Abstract
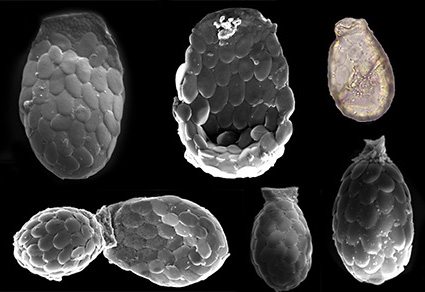
The genus Sphenoderia Schlumberger, 1845 has been recorded for the first time in India. The type species Sphenoderia lenta Schlumberger, 1845 is noticed in the forest biotope of Arunachal Pradesh, and Sphenoderia minuta Deflandre, 1931 and Sphenoderia labiata Thomas & Gauthier- Lièvre, 1959 are recorded from the aquatic habitat of Meghalaya. All three species have been documented from the Northeastern region of India, highlighting the rich biodiversity found in this area. For each species, detailed descriptions and morphometry are provided based on the examination of specimens from the present study. Additionally, a global distribution review of the genus has also been discussed.
References
- Adl, S.M., Bass, D., Lane, C.E., Lukeš, J., Schoch, C.L., Smirnov, A., Agatha, S., Berney, C., Brown, M.W., Burki, F., Cárdenas, P., Cepicka, I., Chistyakova, L., del Campo, J., Dunthorn, M., Edvardsen, B., Eglit, Y., Guillou, L., Hampl, V., Heiss, A.A., Hoppenrath, M., James, T.Y., Karnkowska, A., Karpov, S., Kim, E., Kolisko, M., Kudryavtsev, A., Lahr, D.J.G., Lara, E., Gall, L., Lynn, D.H., Mann, D.G., Massana, R., Mitchell, E.A.D., Morrow, C., Park, J.S., Pawlowski, J.W., Powell, M.J., Richter, D.J., Rueckert, S., Shadwick, L., Shimano, S., Spiegel, F.W., Torruella, G., Youssef, N. & Zhang, Q. (2019) Revisions to the Classification, Nomenclature, and Diversity of Eukaryotes. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 66 (1), 4–119. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12691
- Badewitz, H.J. (2002) Testaceen-Taxozönose (Rhizopoda, Testacea) mit hoher Artendiversität in einem kleinen Quellgewässer des Oberharzes. Lauterbornia, 44, 1–28.
- Barrett, K.D., Sanford, P. & Hotchkiss, S.C. (2021) The ecology of testate amoebae and Cladocera in Hawaiian montane peatlands and development of a hydrological transfer function. Journal of Paleolimnology, 66 (2), 83–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-021-00188-8
- Beyens, L. & Chardez, D. (1995) An annotated list of testate amoebae observed in the Arctic between the longitudes 27 E and 168 W. Archiv für Protistenkunde, 146 (2), 219–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-9365(11)80114-4
- Bobrov, A., Mazei, Y., Buyvolova, A. & Yacher, L. (2019) Testate Amoebae of Peru: filling the gap in the Neotropics. Revista de Biología Tropical, 67 (3), 478–489.
- Booth, R.K. & Zygmunt, J.R. (2005) Biogeography and comparative ecology of testate amoebae inhabiting Sphagnum‐dominated peatlands in the Great Lakes and Rocky Mountain regions of North America. Diversity and Distributions, 11 (6), 577–590. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1366-9516.2005.00154.x
- Booth, R.K., Notaro, M., Jackson, S.T. & Kutzbach, J.E. (2006) Widespread drought episodes in the western Great Lakes region during the past 2000 years: geographic extent and potential mechanisms. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 242 (3–4), 415–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2005.12.028
- Bonnet, L. (1966) Le peuplement Thécamoebien de quelques sols du Chili. Protistologica, 2, 113–140.
- Chardez, D. (1980) Sur quelques Thécamoebiens du Lac Tanganyika. Revue Verviétoise d’Histoire Naturelle, 37 (4–6), 26–29.
- Chardez, D. & Gaspar, C. (1976) Thécamoebiens aquatiques du domaine des Epioux (Ardenne, Belgique) (Protozoa: Rhizopoda testacea). Biologisch Jaarboek Dodonaea, 44, 86–100.
- Charman, D.J. & Warner, B.G. (1997) The ecology of testate amoebae (Protozoa: Rhizopoda) in oceanic peatlands in Newfoundland, Canada: modelling hydrological relationships for palaeoenvironmental reconstruction. Ecoscience, 4 (4), 555–562. https://doi.org/10.1080/11956860.1997.11682435
- Charman, D.J., Hendon, D. & Woodland, W.A. (2000) The identification of testate amoebae (Protozoa: Rhizopoda) in peats. QRA Technical Guide No. 9, Quaternary Research Association, London, 147 pp.
- Charman, D.J. (2001) Biostratigraphic and palaeoenvironmental applications of testate amoebae. Quaternary Science Reviews, 20, 1753–1764. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00036-1
- Charman, D.J., Blundell, A., Chiverrell, R.C., Hendon, D. & Langdon, P.G. (2006) Compilation of non–annually resolved Holocene proxy climate records: stacked Holocene peatland palaeo-water table reconstructions from northern Britain. Quaternary Science Reviews, 25, 336–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2005.05.005
- Chatelain, A.P., Meisterfeld, R., Roussel-Delif, L. & Lara, E. (2013) Sphenoderiidae (fam. nov.), a new clade of euglyphid testate amoebae characterized by small, round scales surrounding the aperture. Protist, 164 (6), 782–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protis.2013.08.001
- Corbet, S.A. (1973) An Illustrated Introduction to the Testate Rhizopods in Sphagnum: With Special Reference to the Area Around Malham Tarn, Yorkshire. Headley Brothers.
- Deflandre, G. (1931) Thécamoebiens nouveaux ou peu connus, I. Annales de Protistologie, 3 (2/3), 81–95, Pls. XI–XVII.
- Esteban, G.F., Clarke, K.J., Olmo, J.L. & Finlay, B.J. (2006) Soil protozoa-an intensive study of population dynamics and community structure in an upland grassland. Applied Soil Ecology, 33 (2), 137–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2005.07.011
- Fernández, L.D., Lara, E. & Mitchell, E.A. (2015) Checklist, diversity and distribution of testate amoebae in Chile. European Journal of Protistology, 51 (5), 409–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejop.2015.07.001
- Foissner, W. (1999) Soil protozoa as bioindicators: pros and cons, methods, diversity, representative examples. Agriculture, Ecosystem & Environment, 74, 95–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8809(99)00032-8
- Jung, W. (1942) Südchilenische Thekamöeben. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 95, 253–356.
- Hoogenraad, H.R. & de Groot, A.A. (1951) Thekamoebe Moss-rhizopoden aus Südamerika. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 45, 346–366.
- Karpińska-Kołaczek, M., Kołaczek, P., Czerwiński, S., Gałka, M., Guzowski, P. & Lamentowicz, M. (2022) Anthropocene history of rich fen acidification in W Poland-Causes and indicators of change. Science of the Total Environment, 838, 155785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155785
- Krashevska, V., Bonkowski, M., Maraun, M. & Scheu, S. (2007) Testate amoebae (protista) of an elevational gradient in the tropical mountain rain forest of Ecuador. Pedobiologia, 51 (4), 319–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedobi.2007.05.005
- Krashevska, V., Maraun, M. & Scheu, S. (2010) Micro-and macroscale changes in density and diversity of testate amoebae of tropical montane rain forests of Southern Ecuador. Acta Protozoologica, 49 (1), 17–28.
- Křoupalová, V., Opravilová, V., Bojková, J. & Horsak, M. (2013) Diversity and assemblage patterns of microorganisms structured by the groundwater chemistry gradient in spring fens. Annales de Limnologie-International Journal of Limnology, 49 (3), 207–223. https://doi.org/10.1051/limn/2013056
- Kutluk, H. & Mazei, Y. (2018) Organic-walled fossil testate amoebae records (late Cretaceous– holocene) from the Neotethyan–mediterranean region. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 48 (2), 121–141. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsjfr.48.2.121
- Lamentowicz, Ł., Lamentowicz, M. & Gąbka, M. (2008) Testate amoebae ecology and a local transfer function from a peatland in western Poland. Wetlands, 28, 164–175. https://doi.org/10.1672/07-92.1
- Lamentowicz, M., Bragazza, L., Buttler, A., Jassey, V.E.J. & Mitchell, E.A.D. (2013) Seasonal patterns of testate amoeba diversity, community structure and species–environment relationships in four Sphagnum-dominated peatlands along a 1300 m altitudinal gradient in Switzerland. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 67, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.08.002
- Laminger, H. (1973) Die testaceen in der umgebung der station Büschelbach (Spessart/BRD). Hydrobiologia, 41, 501–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00016469
- Marcisz, K., Buczek, K., Gałka, M., Margielewski, W., Mulot, M. & Kołaczek, P. (2021) Past testate amoeba communities in landslide mountain fens (Polish Carpathians): The relationship between shell types and sediment. The Holocene, 31 (6), 954–965. https://doi.org/10.1177/0959683621994647
- Mazei, Y.A. & Tsyganov, A.N. (2007) Species composition, spatial distribution and seasonal dynamics of testate amoebae community in a sphagnum bog (Middle Volga region, Russia). Protistology, 5 (2–3), 156–206.
- Myers, N., Mittermeier, R.A., Mittermeier, C.G., Da Fonseca, G.A. & Kent, J. (2000) Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature, 403 (6772), 853–858. https://doi.org/10.1038/35002501
- Mitchell, E.A., Buttler, A.J., Warner, B.G. & Gobat, J.M. (1999) Ecology of testate amoebae (Protozoa: Rhizopoda) in Sphagnum peatlands in the Jura mountains, Switzerland and France. Ecoscience, 6 (4), 565–576. https://doi.org/10.1080/11956860.1999.11682555
- Mitchell, E.A. (2025) A new golden era for research on testate amoebae: Looking back at 30 years of research. Acta Protozoologica, 63 (Special Issue), 23–33. https://doi.org/10.4467/16890027AP.25.004.21793
- O’Donoghue, P. (2010) Catalogue of Testate Amoebae (Protozoa) Recorded from Australia. The University of Queensland, Brisbane, 16 pp.
- Ogden, G.G. & Hedley, R.H. (1980) An atlas of freshwater testate amoebae. Soil Science, 130 (3), 176. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-198009000-00013
- Ogden, C.G. (1984) Shell structure of some testate amoebae from Britain (Protozoa, Rhizopoda). Journal of natural history, 18 (3), 341–361. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222938400770291
- Opravilová, V. & Zahrádková, S. (2003) Some information on testate amoebae of Iceland. Limnologica, 33 (2), 131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0075-9511(03)80042-7
- Opravilová, V. & Hajek, M. (2006) The variation of testacean assemblages (Rhizopoda) along the complete baserichness gradient in fens: a case study from the Western Carpathians. Acta protozoologica, 45 (2), 191.
- Ortner, B. (2017) Beschalte Amöben (Testaceen) und Zieralgen (Desmidiaceae) des Sphagnetums einiger österreichischer Moore. Biologiezentrum des Oberösterreichischen Landesmuseums, 139 pp.
- Payne, R.J. & Mitchell, E.A. (2007) Ecology of testate amoebae from mires in the Central Rhodope Mountains, Greece and development of a transfer function for palaeohydrological reconstruction. Protist, 158 (2), 159–171.
- Schlumberger, P. (1845) Observations sur quelques nouvelles espèces d’Infusoires de la famille des Rhizopodes. Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Series 3, 3, 254–256.
- Siemensma, F.J. (n.d.) Microworld. World of amoeboid organisms. World-wide electronic publication, Kortenhoef. Available from: https://arcella.nl/ (accessed 11 October 2025)
- Shimano, S., Bobrov, A. & Mazei, Y. (2014) Testate amoebae of the imperial palace, Tokyo. Memoirs of the National Museum of Nature and Science, 50, 21–28.
- Shimano, S.D., Bobrov, A., Wanner, M., Lamentowicz, M., Mazei, Y. & Ohtsuka, T. (2017) Testate amoeba diversity of a poor fen on mineral soil in the hilly area of Central Honshu, Japan. Acta protozoologica, 56 (3), 211–216. https://doi.org/10.4467/16890027AP.17.018.7499
- Štěpánek, M. (1967) Testacea des Benthos der Talsperre Vranov am Thayafluss. Hydrobiologia, 29 (1), 1–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00142053
- Sudzuki, M. (1979) On the microfauna of the Antarctic region III. Microbiota of the terretrial interstrices. Memoirs of National Institute of Polar Research, Special Issue, 11, 104–126.
- Swindles, G.T., Holden, J., Raby, C.L., Turner, T.E., Blundell, A., Charman, D.J. & Kløve, B. (2015) Testing peatland water-table depth transfer functions using high-resolution hydrological monitoring data. Quaternary Science Reviews, 120, 107–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.04.019
- Thomas, R. & Gauthier-Lièvre, L. (1959) Note sur quelques Euglyphidae d’Afrique. Bulletin de la Société d’histoire naturelle de l’Afrique du Nord, 50, 204–221.
- Todorov, M. & Bankov, N. (2019) An Atlas of Sphagnum-Dwelling Testate Amoeba in Bulgaria. Pensoft Publishers, Sofia, 286 pp. https://doi.org/10.3897/ab.e38685
- Tolonen, K., Warner, B.G. & Vasander, H. (1992) Ecology of testaceans (Protozoa: Rhizopoda) in mires in southern Finland: I. Autecology. Archiv für Protistenkunde, 142 (3–4), 119–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-9365(11)80076-X
- Van Oye, P. (1949) Rhizopodes de Java. Bijdragen tot de Dierkunde, 28 (1), 327–352. https://doi.org/10.1163/26660644-02801040
- Wailes, G. (1913) Freshwater Rhizopod from North and South America. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 32, 201–218. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1913.tb01776.x
- Wanner, M., Siemensma, F., Acharja, I.P., Tshering, J., Khandu, P., Gajmer, S.L. & Shimano, S. (2024) Testate amoebae from the wetlands of the Phobjikha Valley of Bhutan, the Eastern Himalayas. European Journal of Protistology, 96, 126125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejop.2024.126125