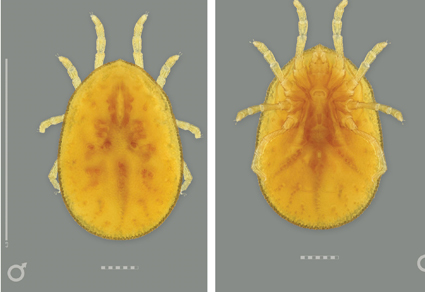
Abstract
We establish Apanaskevichiella gen. nov. for Ornithodoros (Pavlovskyella) macmillani Hoogstraal & Kohls 1966, McMillan’s Australian tree-hollow argasid; and Australpavlovskyella gen. nov. for Ornithodoros (Pavlovskyella) gurneyi Warburton, 1926, the kangaroo soft tick. www.youtube.com/@Tick_video-j2m
References
- Barker, S.C. & Barker, D. (2023) Ticks of Australasia: 125 species of ticks in and around Australia. Zootaxa, 5253 (1), 1–670. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5253.1.1
- Bernt, M., Donath, A., Jühling, F., Externbrink, F., Florentz, C., Fritzsch, G., Pütz, J., Middendorf, M. & Stadler, P.F. (2013) MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Molecular Phylogenetics & Evolution, 69, 313–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2012.08.023
- Burger, T.D., Shao, R., Labruna, M.B. & Barker, S.C. (2014a) Molecular phylogeny of soft ticks (Ixodida: Argasidae) inferred from mitochondrial genome and nuclear rRNA sequences. Ticks & Tick-borne Diseases, 5, 195–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2013.10.009
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S., Silla-Martínez, J.M. & Gabaldón, T. (2009) trimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics, 25, 1972–1973. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp348
- Chen, Y., Ye, W., Zhang, Y. & Xu, Y. (2015) High speed BLASTN: An accelerated MegaBLAST search tool. Nucleic Acids Research, 43, 7762–7768. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv784
- Chen, S., Zhou, Y., Chen, Y. & Gu, J. (2018) fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics, 34, i884–i890. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
- Clifford, C.M., Kohls, G.M. & Sonenshine, D.E. (1964) The systematics of the subfamily Ornithodorinae (Acarina: Argasidae). I. The genera and subgenera. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 57, 429–437. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/57.4.429
- Cooley, R.A. & Kohls, G.M. (1944) The Argasidae of North America, Central America and Cuba. Monograph No1. The American Midland Naturalist, Notre Dame, Indiana, 152 pp. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.4511
- Doube, B.M. (1972) The ecology of the kangaroo tick Ornithodoros gurneyi Warbuton. PhD Thesis. Waite Agricultural Research Institute, South Australia.
- Doube, B.M. (1975a) The biology of the kangaroo tick, Ornithodoros (Pavlovskyella) gurneyi Warburton (Acarina: Argasidae), in the laboratory. Journal of Medical Entomology, 12, 240–243. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/12.2.240
- Doube, B.M. (1975b) Regulation of the circadian rhythm of detachment of engorged larvae and nymphs of the argasid kangaroo tick, Ornithodoros gurneyi. Journal of Medical Entomology, 12, 15–22. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/12.1.15
- Doube, B.M. (1975c) Two races of the kangaroo tick Ornithodoros (Pavlovskyella) gurneyi Warbuton. Journal of the Australian Entomological Society, 14, 329–332. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-6055.1975.tb02048.x
- Doube, B.M. (1975d) Photoperiodic induction of diapause in the kangaroo tick Ornithodoros gurneyi Warburton (Acarina: Argasidae). Journal of the Australian Entomological Society, 14 (3), 221–224. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-6055.1975.tb02030.x
- Fearnhead, E.A. (1962) Investigation on the bionomics of Ornithodoros zumpti Heisch et Guggisberg (Ixodoidea: Argasidae). Zeitschrift für Parasitenkunde, 22, 114–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00329209
- Hoogstraal, H. & Kohls, G.M. (1966) Ornithodoros (Pavlovskyella) macmillani new species (Ixodoidea, Argasidae) a nest parasite of Australian cockatoos (Kakatoe roseicapilla). Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 59, 86–92. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/59.1.86
- Hoang, D.T., Chernomor, O., von Haeseler, A., Minh, B.Q. & Vinh, L.S. (2018) UFBoot2: improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Molecular Biology & Evolution, 35, 518–522. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx281
- Kearse, M., Moir, R., Wilson, A., Stones-Havas, S., Cheung, M., Sturrock, S., Buxton, S., Cooper, A., Markowitz, S., Duran, C., Thierer, T., Ashton, B., Meintjes, P. & Drummond, A. (2012) Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics, 28, 1647–1649. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts199
- Kelava, S., Mans, B.J., Shao, R., Moustafa, M.A.M., Matsuno, K., Takano, A., Kawabata, H., Sato, K., Fujita, H., Ze, C., Plantard, O., Hornok, S., Gao, S., Barker, D., Barker, S.C. & Nakao, R. (2021) Phylogenies from mitochondrial genomes of 120 species of ticks: insights into the evolution of the families of ticks and of the genus Amblyomma. Ticks & Tick-borne Diseases, 12, 101577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2020.101577
- Kelava, S., Mans, B.J., Shao, R., Barker, D., Teo, E.J.M., Chatanga, E., Gofton, A.W., Moustafa, M.A.M., Nakao, R. & Barker, S.C. (2023) Seventy-eight entire mitochondrial genomes and nuclear rRNA genes provide insight into the phylogeny of the hard ticks, particularly the Haemaphysalis species, Africaniella transversale and Robertsicus elaphensis. Ticks & Tick-borne Diseases, 14, 102070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2022.102070
- Keirans, J.E. & Brewster, B.E. (1981) The Nuttall and British Museum (Natural History) tick collections: lectotype designations for ticks (Acarina: Ixodoidea) described by Nuttall, Warburton, Cooper and Robinson. Bulletin of the British Museum of Natural History, Zoology, 41, 153–178.
- Klompen, J.S.H. & Oliver, J.H. Jr. (1993a) Systematic relationships in the soft ticks (Acari: Ixodida: Argasidae). Systematic Entomology, 18, 313–331. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3113.1993.tb00669.x
- Klompen, J.S. & Oliver, J.H. Jr. (1993b) Haller’s organ in the tick family Argasidae (Acari: Parasitiformes: Ixodida). Journal of Parasitology, 79, 591–603. https://doi.org/10.2307/3283387
- Lanfear, R., Frandsen, P.B., Wright, A.M., Senfeld, T. & Calcott, B. (2016) PartitionFinder 2: new methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Molecular Biology & Evolution, 34, 772–773. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw260
- Li, H. (2018) Minimap2: pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics, 34, 3094–3100. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty191
- Lowe, T.M. & Chan, P.P. (2016) tRNAscan-SE On-line: integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Research, 44, W54–W57. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw413
- Mans, B., Featherston, J., Kvas, M., Pillay, K.A., de Klerk, D.G., Pienaar, R., de Castro, M.H., Schwan, T.G., Lopez, J.E., Teel, P., de Leon, A.A.P., Sonenshine, D.E., Egekwu, N.I., Bakkes, D.K., Heyne, H., Kanduma, E.G., Nyangiwe, N., Bouattour, A. & Latif, A.A. (2019) Argasid and ixodid systematics: implications for soft tick evolution and systematics, with a new argasid species list. Ticks & Tick-Borne Diseases, 10, 219–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2018.09.010
- Mans, B.J., Kelava, S., Pienaar, R., Featherston, J., de Castro, M.H., Quetglas, J., Reeves, W.K., Durden, L.A., Miller, M.M., Laverty, T.M., Shao, R., Takano, A., Kawabata, H., Moustafa, M.A.M., Nakao, R., Matsuno, K., Greay, T.L., Evasco, K.L., Barker, D. & Barker, S.C. (2021) Nuclear (18S-28S rRNA) and mitochondrial genome markers of Carios (Carios) vespertilionis (Argasidae) support Carios Latreille, 1796 as a lineage embedded in the Ornithodorinae: re-classification of the Carios sensu Klompen and Oliver (1993) clade into its respective subgenera. Ticks & Tick-borne Diseases, 12, 101688.
- Mans, B.J., Kelava, S., Doube, B.M., Shaw, M.D., Teo, E.J.M., Barker, D., Pienaar, R., de Castro, M.H., Gofton, A., Nakao, R. & Barker, S.C. (2025) Independent lineages from five zoogeographic realms: the mitochondrial genome of Ornithodoros (Pavlovskyella) gurneyi Warburton, 1926 (Acari: Argasidae) confirms paraphyly of the subgenus Pavlovskyella Pospelova-Shtrom, 1950. Zootaxa. [In press]
- Norval, G., Sharrad, R.D., Ross, K.E. & Gardner, M.G. (2021) An instance of parasitism on a human by a nymph of the kangaroo soft tick, Ornithodoros gurneyi Warburton, 1926 (Acari: Argasidae) in South Australia. Ticks & Tick-borne Diseases, 12 (2), 101632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2020.101632
- Norval, G., Sharrad, R.D. & Gardner, M.G. (2022) A mammal tick with a taste for lizard blood: parasitism by the kangaroo soft tick, (Ornithodoros gurneyi) on sleepy lizards (Tiliqua rugosa). Ticks & Tick-borne Diseases, 13 (1), 101859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2021.101859
- Nurk, S., Meleshko, D., Korobeynikov, A. & Pevzner, P.A. (2017) metaSPAdes: a new versatile metagenomic assembler. Genome Research, 27, 824–834. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.213959.116
- Pospelova-Shtrom, M.V. (1950) The genera, species and lower taxonomical ranges of ticks Ornithodorinae of the USSR (In Russian). Meditsnkaia Parazitologia, 19, 55–70.
- Pospelova-Shtrom, M.V. (1969) On the system of classification of ticks of the family Argasidae Can., 1890. Acarologia, 11, 1–22.
- Rambaut, A. (2009) TRACER. Version 1.5. Available from: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/tracer/ (accessed 3 June 2025)
- Rambaut, A. (2012) FigTree. Version 1.4. Available from: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/FigTree/ (accessed 3 June 2025)
- Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., van der Mark, P., Ayres, D.L., Darling, A., Höhna, S., Larget, B., Liu, L., Suchard, M.A. & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2012) MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology, 61, 539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
- Ribeiro, C.C., Faccini, J.L., Cançado, P.H., Piranda, E.M., Barros-Battesti, D.M. & Leite, R.C. (2013) Life cycle of Ornithodoros rostratus (Acari: Argasidae) under experimental conditions and comments on the host-parasite relationship in the Pantanal wetland region, Brazil. Experimental & Applied Acarology, 61, 139–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-013-9669-7
- Stamatakis, A. (2014) RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics, 30, 1312–1313. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033
- Warburton, C. (1926) On three new species of Ticks (Arachnida, Ixodoidea), Ornithodorus gurneyi, Ixodes arvicolae, and Haemaphysalis mjobergi. Parasitology, 18, 55–58. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182000004972