Abstract
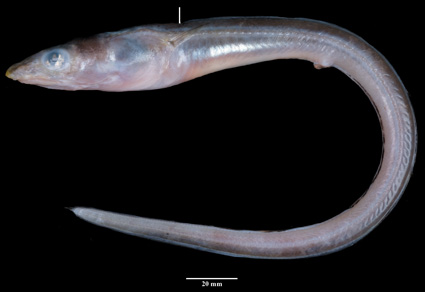
Three new species of the congrid eel genus Gnathophis viz., Gnathophis ajithi, Gnathophis anilmohapatrai, and Gnathophis arabicus are described herein. Gnathophis ajithi is collected from 264–450 m depth along the Arabian Sea and differs from its congeners in having 2nd, and 7th–8th through 13th–15th pores elevated; small eye, 15.7–17.7% HL; lateral-line pores before anus 27–33, stomach grey to black. Gnathophis anilmohapatrai is collected from 264 m depth and differs from its congeners in that the lateral-line pores above pectoral fin are not elevated, lateral-line pores before anus 36–40, stomach pale. Gnathophis arabicus is collected from 450–600 m depth and differs from its congeners in that the lateral-line pores above pectoral fin are not elevated, lateral-line pores before anus 36–41; SO pores 5, SO5 absent, SO6 present, stomach pale and black posteriorly. Further, CO1 mtDNA sequences are generated and discussed with the sequences available at public domain.
References
- Alcock, A.W. (1894) Natural history notes from H.M. Indian marine survey steamer `Investigator’. Series II. No. 11. An account of a recent collection of bathybial fishes from the Bay of Bengal and from the Laccadive Sea. Journal and Proceedings of the Asiatic Society of Bengal, 63 (Pt 2), 115–137, pls. 6–7. [also as a separate, pp. 1–23, with original pagination at bottom]
- Asano, H. (1958) Studies on the conger eels of Japan. II. Description of two new fishes referable to the genera Rhynchocymba and Promyllantor. Dobutsugaku Zasshi [Zoological Magazine Tokyo], 67 (7), 197–201. [in Japanese, English summary]
- Bleeker, P. (1858) Vijfde bijdrage tot de kennis der ichthyologische fauna van Japan. Acta Societatis Regiae Scientiarum Indo-Neêrlandicae, 5, 1–12, pls. 1–3.
- Böhlke, E.B. (1982) Vertebral formulae for type specimens of eels (Pisces: Anguilliformes). Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, 134, 31–49.
- Böhlke, E.B. (1989) Methods and Terminology. In: Böhlke, E.B. (Ed.), Fishes of the Western North Atlantic. Memoirs of the Sears Foundation for Marine Research, 1 (Part 9), pp. 1–7.
- Castle, P.H.J. (1995) Alcock’s congrid eels from the “Investigator” collections in Indian Seas 1888–1894. Copeia, 3, 706–718. https://doi.org/10.2307/1446768
- Delaroche, F.E. (1809) Suite du mémoire sur les espèces de poissons observées à Iviça. Observations sur quelques-uns des poissons indiqués dans le précédent tableau et descriptions des espèces nouvelles ou peu connues. Annales du Muséum d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris, 13, 313–361, pls. 20–25. [also as a separate, pp. 27–75, pls. 1–6. Names appeared without distinguishing features in Delaroche 1809 (ref. 17379)]
- Fricke, R., Eschmeyer, W.N. & Laan, R. (Eds.) (2025) Guide to fish collections in Eschmeyer’s Catalog of fishes. California Academy of Sciences, San Francisco, California. Electronic Version 20 May 2025. Available from: https://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/collections.asp (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Hoang, D.T., Chernomor, O., Von Haeseler, A., Minh, B.Q. & Vinh, L.S. (2018) UFBoot2: improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Molecular biology and evolution, 35 (2), 518–522. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx281
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S., Minh, B.Q., Wong, T.K., Von Haeseler, A. & Jermiin, L.S. (2017) ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nature methods, 14 (6), 587–589. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4285
- Karmovskaya, E.S. & Paxton, J.R. (2000) Revision of the Australian congrid eels of the genus Gnathophis (family Congridae), with descriptions of six new species. Journal of Ichthyology, 40 (1), S1–S14.
- Karmovskaya, E.S. (1990) New species of conger eels (Congridae) from southeastern Pacific Seamounts. Voprosy Ikhtiologii, 30 (5), 764–772. [in Russian. English translation in Journal of Ichthyology, 30 (7), 1–10]
- Karmovskaya, E.S. (2004) Benthopelagic bathyal conger eels of families Congridae and Nettastomatidae from the western tropical Pacific, with descriptions of ten new species. Journal of Ichthyology, 44 (1), S1–S32. [published only in English]
- Karrer, C. (1983) Anguilliformes du Canal de Mozambique (Pisces, Teleostei). Fauna Tropicale, 23, 1–116.
- Kaup, J.J. (1856) Catalogue of the apodal fish in the collection of the British Museum. Published by order of the Trustees, London, 163 pp., 19 pls. [Many new genera appeared first in Kaup 1856, ref. 2572. Date possibly 1857, as used by Whitley]
- Kaup, J.J. (1860) Neue aalaehnliche Fische des Hamburger Museums. Abhandlungen Naturwissenschaftlichen Vereins in Hamburg, 4 (2), 1–29 + 1–4 (Supplement), pls. 1–5. [possibly published as separate in 1859]
- Kotthaus, A. (1968) Fische des Indischen Ozeans. A. Systematischer Teil. III. Ostariophysi und Apodes. Meteor Forschungsergebnisse, Reihe D, Biologie, 3, 14–56.
- Leigh, J.W. & Bryant, D. (2015) POPART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 6 (9), 1110–1116. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12410
- Letunic, I. & Bork, P. (2024) Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Research, 52, 78–82. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkae268
- Matsubara, K. & Ochiai, A. (1951) On the conger eels related to Arisoma nystromi (Jordan et Snyder) found in the waters of Japan and China. Memoirs of the College of Agriculture Kyoto University, 59, 1–18.
- Maul, G.E. (1972) On a new species of eel of the genus Gnathophis (Apodes, Congridae) from the Meteor Seamount. Museu Municipal do Funchal (História Natural), 31, 1–7.
- Minh, B.Q., Schmidt, H.A., Chernomor, O., Schrempf, D., Woodhams, M.D., Von Haeseler, A. & Lanfear, R. (2020) IQ-TREE 2: new models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Molecular biology and evolution, 37 (5), 1530–1534. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaa015
- Pakhorukov, N. P. (2005). Behavior and distribution of bottom and demersal fishes on the underwater Emperor Ridge (Pacific Ocean). Journal of Ichthyology, 45 (1) 103–110.
- Prokofiev, A.M., Frable, B.W., Emelianova, O.R., Saveleva, S.Y. & Orlov, A.M. (2025) A New Species of the Eel Genus Gnathophis (Congridae, Anguilliformes) from the Seamounts of the Emperor–Hawaiian Chain, Western and Central North Pacific. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13 (4), Art. 772, 1–28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040772
- Puillandre, N., Lambert, A., Brouillet, S. & Achaz, A. (2011) ABGD, Automatic barcode gap discovery for primary species delimitation. Molecular Ecology, 21 (8), 1864–1877. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05239.x
- Ramsay, E.P. & Ogilby, J.D. (1888) Descriptions of two new fishes from Port Jackson. Proceedings of the Linnean Society of New South Wales, 2 (4), 1021–1023. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.29227
- Richardson, J. (1844–48) Ichthyology of the voyage of H.M.S. Erebus & Terror, under the command of Captain Sir James Clark Ross. In: Richardson, J. & Gray, J.E., The zoology of the voyage of the H.M.S. Erebus & Terror, under the command of Captain Sir James Clark Ross, during the years 1839 to 1843. Ichthyology of the voyage of H.M.S. Erebus & Terror, 2 (2), pp. i–viii + 1–139, pls. 1–60. [pp. 1–16 (1844) + 17–52 (1845) + 53–74 (1846) + i–viii + 75–139 (1848), see Bauchot et al. 1982: 66 (ref. 6562)] https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.7364
- Smith, D.G. & Kanazawa, R.H. (1977) Eight new species and a new genus of congrid eels from the western north Atlantic with redescriptions of Ariosoma analis, Hildebrandia guppyi and Rhechias vicinalis. Bulletin of Marine Science, 27 (3), 530–543.
- Smith, D.G., Jawad, L.A. & Al-Kharusi, L.H. (2017) New records and new information on four eel species from Oman (Teleostei: Anguilliformes: Congridae, Muraenesocidae). Journal of the Ocean Science Foundation, 28, 34–46.
- Smith, D.G. & Heemstra, P.C. (2022) Family Congridae, Conger and Garden eels. In: Heemstra, P.C., Heemstra, E., Ebert, D.A., Holleman, W. & Randall, J.E. (Eds.), Coastal Fishes of the Western Indian Ocean. Vol. 2. South African Institute for Aquatic Biodiversity, Makhanda, pp. 86–96.
- Whitley, G.P. (1948) Studies in ichthyology. No. 13. Records of the Australian Museum, 22 (1), 70–94. https://doi.org/10.3853/j.0067-1975.22.1948.592