Abstract
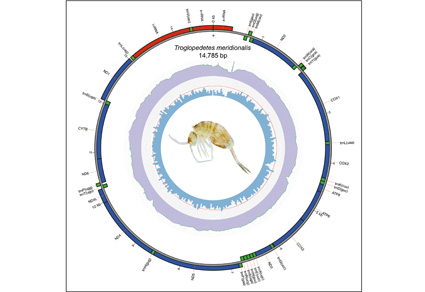
The mitochondrial genome (mitogenome) has recently emerged as an essential tool for investigating evolutionary relationships of organisms. In this study, the complete mitogenome of a Collembola species, Troglopedetes meridionalis Jantarit, Surakhamhaeng & Deharveng, 2020 (Entomobryidae, Paronellinae) was sequenced using low-coverage whole-genome sequencing techniques. The circular mitogenome is 14,785 bp and contains 37 genes, including 22 transfer RNAs (tRNAs), 13 protein coding sequences (CDS), and two ribosomal RNA (rRNAs). The nucleotide composition analysis revealed that the stop codon of all protein-coding genes, except COX2, is TAA. Phylogenetic analysis, incorporating representative other species of Entomobryidae, indicates that the subfamily Paronellinae is monophyletic, with T. meridionalis and T. dispersus Deharveng & Gers, 1993 being closely related. This phylogenetic framework offers a valuable reference for future research on the evolutionary relationships within Paronellinae and the broader Entomobryidae family. In Thailand, the distribution of Troglopedetes Joseph, 1872 is largely restricted to areas north of the Isthmus of Kra, whereas the closely related genus Cyphoderopsis Carpenter, 1917 is confined to the southern region. A distribution map illustrating the geographic ranges of both genera within Thailand is also provided.
References
- Bellinger, P.F., Christiansen, K.A. & Janssens, F. (1996–2024) Checklist of the Collembola of the world. Available from: http://www.collembola.org/ (accessed 5 January 2025)
- Bellini, B.C., Cipola, N.G. & Godeiro, N.N. (2015) New species of Lepidocyrtus Bourlet and Entomobrya Rondani (Collembola: Entomobryoidea: Entomobryidae) from Brazil. Zootaxa, 4027 (2), 227–242. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4027.2.3
- Bellini, B.C. & Zeppelini, D. (2011) A new species of Seira (Collembola: Entomobryidae: Seirini) from the Northeastern Brazilian coastal region. Zoologia, 28 (3), 403–406. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-46702011000300015
- Bellini, B.C., Zhang, F., Souza, P.G.C., Santos-Costa, R.C., Medeiros, G.S. & Godeiro, N.N. (2023) The Evolution of Collembola Higher Taxa (Arthropoda, Hexapoda) Based on Mitogenome Data. Diversity, 15 (1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010007
- Birney, E., Clamp, M. & Durbin, R. (2004) GeneWise and Genomewise. Genome Research, 14, 988–995. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1865504
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S., Silla-Martínez, J.M. & Gabaldón, T. (2009) trimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics, 25, 1972–1973. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp348
- Carpenter, G.H. (1917) Zoological results of the Abor Expedition 1911–12: Collembola. Records of the Indian Museum, Calcutta, 8, 561–568. https://doi.org/10.26515/rzsi/v8/i10/1917/163141
- Chen, S., Zhou, Y. & Chen, Y. (2018) fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics, 34 (17), i884–i890. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
- Deharveng, L. (1988) A new Troglomorphic Collembola from Thailand: Troglopedes fredstonei, new species (Collembola: Paronellidae). Bishop Museum Occasional Papers, 28, 95–98.
- Deharveng, L. (1990) Fauna of Thai caves II. New Entomobryoidea Collembola from Chiang Dao cave, Thailand. Bishop Museum Occasional Papers, 30, 279–287.
- Deharveng, L. (2004) Recent advances in Collembola systematics. Pedobiologia, 48 (5–6), 415–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedobi.2004.08.001
- Deharveng, L. & Gers, C. (1993) Ten new species of Troglopedetes Absolon, 1907 from caves of Thailand (Collembola, Paronellidae). Bijdragen tot de Dierkunde, 63 (2), 103–113. https://doi.org/10.1163/26660644-06302002
- Deharveng, L., Jantarit, S. & Bedos, A. (2018) Revisiting Lepidonella Yosii (Collembola: Paronellidae): character overview, checklist of world species and reassessment of Pseudoparonella doveri Carpenter. Annales de la Société entomologique de France, 54 (5), 381–400. https://doi.org/10.1080/00379271.2018.1507687
- Denis, J.R. (1929) Notes sur les collemboles récoltés dans ses voyages par le Prof. F. Silvestri. I. Seconde note sur les collemboles d’Extrême-Orient. Bolletino di Zoologia Generale e Agricola Portici, 22, 305–320.
- Folsom, J.W. (1897) Japanese Collembola. Bulletin of the Essex Institute, 29, 51–57. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.14789
- Gertz, E.M., Yu, Y.K., Agarwala, R., Schäffer, A.A. & Altschul, S.F. (2006) Composition-based statistics and translated nucleotide searches: improving the TBLASTN module of BLAST. BMC Biology, 4, 41. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-4-41
- Godeiro, N.N., Bellini, B.C., Ding, N., Xu, C., Ding, Y. & Zhang, F. (2021) A mitogenomic phylogeny of the Entomobryoidea (Collembola): A comparative perspective. Zoologica Scripta, 50 (5), 658–666. https://doi.org/10.1111/zsc.12487
- Godeiro, N.N., Ding, Y., Cipola, N.G., Jantarit, S., Bellini, B.C. & Zhang, F. (2023) Phylogenomics and systematics of Entomobryoidea (Collembola): marker design, phylogeny and classification. Cladistics, 39 (2), 101–115. https://doi.org/10.1111/cla.12521
- Godeiro, N.N., Zhang, F. & Cipola, N.G. (2020) First partial mitogenome of a new Seira Lubbock species (Collembola, Entomobryidae, Seirinae) from Cambodia reveals a possible separate lineage from the Neotropical Seirinae. Zootaxa, 4890 (4), 451–472. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4890.4.1
- Godeiro, N.N., Palacios-Vargas, J.G., Gao, Y. & Bu, Y. (2022) Complete mitochondrial genome of the Mexican marine littoral hygrophilous Spinactaletes boneti (Collembola: Actaletidae) and its phylogenetic placement. Mitochondrial DNA, Part B, 7, 755–757. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2022.2068982
- Guindon, S., Dufayard, J.F., Lefort, V., Anisimova, M., Hordijk, W. & Gascuel, O. (2010) New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Systematic Biology, 59, 307–321. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syq010
- Hoang, D.T., Chernomor, O., von Haeseler, A., Minh, B.Q. & Vinh, L.S. (2018) UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35, 518–522. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx281
- Jantarit, S., Satasook, C. & Deharveng, L. (2013) The genus Cyphoderopsis Carpenter (Collembola: Paronellidae) in Thailand and a faunal transition at the Isthmus of Kra in Troglopedetinae. Zootaxa, 3721 (1), 49–70. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3721.1.2
- Jantarit, S., Bedos, A. & Deharveng, L. (2016) An annotated checklist of the Collembolan fauna of Thailand. Zootaxa, 4169 (2), 301–360. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4169.2.4
- Jantarit, S., Surakhamhaeng, K. & Deharveng, L. (2020) The multiformity of antennal chaetae in Troglopedetes Joseph, 1872 (Collembola, Paronellidae, Troglopedetinae), with descriptions of two new species from Thailand. ZooKeys, 987, 1–40. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.987.54234
- Joseph, G. (1872) Beobachtungen über die Lebensweise und Vorkommen den in den Krainer Gebirgsgrotten einheimischen Arten der blinden Gattungen Machaerites, Leptodirus, Oryotus und Troglorrhynchus. Jahres-Bericht der Schlesischen Gesellschaft für Vaterländische Cultur, 49, 171–182.
- Jühling, F., Putz, J., Bernt, M., Donath, A., Middendorf, M., Florentz, C. & Stadler, P.F. (2012) Improved systematic tRNA gene annotation allows new insights into the evolution of mitochondrial tRNA structures and into the mechanisms of mitochondrial genome rearrangements. Nucleic Acids Research, 40, 2833–2845. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr1150
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S., Minh, B.Q., Wong, T.K., Von Haeseler, A. & Jermiin, L.S. (2017) ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nature Methods, 14, 587–589. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4298
- Karlicki, M., Antonowicz, S. & Karnkowska, A. (2022) Tiara: deep learning-based classification system for eukaryotic sequences. Bioinformatics, 38 (2), 344–350. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btab672
- Katoh, K. & Standley, D.M. (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 772–780. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst010
- Krzywinski, M., Schein, J., Birol, I., Connors, J., Gascoyne, R., Horsman, D., Jones, S.J. & Marra, M.A. (2009) Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Research, 19, 1639–1645. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.092759.109
- Kück, P. & Longo, G.C. (2014) FASconCAT-G: Extensive functions for multiple sequence alignment preparations concerning phylogenetic studies. Frontiers in Zoology, 11, 81. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12983-014-0081-x
- Lartillot, N., Rodrigues, N., Stubbs, D. & Richer, J. (2013) PhyloBayes MPI: Phylogenetic reconstruction with infinite mixtures of profiles in a parallel environment. Systematic Biology, 62, 611–615. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syt022
- Lavrov, D.V. & Pett, W. (2016) Animal mitochondrial DNA as we do not know it: mt-genome organization and evolution in nonbilaterian lineages. Genome Biology and Evolution, 8 (9), 2896–2913. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evw195
- Li, H. & Durbin, R. (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics, 25, 1754–1760. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
- Li, H., Handsaker, B., Wysoker, A., Fennell, T., Ruan, J., Homer, N., Marth, G., Abecasis, G. & Durbin, R. (2009) 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics, 25, 2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
- Meng, G., Li, Y., Yang, C. & Liu, S. (2019) MitoZ: a toolkit for animal mitochondrial genome assembly, annotation and visualization. Nucleic Acids Research, 47 (W1), W451–W455. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz173
- Minh, B.Q., Schmidt, H.A., Chernomor, O., Schrempf, D., Woodhams, M.D., von Haeseler, A. & Lanfear, R. (2020) IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 37 (5), 1530–1534. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaa015
- Nardi, F., Carapelli, A., Fanciulli, P.P., Dallai, R. & Frati, F. (2001) The complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the basal hexapod Tetrodontophora bielanensis: Evidence for heteroplasmy and tRNA translocations. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 18, 1293–1304. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a003914
- Nawrocki, E.P. & Eddy, S.R. (2013) Infernal 1.1:100-fold faster RNA homology searches. Bioinformatics, 29, 2933–2935. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt509
- Nicolet, H. (1842) Recherches pour servirà l’histoire des podurelles. Nouveaux Mémoires de la Société Helvétique des Sciences Naturelles, 6, 1–88.
- Simon, S. & Hadrys, H. (2013) A comparative analysis of complete mitochondrial genomes among Hexapoda. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 69 (2), 393–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2013.03.033
- Soto-Adames, F.N., Barra, J.A., Christiansen, K. & Jordana, R. (2008) Suprageneric Classification of the Entomobryomorpha Collembola. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 101, 501–513. https://doi.org/10.1603/0013-8746(2008)101[501:SCOCE]2.0.CO;2
- Sun, X., Yu, D., Xie, Z., Dong, J., Ding, Y., Yao, H. & Greenslade, P. (2020) Phylomitogenomic analyses on collembolan higher taxa with enhanced taxon sampling and discussion on method selection. PLoS One, 15, 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0230827
- Szeptycki, A. (1979) Morpho-systematic studies of Collembola. IV. Chaetotaxy of the Entomobryidae and its phylogenetical significance. Polska Akademia Nauk, ZakBad Zoologii Systematycznej i Doświadczalnej, Państwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe, Warszawa, Kraków, 218 pp.
- Surakhamhaeng, K., Deharveng, L. & Jantarit, S. (2021) Three new species of cave Troglopedetes (Collembola, Paronellidae, Troglopedetinae) from Thailand, with a key to the Thai species. Subterranean Biology, 40, 129–174. https://doi.org/10.3897/subtbiol.40.73143
- Taanman, J.W. (1999) The mitochondrial genome: structure, transcription, translation and replication. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 1410 (2), 103–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2728(98)00161-3
- Wang, F., Chen, J.X. & Christiansen, K. (2002) A new species of Pseudosinella from Nanjing, China (Collembola: Entomobryidae). Entomological News, 113 (4), 243–246.
- Wheeler, T.J. & Eddy, S.R. (2013) nhmmer: DNA homology search with profile HMMs. Bioinformatics, 29, 2487–2489. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt403
- Woodruff, D.S. (2003) Neogene marine transgressions, palaeogeography and biogeographic transitions on the Thai-Malay Peninsula. Journal of Biogeography, 30, 551–567. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2699.2003.00846.x
- Wray, D.L. (1953) Some new species of springtail insects (Collembola). Nature Notes, 1, 1–7.
- Xue, X.F., Deng, W., Qu, S.X., Hong, W.Y. & Shao, R. (2018) The mitochondrial genomes of sarcoptiform mites: are any transfer RNA genes really lost? BMC Genomics, 19, 466. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4868-6
- Yosii, R. (1960) On some Collembola of New Caledonia, New Britain and Solomon Islands. Bulletin of the Osaka Museum of Natural History, 12, 9–38.
- Zhang, F., Bellini, B.C. & Soto-Adames, F.N. (2019) New insights into the systematics of Entomobryoidea (Collembola: Entomobryomorpha): First instar chaetotaxy, homology and classification. Zoological Systematics, 44 (4), 249–278. https://doi.org/10.11865/zs.201926
- Zhang, F. & Deharveng, L. (2015) Systematic revision of Entomobryidae (Collembola) by integrating molecular and new morphological evidence. Zoologica Scripta, 44 (3), 298–311. https://doi.org/10.1111/zsc.12100
- Zhang, F., Ma, Y. & Greenslade, P. (2017) New Australian Paronellidae (Collembola) reveal anomalies in existing tribal diagnoses. Invertebrate Systematics, 31, 375–393. https://doi.org/10.1071/IS16073