Abstract
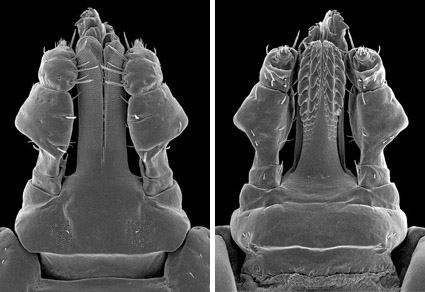
We establish Sharifiella Santos Dias, 1958 (Acari: Ixodidae), formerly considered a subgenus of Haemaphysalis Koch, 1844, at full genus rank. The only species of this genus, S. theilerae (Hoogstraal, 1953), is a specific parasite of tenrecs (Afrosoricida: Tenrecidae) on Madagascar. Several morphological characters, including the unique shape of palpal segment II, allow discrimination of this genus and species from any other ixodid ticks. Male, female, nymph, and larva of S. theilerae are redescribed here. Through short-read genomic sequencing we assembled and annotated the entire mitochondrial genome of S. theilerae, as well as assembled the nuclear 28S large ribosomal subunit gene. On the basis of our phylogenies using a nucleotide alignment of the 10 mitochondrial protein-coding genes, as well as the 28S rDNA gene, S. theilerae, is basal to the rhipicephaline lineage (Dermacentor Koch, 1844, Hyalomma Koch, 1844, Rhipicephalus Koch, 1844, and Rhipicentor Nuttall & Warburton, 1908), and not the haemaphysaline lineage.
References
- Burger, T.D., Shao, R. & Barker, S.C. (2013) Phylogenetic analysis of the mitochondrial genomes and nuclear rRNA genes of ticks reveals a deep phylogenetic structure within the genus Haemaphysalis and further elucidates the polyphyly of the genus Amblyomma with respect to Amblyomma sphenodonti and Amblyomma elaphense. Ticks &Tick-Borne Diseases, 4, 265–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2013.02.002
- Castresana, J. (2000) Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Molecular Biology & Evolution, 17, 540–552. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026334
- Chen, Y., Ye, W., Zhang, Y. & Xu, Y. (2015) High speed BLASTN: An accelerated MegaBLAST search tool. Nucleic Acids Research, 43, 7762–7768. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv784
- Dierckxsens, N., Mardulyn, P. & Smits, G. (2017) NOVOPlasty: De novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Research, 45, e18. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw955
- Donath, A., Jühling, F., Al-Arab, M., Bernhart, S.H., Reinhardt, F., Stadler, P.F., Middendorf, M. & Bernt, M. (2019) Improved annotation of protein-coding genes boundaries in metazoan mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Research, 47, 10543–10552. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz833
- Everson, K.M., Soarimalala, V., Goodman, S.M. & Olson, L.E. (2016) Multiple loci and complete taxonomic sampling resolve the phylogeny and biogeographic history of tenrecs (Mammalia: Tenrecidae) and reveal higher speciation rates in Madagascar’s humid forests. Systematic Biology, 65, 890–909. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syw034
- Hoogstraal, H. (1953) Ticks (Ixodoidea) of the Malagasy faunal region (excepting the Seychelles). Bulletin of Museum of Comparative Zoology, 111, 37–113.
- Hoogstraal, H. (1959) On Allophysalis, a new subgenus of Haemaphysalis (Ixodoidea, Ixodidae). Journal of Egyptian Public Health Association, 34, 37–42.
- Hoogstraal, H. (1971) Haemaphysalis (Allophysalis) warburtoni Nuttall: Description of immature stages, adult structural variation, and hosts and ecology in Nepal, with a redefinition of the subgenus Allophysalis Hoogstraal (Ixodoidea: Ixodidae). Journal of Parasitology, 57, 1083–1095. https://doi.org/10.2307/3277868
- Hoogstraal, H. & Kim, K.C. (1985) Tick and mammal coevolution, with emphasis on Haemaphysalis. In: Kim, K.C. (Ed.), Coevolution of parasitic arthropods and mammals. Wiley, New York, New York, pp. 506–568.
- Kelava, S., Apanaskevich, D.A., Shao, R., Gofton, A.W., Mans, B.J., Teo, E.J.M., Norval, G., Barker, D., Nakao, R. & Barker, S.C. (2024) Insights from entire mitochondrial genome sequences into the phylogeny of ticks of the genera Haemaphysalis and Archaeocroton with the elevation of the subgenus Alloceraea Schulze, 1919 back to the status of a genus. Medical and Veterinary Entomology, 38, 189–204. https://doi.org/10.1111/mve.12708
- Kelava, S., Mans, B.J., Shao, R., Moustafa, M.A.M., Matsuno, K., Takano, A., Kawabata, H., Sato, K., Fujita, H., Ze, C., Plantard, O., Hornok, S., Gao, S., Barker, D., Barker, S.C. & Nakao, R. (2021) Phylogenies from mitochondrial genomes of 120 species of ticks: Insights into the evolution of the families of ticks and of the genus Amblyomma. Ticks Ticks & Tick Borne Diseases, 12, 101577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2020.101577
- Kelava, S., Mans, B.J., Shao, R., Barker, D., Teo, E.J.M., Chatanga, E., Gofton, A.W., Moustafa, M.A.M., Nakao, R. & Barker, S.C. (2023) Seventy-eight entire mitochondrial genomes and nuclear rRNA genes provide insight into the phylogeny of the hard ticks, particularly the Haemaphysalis species, Africaniella transversale and Robertsicus elaphensis. Ticks & Tick Borne Diseases, 14, 102070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2022.102070
- Lanfear, R., Frandsen, P.B., Wright, A.M., Senfeld, T. & Calcott, B. (2017) PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Molecular Biology & Evolution, 34, 772–773. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw260
- Lowe, T.M. & Chan, P.P. (2016) tRNAscan-SE On-line: Integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Research, 44, W54–W57. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw413
- Rambaut, A. (2009) TRACER. Version 1.7.1. 1 May 2018. Available from: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/tracer/ (accessed 9 November 2023)
- Rambaut, A. (2012) FigTree. Version 1.4.4. 25 November 2018. Available from: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/FigTree/ (accessed 9 November 2023)
- Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., van der Mark, P., Ayres, D.L., Darling, A., Höhna, S., Larget, B., Liu, L., Suchard, M.A. & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2012) MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology, 61, 539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
- Santos Dias, J.A.T. (1958) Notes on various ticks (Acarina-Ixodoidea) in collection at some entomological institutes in Paris and London. Anais do Instituto de Medicina Tropical, 15, 459–563.
- Sharif, M. (1928) A revision of the Indian Ixodidae with special reference to the collection in the Indian Museum. Records of the Indian Museum, 30, 217–344. https://doi.org/10.26515/rzsi/v30/i3/1928/162556
- Uilenberg, G., Hoogstraal, H. & Klein, J.M. (1979) Les tiques (Ixodoidea) de Madagascar et leur rôle vecteur. Archives de l’Institut Pasteur de Madagascar, Numéro Spécial, 1–153.