchi, L. (2015) Phylum Tardigrada. In: Thorp, J. & Rogers, D.C. (Eds.), Thorp and Covich's freshwater invertebrates. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp. 347–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-385026-3.00017-6
- Noda, H. (1985) Description of a new subspecies of Angursa biscuspis Pollock (Heterotardigrada, Halechiniscidae) from Tanabe Bay, Japan. Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory, 30 (4–6), 269–276. https://doi.org/10.5134/176110
- Pollock, L.W. (1979) Angursa bicuspis ng, n. sp., a marine arthrotardigrade from the Western North Atlantic. Transactions of the American Microscopical Society, 98 (4), 558–562. https://doi.org/10.2307/3225907
- Poore, G.C. (2002) The Expeditions ANTARKTIS-XIW3-4 of the Research Vessel POLARSTERN in 2002 (ANDEEP I and 11: Antarctic benthic deep-sea biodiversity-colonization history and recent community patterns). Available from: https://epic.awi.de/id/eprint/26649/1/BerPolarforsch2003470.pdf (accessed 22 October 2024)
- Ramazzotti, G. (1962) Il Phylum Tardigrada. Memorie dell'Istituto Italiano di Idrobiologia, 16, 1–595.
- Renaud-Mornant, J. (1974) Une nouvelle famille de Tardigrades marins abyssaux: les Coronarctidae fam. nov. (Heterotardigrada). Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Séances de l’Académie des Sciences, Paris, 278, 3087–3090.
- Renaud-Mornant, J. (1975) Occurrence of the genus Tanarctus Renaud-Debyser, 1959 in Northeastern Atlantic waters with a description of T. ramazzotti n. sp. (Arthrotardigrada). Memorie dell′Istituto Italiano di Idrobiologia, 32 (Supplement), 325–332.
- Renaud-Mornant, J. (1981) Deux nouveaux Angursa Pollock, 1979, du domaine abyssal (Tardigrada, Arthrotardigrada). Tethys, 10, 161–164.
- Renaud-Mornant, J. (1983) Tardigrades abyssaux nouveaux de la sous-famille des Euclavarctinae n. subfam (Arthrotardigrada,Halechiniscidae). Bulletin du Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle, Section A, Zoologie Biologie et Ecologie Animales, 5 (1), 201–219. https://doi.org/10.5962/p.285998
- Richters, F. (1909) Tardigraden-Studien. Bericht der Senckenbergische Naturforschenden Gesellschaft, 40, 28–45.
- Richters, F. (1926) Tardigrada. In: Kükenthal, W. & Krumbach, T. (Eds.), Handbuch der Zoologie. Vol. 3. Walter de Gruyter & Co., Berlin and Leipzig, pp. 1–68.
- Rubal, M., Veiga, P., Fontoura, P. & Sousa-Pinto, I. (2017) A new Batillipes (Tardigrada, Heterotardigrada, Batillipedidae) from North Portugal (Atlantic Ocean). Marine Biodiversity, 47, 921–928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-016-0526-x
- Saeedi, H., Simões, M. & Brandt, A. (2020) Biodiversity and distribution patterns of deep-sea fauna along the temperate NW Pacific. Progress in Oceanography, 183, 102296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2020.102296
- Sáiz-Salinas, J.I., Ramos, A., García, F.J., Troncoso, J.S., San Martin, G., Sanz, C. & Palacin, C. (1997) Quantitative analysis of macrobenthic softbottom assemblages in South Shetland waters (Antarctica). Polar Biology, 17, 393–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00013382
- Santos, E., Veiga, P., Rubal, M., Bartels, P.J., da Rocha, C.M. & Fontoura, P. (2019) Batillipes pennaki Marcus, 1946 (Arthrotardigrada: Batillipedidae): deciphering a species complex. Zootaxa, 4648 (3), 549–567. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4648.3.9
- Saulenko, A.A., Maiorova, A.S., Martínez Arbizu, P. & Mordukhovich, V.V. (2022) Deep-sea tardigrades from the North-Western Pacific, with descriptions of two new species. Diversity, 14 (12), 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14121086
- Schindelin, J., Arganda-Carreras, I., Frise, E., Kaynig, V., Longair, M., Pietzsch, T., Preibisch, S., Rueden, C., Saalfeld, S., Schmid, B., Tinevez, J.-Y., White, D.J., Hartenstein, V., Eliceiri, K., Tomancak, P. & Cardona, A. (2012) Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nature Methods, 9 (7), 676–682. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2019
- Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. (2001) Tardigrades—are they really miniaturized dwarfs? Zoologischer Anzeiger, 240 (3–4), 549–555 https://doi.org/10.1078/0044-5231-00066
- Steiner, G. (1926) Bathyechiniscus tetronyx n.g. n.sp. Ein neuer mariner Tardigrade. Deutsche Südpolar-Expedition 1901–1903, Zoology, 10, 477–481.
- Stec, D., Krzywański, Ł., Arakawa, K. & Michalczyk, Ł. (2020) A new redescription of Richtersius coronifer, supported by transcriptome, provides resources for describing concealed species diversity within the monotypic genus Richtersius (Eutardigrada). Zoological Letters, 6, 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40851-020-0154-y
- Strugnell, J.M., Rogers, A.D., Prodöhl, P.A., Collins, M.A. & Allcock, A.L. (2008) The thermohaline expressway: the Southern Ocean as a centre of origin for deep‐sea octopuses. Cladistics, 24 (6), 853–860. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-0031.2008.00234.x
- Thulin, G. (1928) Über die Phylogenie und das System der Tardigraden. Hereditas, 11 (2–3), 207–266. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-5223.1928.tb02488.x
- Thulin, G. (1942) Ein neuer Mariner Tardigrad. Göteborgs Kungliga Vetenskaps- och Vitterhets-Samhälles Handlingar, Sjätte följden, Series B, 2 (5), 1–10.
- Trokhymchuk, R. & Kieneke, A. (2024) Novel distribution records of marine Tardigrada from abyssal sediments of the Northwest Atlantic Ocean. Organisms Diversity & Evolution, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13127-024-00641-2
- Utevsky, A., Utevsky, S., Cichocka, J. M., Bielecki, A., Santoro, M. & Trontelj, P. (2023) Return of the prodigal son: morphology and molecular phylogenetic relationships of a new Antarctic fish leech (Hirudinea: Piscicolidae) imply a bipolar biogeographic pattern. Systematics and Biodiversity, 21 (1), 2246476. https://doi.org/10.1080/14772000.2023.2246476
- Veit-Köhler, G., Guilini, K., Peeken, I., Quillfeldt, P. & Mayr, C. (2013) Carbon and nitrogen stable isotope signatures of deep-sea meiofauna follow oceanographical gradients across the Southern Ocean. Progress in Oceanography, 110, 69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2013.01.001
- Víllora-Moreno, S. (1998) Deep-sea Tardigrada from South Shetland Islands (Antarctica) with description of Angursa antarctica sp. nov. (Arthrotardigrada, Halechiniscidae). Polar Biology, 19, 336–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003000050255
- Wang, X., Bai, L., Wang, C., Lu, B., Li, Y., Lin, Q., Huang, X. & Fontoura, P. (2023) Preliminary studies of the Tardigrada communities from a polymetallic nodule area of the deep South China Sea. Frontiers in Marine Science, 10, 1110841. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2023.1110841